
by Gideon Marcus
Nonstandard Deviation
Mr. Campbell of the good ship Analog is an interesting character. Known for his strident, occasionally downright offensive editorials, his fetish for pseudoscience, and his increasingly inconsistent (one might say half-hearted) story selection, he is both much-loved and much-maligned.
But, as Galactic Journey's editor likes to say, people contain multitudes. Or more simply, he and his magazine aren't all bad. If Analog sometimes hits disappointing lows, it also still reaches highs reminiscent of Analog's golden days (when it was called Astounding). His story sets are not monolithic. Sometimes they're downright surprising.
As Exhibit A, I submit the September 1966 Analog, a most unusual issue:
Charting new terrain

by John Schoenherr
The Mechanic, by Hal Clement
Hal Clement is best known for his nuts-and-bolts science fiction, as crunchy as unmilked cereal — and often as dry. This piece tells the tale of a near-future hydrofoil dispatched to the Arctic to determine what's causing the extinction of zeowhales. These cybernetic creatures have metal bodies but psuedoliving flesh, and some disease is dissolving them from the inside out.
Of course, the hydrofoil is also metallic, and bad things happen to a disintegrating ship zooming along at hundreds of miles per hour.

by Kelly Freas
Slow to start and very very explanatory, but the ideas are interesting and the latter half riveting if gruesome.
Three stars.
A Matter of Reality, by Carole E. Scott
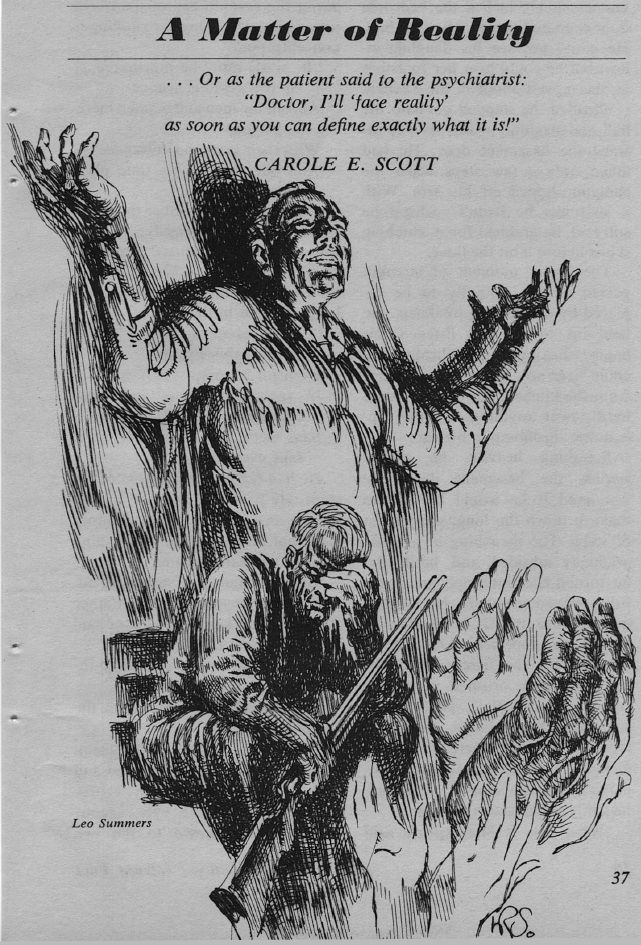

by Leo Summers
A common charge leveled at Campbell is that he doesn't like to publish women. I don't think that's fair. The industry as a whole has an unfortunate shortage of woman-penned stories. If Analog tends to be mostly a stag mag, it's just at one end of the bell curve, not a true outlier. Indeed, Campbell discovered Pauline Ashwell and Katherine Maclean, two of the field's brightest lights.
Women not only write for Analog, they read it, too: A Matter of Reality came off the slush pile, submitted by Ms. Scott, a self-proclaimed admirer of Campbell and his mag for nearly two decades.

Her first story contains none of the Campbellian touchstones: no psionics, no smugly superior Terrans, etc. Instead, it's an interesting piece about an old man's final act, a literal embodiment of the phrase, "All the world's a stage."
I'd expect to find such a fantastic piece in Galaxy or F&SF, but Scott likes Analog the best, and her story makes for a nice change of pace in Campbell's mag.
Three stars, and I look forward to her next piece.
… Not a Prison Make, by Joseph P. Martino

by John Schoenherr
With the Vietnam war escalating and the President calling for double the troops (600,000 — this proposal just rejected by Congress), it's not surprising that the situation is finding echoes in our science fiction.
Martino offers up a proxy war between the Terrans and the Kreg on a third-party planet peopled by primitives. The humans are subject to the most debilitating hit and run raids by the indigenes, who possess the powers of teleportation and limited clairvoyance.
Two viewpoints are espoused in the story: the military leader opines that the raiders are bandits, and the best bandit is a dead one. The civilian expert believes that the hearts and minds of the populace must be won or the insurgency will have infinite longevity.
Some clever defenses are built up against the natives, but they only constitute delaying actions. The paradigm must be radically altered if success is to be had.
This story really had potential, but it ended just as it was getting interesting, and with none of the more profound points addressed. Of course, no one really knows how to end a guerilla insurgency (predicting its death by the close of this century seems optimistic), but I'm dissatisfied with a story that concludes essentially with "then we won!" I did appreciate that the characters were all South/Southeast Asian (from what I know of surnames).
Three stars.
Challenge, by Joe Poyer

The fictional piece is followed by an in-depth analysis of insurgency and counter-insurgency. The author suggests that until the counter-insurgents learn to fight the insurgent game, and better than the insurgents, they won't win. Interestingly, the latest plan for Vietnam is to field division-sized battlefield units, not just to quell the VC, but also to engage in peaceful, nation-building activities. I'm not hopeful.
Anyway, Challenge is not a bad piece, though I don't know that it qualifies as "science." Also, I would not classify the Watts riots as an insurrection.
I miss Robert S. Richardson's astronomy articles. Three stars.
Symbols, by Christopher Anvil

by Kelly Freas
The river has frozen a month early, and the Gurt are under attack. The Ghisrans are pouring across the ice now, threatening a precious mine that is vital to the Terran Navy. If a handful of agents with an unarmed spaceboat are unable to stop them, the sector may fall.
I'm not sure what's more offensive: the portrayal of the lone female character as "hysterical" or the padding of this vignette to double size with Campbell-pleasing folderol about symbolic logic.
Definitely the most reactionary of this month's pieces. Two stars.
Too Many Magicians (Part 2 of 4), by Randall Garrett

by John Schoenherr
Ahh, but all that is washed away with the latest installment of the adventures of Lord Darcy, investigator in an alternate 1966 where thaumaturgy has trumped science. As we saw last time, there had been two murders by unknown assailants, both by similar knives. One of the victims was an Imperial double agent, killed while trying to ferret out a traitorous Anglo-Frenchman. The other was an exalted state wizard.
The bombshell of this installment is that the two murders are connected, tightly.
A lot of great detective work in this one, as well as a tour to magical London's equivalent of a World Expo. Garrett channels Doyle more and more these days, but so far it's working.
Four stars!
Charting a New Course

This experimental issue of Analog doesn't break any records, finishing dead-averagely at 3 stars. Nevertheless, I applaud Campbell's willingness to experiment, and I enjoyed the issue. Finishing above it were the superlative New Worlds (3.8 stars), the fine Fantasy and Science Fiction (3.5 stars), and the decent (but mostly because of a reprint) SF Impulse (3.2 stars).
Analog barely edged out IF (3 stars) and decidedly beat Fantastic (2.7 stars).
It was a good month overall for reading. If one took all the magazine stories/serials that got 4 or 5 stars, they could potentially fill three magazines! Also, women were responsible for 15.6% of all new fiction, a high water mark for sure.
On this triumphant note, I am off to Cleveland for this year's Worldcon. Who will win the Hugos? We'll have to wait a week to find out! Rest assured, you'll be able to read all about it here long before the next edition of Ratatosk or Focal Point (or Skyrack, for my British friends) hits your mailbox.

And if you are in Cleveland next weekend, be certain to join us for the showing of the first Star Trek pilot at 7pm Eastern (4pm Pacific!).





![[July 31, 1970] Not so Brillo… (August 1970 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/700731analogcover-672x372.jpg)

![[June 30, 1970] Star light… per stratagem (July 1970 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/700630analogcover-353x372.jpg)



![[May 31, 1970] A Compulsion to read (June 1970 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/700531analogcover-672x372.jpg)



![[August 2, 1968] Dreams and Nightmares (September 1968 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/IF-1968-09-Cover-672x372.jpg)

 Red Guard rebels march in Shanghai last year.
Red Guard rebels march in Shanghai last year. Those are supposed to be radiators, not rocket thrusters. Art by McKenna
Those are supposed to be radiators, not rocket thrusters. Art by McKenna![[November 4, 1967] Conflicts (December 1967 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/IF-1967-12-Cover-672x372.jpg)
 Joan Baez is arrested in Oakland.
Joan Baez is arrested in Oakland. Fr. Berrigan pouring blood into a file drawer.
Fr. Berrigan pouring blood into a file drawer. Futuristic combat in The City of Yesterday. Art by Chaffee
Futuristic combat in The City of Yesterday. Art by Chaffee![[October 2, 1967] Switching Sides (November 1967 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/IF-1967-11-Cover-672x372.jpg)
 The logo for the traffic changeover.
The logo for the traffic changeover. This photo was staged several months ago as part of the education campaign. The real thing was much less chaotic.
This photo was staged several months ago as part of the education campaign. The real thing was much less chaotic. A newcomer gets the cover. Does he deserve it? Art by Vaughn Bodé
A newcomer gets the cover. Does he deserve it? Art by Vaughn Bodé![[September 2, 1967] Of Genies and Bottles (October 1967 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/IF-Cover-1967-10-672x372.jpg)
 William C. Foster, the chief American representative to the Eighteen Nation Committee on Disarmament.
William C. Foster, the chief American representative to the Eighteen Nation Committee on Disarmament. The art is intriguing, but none of this happens in Hal Clement’s new novel. Art by Castellon
The art is intriguing, but none of this happens in Hal Clement’s new novel. Art by Castellon











![[July 2, 1966] The Big Thud (August 1966 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/IF-1966-08-Cover-644x372.jpg)


![[April 2, 1965] SPEAKING A COMMON LANGUAGE (May 1965 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/IF-April-cover-647x372.jpg)


