
by Mark Yon
Scenes from England
Hello again!
As I type this, we’re a few days away from the 23rd Worldcon in London. Worldcons outside of the US don’t happen very often – the last one here was in 1957 – but it somehow seems right at the moment. Despite my feeling of lethargy last month, there’s a lot of optimism about in England, more than I’ve felt for a while. The reasons for it are perhaps many and varied – a young Labour government, the Beatles dominating the world and who seem to be a voice for the young generation, even the New Wave of science fiction that seems to be gaining headway and shaking things up.
To me, a Worldcon in Britain seems to encapsulate this. It promises to be new and exciting, at the cutting edge of the genre, with original writing and new writers out there to make things interesting. If you are attending, I hope it is everything it deserves to be.

With the Worldcon in mind, the magazines have steadily been building up pressure over the year. In this month of Worldcon ‘65, their issues seem to reflect the pent-up feeling of excitement, as both issues have some connection with the convention.
I’ll explain as we go along. As per usual, the issue that arrived first in the post this month was Science Fantasy.

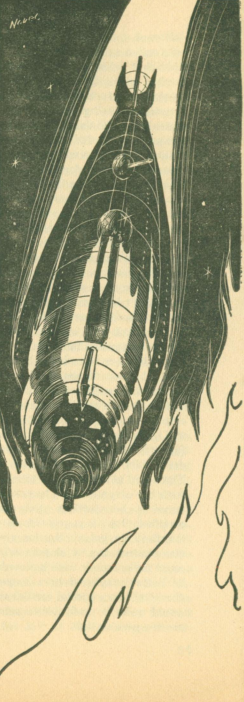
Well, after the comparative lightness of last month’s cover, we seem to have taken on a much darker hue this month. That cover by an unknown artist is a bit too murky for me, almost to the point where I might say that I miss the usual Keith Roberts covers.
However, there may be subtle persuasion at work here, in that because the picture is so dark, the attention of the casual reader may be focused on the magazine’s heading. If, as they say, ‘sex sells’, then this might do it.
The Editorial this month is not usual. Instead of the usual debate created by Kyril, we have instead an article by Brian Aldiss (wonder why?) that seems to do little else but point out that his first-published novel Non-Stop has been republished in England. Whilst the cynical amongst-us might see this as an extended advertisement, it is written with Brian’s own endearing and self-deprecating tone. He explains the background to the original publication, how the American publishers gave away the twist in the story by changing the title, and finally tells us what he would do to revise the novel if he was writing it now. It is quite charming – rather like the man himself. I’ll mention the novel again later.
To the actual stories.
Boomerang, by E. C. Tubb
The return of the prodigious E C Tubb after his popular last serial story, The Life Buyer in the April – June 1965 issues of New Worlds. Boomerang is a story of murder and revenge. Told in the first person, Marlow is a man who from the start freely admits that he went on a murderous rampage against Granger, who he hates. As a result, Marlow burned down Granger’s house, “poisoned his friends, mutilated his pets and did things to his family” – nice chap!
Marlow’s punishment is to be exiled on his own to Hades, which as you might expect from its name is a barely tolerable planet to live out the rest of his days. The story here goes all Robinson Crusoe, and I rather expected it to become an Analog style story of a man overcoming adversity. But wait! The ‘boomerang’ of the title is that – wait for it! – his victim comes to the planet to finish him off! It’s nicely done overall, and reminded me a little of Alfred Bester’s Tiger! Tiger! in the sense of total hate that seems to exude off the page. With this in mind, the ending is satisfying. 3 out of 5.
Coming-Of-Age Day, by A K Jorgenssen
Warning! Warning! Kyril begins this with an explanation that he’s used before. It goes something like – “I read this one and thought. 'I can’t possibly publish this one!' And then I thought some more and decided 'Why not?'”
I must admit that given the lurid blurb on the front cover of a “startling story of sex in the future”, I was rather grimly expecting an over-heated story of a future where the coming-of-age is celebrated by some sort of sexual rite-of-passage, with some pretty obvious clichés and awful sex scenes.
To my surprise, it’s rather a restrained work. The main premise is that in the future everyone who enters puberty is fitted with what I will politely describe as a sexual appliance known as a consex. Andrews, the male character of the narrative tells of the process and explains why most people, male or female, has one fitted. He is fairly happy with the idea, especially when the 'sexiatrist' (doctor) explains that having one fitted is good, because every adult has one. The suggestion also that it is better than sex is also a pretty winning argument.
In a wider perspective, it has solved many social issues and has become a culturally accepted thing for both males and females, reducing basic urges and satisfying the needs of couples and bachelors alike. The story seems to be more about the need for cultural compliance rather than sex, although Andrews overhears Topolski, another more reluctant young man who, despite being put under pressure to comply, appears to refuse the fitting.
Whilst the story fizzles out at the end, it is one that made me think. Is the device a future version of contraception? How would a society, especially a British society, known for its stiff upper lip and reserve, become so accepting of something that would affect everyone at a personal level? Could it happen?
If the sign of a good story is that it makes you think, then this one scores – if you can buy into the idea working. 4 out of 5.
Temptation for the Leader, by R W Mackelworth
The return of RW, last seen in the July 1965 issue of Science Fantasy. Most of Mackelworth’s stories tend to deal with the issues of identity and responsibility in a future society, and this one is no different. A meeting between an alien who names itself “Poniard”, and “the President” of a capitalist nation (who may be the leader of the USA, though it is never clearly stated) leads to an offer of help and guidance for the human race – but at a price. In the end, the offer is rejected because of the effect it would have on individuality and capitalist values.
This is a very talky story, the conclusion is straight out of Arthur C Clarke’s Childhood’s End. There’s some good ideas here but the author seems to go about them in a rather roundabout way. 3 out of 5.
At Last, the True Story of Frankenstein, by Harry Harrison
Over at New Worlds, Harry is having his latest novel serialised. Here he tells a simpler and more serious shaggy-dog story by telling of Victor Frankenstein V, now reduced to being part of a carnival show and in need of a new animated body. At the same time Harry rewrites Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley’s seminal story in six pages, with a clever mix of humour and horror. Ray Bradbury would be proud of this one. 4 out of 5.
Sule Skerry, by Rob Sproat
Not an author’s name that I remember, so this seems to be the latest ‘new writer’ to grace the magazine. The idea is that Sule Skerry is a folksong collected by people recording old legends but then turned into prose. Whilst I don’t know if this Northumbrian story of the selkie is based on a real folk-song, I found the story quite sad and remarkably moving. A mythic folktale that was better than I thought it was going to be. 4 out of 5.
The Jobbers, by Johnny Byrne
Johnny has produced some very strange stories in the past. They are often too odd for my tastes, although this one was less obtuse than many. It begins with an unnamed man talking to two very small people who then appear to climb into his brain. They are ‘Jobbers’, whose purpose is to get into a person’s brain and prepare their body ready for the next inhabitant. It starts quite light-hearted but by the end becomes rather creepy. The twist in the tale, of whether what is happening is real or some imagined attack of insanity, is left up to the reader to decide. 3 out of 5.
Omega and Alpha, by Robert Cheetham
This month’s offering from a debut author, a bleak short story told in the form of a diary by an author and his wife who have gone to get away from it all on a tropical island. When a missile station on the far side of the island is destroyed – it is not clear whether it is just the island that is affected or a global event – the resultant radiation and ash leads to death. Another post-apocalyptic story of the sort that we’ve had a lot of lately, but it is quite effective in showing what the effects of a nuclear war would be after the bombs have gone off. An interesting debut, even if it treads a familiar path. 3 out of 5.
The Furies (Part 3 of 3), by Keith Roberts
To Keith’s last part of this story, which in my opinion has been one of the magazine’s strengths of the last few months.
Last issue we were left with Bill Sampson, having begun the human fight-back against the wasps, attempting to go and find his young friend Jane in France, only to be shot at by an army patrol and crashing his car.
This final part picks up where we left off. Bill is retrieved and brought back to health by two of his friends still hidden away in the Mendip Hills – Greg and Pete. Once he has recovered, the group hiding in the Chill Leer caves continue their guerrilla attacks upon the wasps, with varying degrees of success. There is an attack by the wasps inside the caves the humans have been hiding in. Eventually Bill and the traumatised girl 'Pete' are captured. To their surprise, rather than be killed, as many of their friends have been, they are spoken to by the Queen Wasp in a deus ex machina conclusion that explains the purpose of the wasps and leaves them with one message – that the wasps are dying because their determination to evolve rapidly has caused racial regression and that the humans must carry on and continue the Wasp’s purpose – to continue Life.
There are questions raised about the importance of hive intelligence, but this all ends rather suddenly, with a huge dollop of exposition and everything being tied up rather too abruptly for my liking. Most of all, the big plot reveal at the end is a bit of a stinker after such a great set-up. It rather feels like the author felt he was running out of time or space to finish the story and it all ends far too conveniently.
Although I couldn’t put this story down, it doesn't have the quality ending I was hoping for. Shame. 3 out of 5.
Summing up Science Fantasy
Despite The Furies not ending quite as well as I hoped it would, I’m very pleased that the story is still fairly strong. The whole issue is generally good, with Rob Sproat’s Sule Skerry being a surprisingly memorable tale.
But is it as good as New Worlds this month? Let’s go to my second magazine to find out!
The Second Issue At Hand

Unlike Science Fantasy, it may not be too surprising to find that New Worlds has gone all out to celebrate the London Worldcon’s Guest of Honour this month. From the enthusiastic comment on the back cover to appreciations by Edmund Crispin and Peter White, most of this issue is about Brian Aldiss. There’s a review of Aldiss’s novel Non-Stop by Mike Moorcock – you know, the one that Brian has reviewed himself in this month’s Science Fantasy. Even when it is not, it includes material from his friends – Harry Harrison’s serialised novel Bill, the Galactic Hero continues with its second part under the title A Dip in the Swimming Pool Reactor.
This month’s editorial from Mike Moorcock is one of two halves. The first tells us how great Harry Harrison’s novel is (I’ll comment on that later) before going on to entice us with future attractions. The second part reminds us that we have a Worldcon in London in about one month’s time, which we should be excited about. (Have I said in the last few minutes that Brian will be Guest of Honour at this month’s Worldcon in London?)
To the stories!
Girl and Robot with Flowers, by Brian Aldiss
So we begin this Aldiss issue with an Aldiss story that at first might make new readers a bit puzzled. It’s set in modern times, reading as if it was in The Times Literary Supplement. The science-fictional element is that the story is of a writer who, after a time has decided to begin writing again. You see, the author writes science fiction! (Tenuous link initiated.) What begins as an initially cosy domestic tale slowly changes, as our writer talks through the story he is thinking of writing comparing it with the reality of the place he is at and the woman he is with. And bam – Brian’s got your attention again, sneaking in a science fiction story without the reader realising it. It’s a gently subversive tale, questioning the purpose of science fiction, and of writing it – and gets extra credit for adding a few sf names in as well (Ballard, Pohl, Moorcock, for example.) Better than last month’s Jungian effort. 4 out of 5.
Old Time’s Sake, by Brian Aldiss
The first Aldiss story is immediately followed by a second, different type of story. As the title might suggest, this is a story about the passage of time. Brian is a fan of HG Wells, and it shows in this story of Alec Sampson, the world’s first immortal man. Aldiss says that it is a story written in 1954, and was meant to be the first of a series which never materialised. It’s a story of loss and envy, cloaked in academia, as Alec meets his peers knowing that the next time his progress is reviewed, most if not all of these people will have died. I would’ve been interested to see where Aldiss would have gone with this, had he taken the story further. I enjoyed it, but it is clearly an early Aldiss. It is interesting reading the two stories together though, as they show how Brian has matured as a writer. 3 out of 5.
 Illustration by Douthwaite
Illustration by Douthwaite
Traveller’s Rest, by David Masson
Time travel of a different type now, from this debut author. Traveller’s Rest is this month’s most challenging read. Our main character, Hadolaris, is fighting a permanent war against a never seen enemy. After his latest sortie he is ‘Relieved’ (retired) and moves to a civilian life southwards away from the Front. He settles down with a job as a sales manager, marries and has three children, only to be re-enlisted and back at the front-line at the end of the story.
There’s not a lot of plot. What makes this story unusual is the idea that the war messes with Time and as you travel south away from the war zone time seems to get slower, whereas as you travel north time appears to be faster. Though to Hadol he has been away from the war for twenty years, it is no more than about twenty minutes at the front.
Traveller's Rest is perhaps the densest story in this issue and took me a while to determine what was going on. This complexity is helped by the author’s invention of words throughout to illustrate the plot. There are also interesting little ideas throughout – speech changes as you travel North or South – names become shorter or longer the nearer you are to the Front, for example. I also got a feeling that the time distortion may affect the soldier’s perceptions. The descriptions of war at the front are almost dream-like.
Those who relish untangling the story, deciphering the complexities of language and wrestling with the key concept of time dilation will find this one interesting. An impressive debut, although one that gains credit for the ideas rather than the plot. 4 out of 5.
Bill, the Galactic Hero, Part 2: A Dip in the Swimming pool Reactor, by Harry Harrison
I’m not going to say much about this one, as like I said last month, you will either love it or be unimpressed by it. In this part, blasé Bill stumbles his way through the continuing war against the Chingers. He visits the Imperial planet Helior – a planet plated with gold – to get a medal, meets the Emperor (or someone like him) and goes on furlough. He has things stolen, which upon reporting to the police leads to poor old Bill getting into trouble himself. To solve his troubles he becomes a Garbage-Man (G-Man for short) but is then persuaded by the Opposition Party to become an Anarchist, before being arrested as a deserter. It’s busy life for Bill… still silly but I enjoyed this part more than the first part. 3 out of 5.
 Illustration by James Cawthorn
Illustration by James Cawthorn
The Pleasure Garden of Felipe Sagittarius, by James Colvin
In which the New Worlds Book Reviewer wanders into the weird world that Mike Moorcock seemed to inhabit in last month’s issue… except that James is really Mike Moorcock!
This has the manner of a detective story, but one from an alternate world. Minos Aquilinas, Metatemporal Investigator of Europe, is asked to investigate the murder of a man in the garden of Police Chief Bismarck in Berlin.
Set in what might be an alternate timeline somewhere between now and the 1920s, this story reminded me of Moorcock’s tale of Jeremiah Cornelius last month. It is fast-paced and determinedly anarchic. Whilst it tries to be provocative – Eva Braun, Adolf Hitler and Stalin all appear, although not as we would expect to see them – the fast pace and attempt to use well-known people in a different way is refreshing. This Hitler is a very different one to the one we all know. Odd, but I liked it. 3 out of 5.
At the End of Days
And here’s this month’s effort from across the seas. Last month it was Mack Reynolds, this month Robert Silverberg, who I appreciate readers in the US will know pretty well as an up-and-coming young writer. End of Days is short, but works well in the space given to it. 140-years-old Thomas Narin watches people around him as the world is slowly dying. He is suddenly met by a young boy, Jorid Dayson, from Rigel-Six, who is impressed to meet someone from Earth. Earth has become almost mythical to Jorid and his young friends. It’s an elegiac tale that hints of a bright future ahead for the human race – just not on Earth. Though The End of Days covers a relatively common theme, the style is pleasantly lyrical. 3 out of 5.
Book Reviews, Articles and Letters
With all of this Aldiss-adulation (Aldissulation?), the reviews are shorter this month.
Edmund Crispin’s appreciation of Brian emphasises his ability to create visual images through prose. Peter White summarises Aldiss’s work to date and talks of his influence on British Sf today. Both articles are, as expected, pretty effervescent, although Mr. Crispin’s article, as you might expect from the author of the acclaimed Best Of… series of anthologies, is perhaps a more considered response.
Interestingly, Mr. White makes the claim that Brian’s best work to date is not science fiction, but The Male Response, a non-science fictional tale of sexual habits. I would disagree in that the book is not science fiction, as there are aspects that are science fictional – the rise of a future super-state in Africa, for example. I am sure readers will want to debate this further.
James Colvin (aka Mike Moorcock) reviews Aldiss’s Non-Stop, which makes interesting reading when compared with the author’s own review in Science Fantasy. Colvin’s review is unsurprisingly glowing. He then goes on to review in less detail Best SF Four, edited by fellow contributor this month, Edmund Crispin, and finds the story collection “only average in general standard.” By contrast, New Writings in SF Three, edited by John Carnell is “perhaps the best in the series so far.” Next, Colin Kapp’s The Dark Mind is reviewed with the suggestion that the author should spend more time on studying his craft before writing his next novel. Ouch!
The last review is a more detailed one of J G Ballard’s The Drought, which you may know in the US as The Burning World. It is typically enthusiastic: “The Drought is refreshing, original and an authentic creative work which, in its own terms, can only be emulated, one suspects, by Mr. Ballard himself.”
No “Dr. Peristyle” this month – perhaps we have enough Mr. Aldiss this month already! Instead, we’re back to the Letters pages, albeit very briefly. The first letter echoes the common theme of moving the genre forward and not looking back, whilst John Brunner himself replies with a correction to Langdon Jones’ review of his novel The Telepathist, back in issue 151, and there’s an effusive letter from Edward Mackin on E C Tubb’s The Life Buyer back in issue 150.
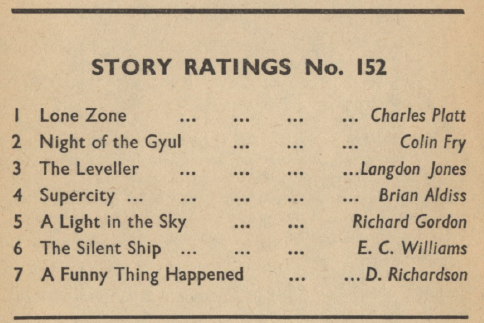
In terms of Ratings, the great surprise for me from issue 152 in July is how well Night of the Gyul was received. However, Dikk Richardson’s last placing is what A Funny Thing Happened deserved, sadly.
Summing up New Worlds
It is always risky focussing an issue mainly on one writer. If readers are not a fan of the particular author, will they buy the issue? However, I think that it has worked this time around. This feels like a strong issue – all the more so when I think of how New Worlds was two years ago. Again, how much you like this issue will I think depend a little on your love of Bill, the Galactic Hero, but the other elements I personally enjoyed more.
There’s a lot of mischievous fun in this issue, as well as some well-deserved plaudits for one of Britain’s best writers at the moment. The Masson story is a startling debut, which despite its weaknesses reflects the impressive range possible in science fiction at the moment.
Summing up overall
It’s difficult to knock the Aldiss coverage this month, although I’m not sure that the stories given here are his best. The audacious debut by Masson surprises most. I also liked the E C Tubb story in Science Fantasy, whilst continuing to be less impressed than many by Harrison’s silliness. However, the slightly disappointing conclusion of The Furies and the impressive range of material in the Brian Aldiss issue means that for me, this month’s issue of quality is New Worlds.

And with all of this love of Aldiss shared around the genre, that’s it for this time. Anyone going to Worldcon, have a wonderful time. I look forward to hearing the stories!
Until the next…
[Don't miss the next episode of The Journey Show, featuring a panel of amazing artists who will be doodling to YOUR specification!]









![[April 14, 1967] Earth, Air, Fire, and Water (April 1967 Galactoscope)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/670414covers-672x372.jpg)

![[December 2, 1966] Mixed Bags (January 1967 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/IF-1966-12-Cover-665x372.jpg)


![[October 2, 1966] At Heart (November 1966 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/IF-1966-10-Cover-646x372.jpg)


![[May 10, 1966] Rocky Jaunts (June 1966 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/660510cover-672x372.jpg)













![[March 10, 1966] Top Heavy (April 1966 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/660310cover-388x372.jpg)







![[January 8, 1966] Seems like old times (February 1966 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/660108cover-530x372.jpg)



![[November 10, 1965] Strangers in Strange Lands (December 1965 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/651110cover-672x372.jpg)







![[September 12, 1965] So Far . . . Well, Fair (October 1965 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/amz1065-cover-497x372.png)






![It’s (Nearly) All About Aldiss [August 22, 1965] <i>Science Fantasy</i> and <i>New Worlds</i>, September 1965](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Nw-Sciene-Fant-Sept-1965-672x372.png)




 Illustration by Douthwaite
Illustration by Douthwaite Illustration by James Cawthorn
Illustration by James Cawthorn


![[July 14, 1965] The New Dispensation (August 1965 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/amz0865-cover-500x372.png)





