
by Victoria Silverwolf
The Acid Test
I believe that certain young people — hippies is the term, I think — are using the word trip to refer to something other than hopping on a bus, train, or airplane. In particular, they often mean taking a dose of lysergic acid diethylamide, understandably shortened to LSD, and known informally as acid.

A poster for an event held in Vancouver earlier this year.
Note the name of the festival, and the psychedelic art.
I'll bet lots of attendees took a trip to Canada in order to take a trip elsewhere.
Until this month, this hallucinogenic drug was legal everywhere in the USA. On October 6, it became illegal in the state of California. In response to the new law, on the same day thousands of people showed up for a so-called Love Pageant Rally in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park. They enjoyed music from local artists, and many took doses of LSD in defiance of the law.

Some guys calling themselves the Grateful Dead entertain the crowd. There was also a young blues singer from Texas named Janis Joplin.
Even if you live in California, you can enjoy a trip deep into your imagination in a perfectly legal manner, simply by opening the latest issue of Worlds of Tomorrow. Fittingly, almost all the fiction takes place in the far reaches of interstellar space.

Cover art by Sol Dember.
Crown of Stars, by Lin Carter

Illustrations by Jack Gaughan.
Here's a lighthearted, tongue-in-cheek adventure yarn featuring an ultra-competent protagonist. The editor's blurb compares him to James Bond and Sherlock Holmes, but he reminds me more of Derek Flint.

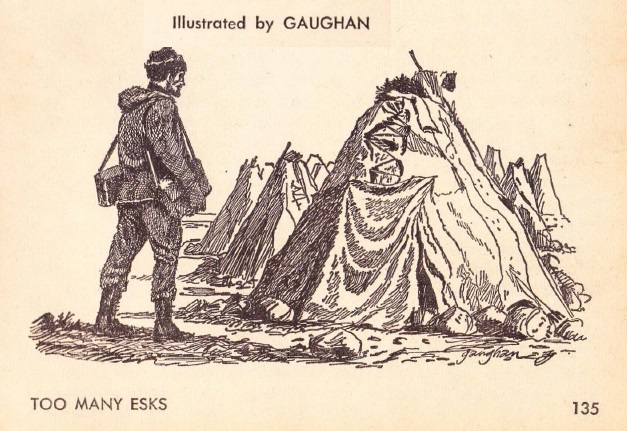
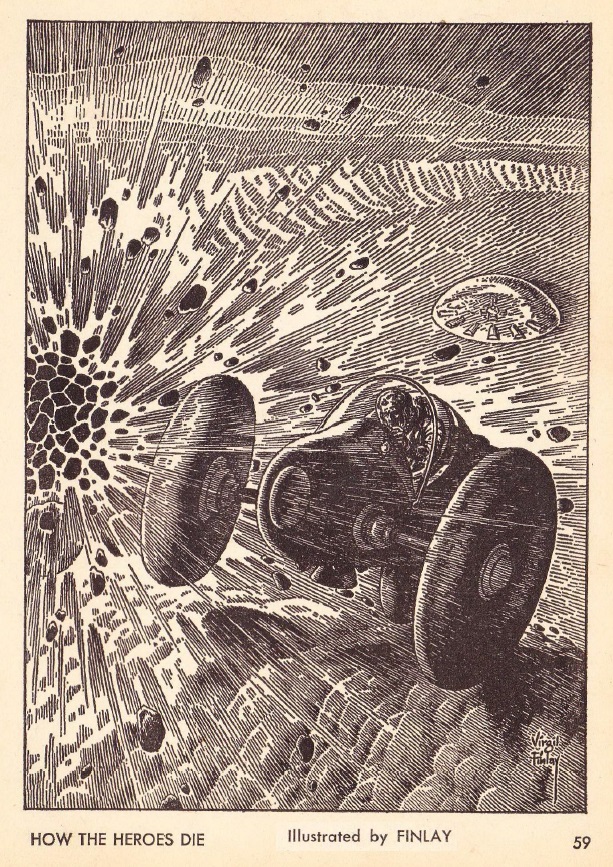
Our hero and his pet dragon.
Mister Quicksilver is a professional, legal thief. (There's some nonsense about how crime is legal and legal activity is outlawed, but forget about that. This isn't the most logical story in the world.) He lives in a castle on an asteroid, hidden among other chunks of rock orbiting a distant star. This method of concealing his location — which doesn't seem to prevent folks from finding him — offers the opportunity for the reader to enjoy the first of several bits of doggerel that present Quicksilver's philosophy in poetic form.

Home Sweet Home.
Three people show up, one at a time, each wanting to hire Quicksilver to steal a jeweled crown, a relic of an ancient, extinct race of reptilian aliens. The prize is guarded by a sect of fanatical cultists. The three clients include a scholar who turns out to be an imposter, an aristocrat, and a government agent. The latter is a woman who is in love with him. For his part, Quicksilver prefers women who (unsuccessfully) resist his charms.
The quest involves a trip to a planet of criminals, to learn the current whereabouts of the only thief who escaped from the cultists with his life. A clue leads Quicksilver to Earth, where the fellow resides. Meanwhile, multiple assassins make attempts on our hero's life.
Eventually, with the help of the government agent, Quicksilver arrives on the planet of the cultists, where a surprise awaits him. Is there any doubt that Quicksilver will prevail, and that the woman will fall into his arms?

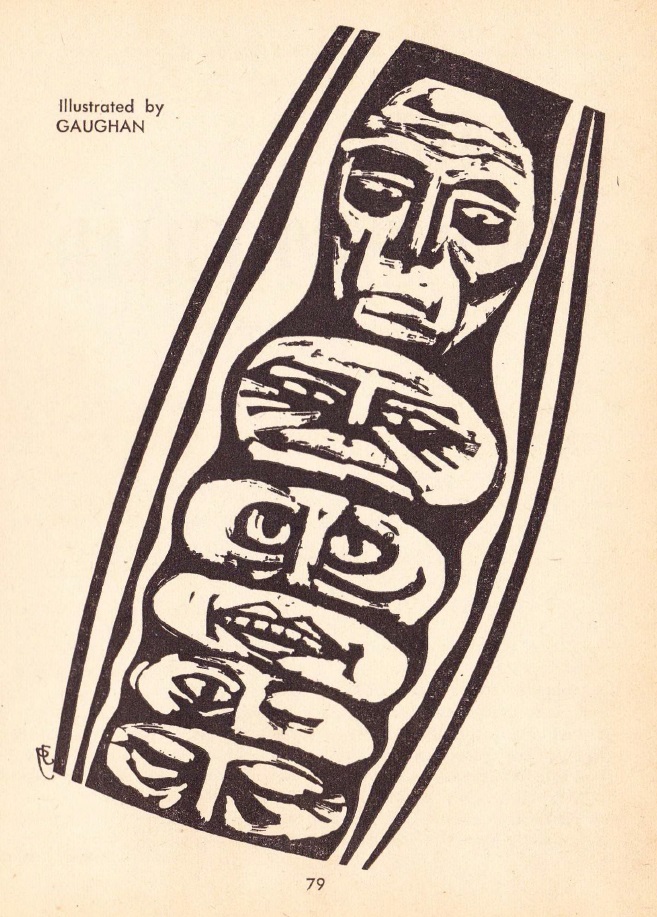
The reptilian aliens, who don't actually show up in the story.
The author revels in the clichés of space adventure, offering tons of odd names and exotic details. Although it's not an out-and-out comedy, there are silly jokes along the way. (There's a reference to various folk heroes from the local religion of far future Earth: Abe Lincoln, Mickey Mouse, Fidel Castro, and Joan Blondell.) These quips tend to take the reader out of the story, which is pretty hard to take seriously anyway.
Quicksilver is an arrogant son-of-a-gun, and the way he forces a kiss on the protesting heroine at the end isn't very pleasant. The whole thing is like a great big bowl of whipped cream; tasty at first, maybe, but you'll soon wish for something more substantial.
Two stars.
The 1991 Draftee, by Joseph Wesley
The author has written about the future of the military several times for the magazine. This latest article includes letters from a young guy serving in the army a quarter of a century from now. It's a pretty depressing picture.
The military secretly induces hypnotic suggestions into the minds of its recruits. There's also some discussion of small robotic weapons that crawl like spiders or fly like insects. Nonlethal but debilitating gases fill the battlefield, so the soldiers wear protective, air-conditioned suits.
It's all highly speculative, particularly the idea that young men of the future will want to shave their heads bald, so the army has to give them regulation haircuts by applying hair-growing treatments! (A wry comment on today's fad for long hair on male hippies?)
Two stars.
Frost Planet, by C. C. MacApp

Illustrations by Gray Morrow.
With the permission of the bear-like aliens who inhabit the place, humans have set up mining facilities and a colony under the ice of a frozen world. A crisis threatens to upset the uneasy relationship between the two species when a man is found stabbed to death with an alien knife. A military officer investigates the crime.
Things get even worse when small atomic heating devices go missing. It turns out that several of them have been placed in the ice near the human outpost, intended to destroy the colony. Later, an alien is killed by a human rifle, leading to open conflict. Can our hero prevent disaster?

Firing at a mysterious enemy.
This is a pretty decent science fiction suspense story, which develops quite a bit of tension. You may be able to figure out the whodunit aspect of the plot. The aliens are intriguing, but not enough is done with them.

A duel to the death.
I had to wonder why people are here in the first place. The extreme cold (effectively conveyed, by the way) is hardly conducive to human habitation, and we never find out what the mines produce.
As in many SF stories, the assumption seems to be that future folks will inhabit lots and lots of alien worlds, even those with their own native population. In any case, it's a lot better than the author's seemingly endless Gree series.
Three stars.
Report on the Slow Freeze, by R. C. W. Ettinger
From fictional cold to (possibly) factual cold. The magazine has discussed the possibility of freezing people at the time of death and then reviving them in the future a couple of times before. In this current variation on the theme, the author offers a history of the idea, and speculates about why it has failed to catch on.
A lot of this is going over old ground. The most interesting aspect of the article may be that the author seems to believe that appealing to the emotions, rather than the intellect, is the most effective way to promote the technique.
Two stars.
To the War is Gone, by Richard C. Meredith

Illustrations by Burns. I have been unable to discover the artist's first name.
There's a war going on between ordinary humans and those who have become attached to alien symbiotes that give them a single group mind. After a space battle that destroyed both ships, a lone human survivor with a broken leg waits for death, stranded in a detached segment of the vessel. There's an intact lifeboat not too far away, but he has no way to get to it.

The man. That buzz is goofy.
The only living inhabitant of the enemy ship shows up, floating through the void in a spacesuit. She can reach the lifeboat, but can't operate it. The two can communicate through radio, but can they work together to survive? More importantly, can they trust each other?

The woman, apparently producing the buzz.
I was reminded both of Robert A. Heinlein's novel The Puppet Masters (1951) and Tom Godwin's story The Cold Equations (1954) when I read this piece. Unfortunately, although it was compelling at first, it collapsed into melodrama by the end.
One interesting aspect of the story is the fact that the protagonist is a musician, and the text includes excerpts from real folk songs, as well as fictional ones of the future. Less enjoyable was making the other character a member of a group of women noted for their erotic appeal. This makes the man's decision to help her a matter of sheer lust. (Many of his folk songs are pretty bawdy, too.)
Two stars.
Until Armageddon, by Dannie Plachta
As a break from all this deep space stuff, we have a tiny story set on good old Mother Earth. The Pope and the Premier of Israel (sounds like the start of a joke) meet to ask a super-computer how to achieve world peace. The response is unexpected.
I said a joke, and this thing ends with a punch line, but it's not intended to be funny, as far as I can tell. I don't really know what to think about the twist the author throws at me.
One star.
The Jew in Science Fiction, by Sam Moskowitz
Starting with an analysis of the 1959 novel A Canticle for Leibowitz by Walter M. Miller, Jr., the author delves into the way that science fiction has depicted the Chosen People. With a few exceptions, it's a depressing account of virulent antisemitism. The article includes a discussion of the many talented Jewish writers and editors in the field, noting that they have produced hardly any works relating to the topic.
This was much more interesting than the author's previous scholarly but lifeless articles. I suspect this is because he cares passionately for the subject. The conclusion serves as something as an indictment of the supposedly progressive genre of science fiction, which Moskowitz sees as less enlightened than mainstream fiction.
Three stars.
Seventy Light-Years From Sol, by Stephen Tall

Illustrations by Dan Adkins
Back to voyages to faraway worlds. A team of experts explore an Earth-like but very strange planet. The only form of life seems to be plants resembling lettuce covering the ground. While investigating holes in the dirt, they discover what appear to be millstones.
That's weird enough, but things really get odd when big cubes of various colors show up out of nowhere. (They're actually quite a bit larger than shown in the illustrations.)

The team's biologist, surrounded by cubes.
It seems that the cubes are alive, and are able to communicate, to some extent, with the humans telepathically. The millstones are predators of the cubes, spewing out a substance — which turns out to be aspirin! — that dissolves their prey so they can absorb them.
Adding to the confusion is the fact that the planet's other continent is inhabited by gray, imperfect cubes, that threaten to invade the land of the perfect, colorful cubes.
As you can see, this is a really nutty plot, almost like something out of one of Lafferty's tall tales. What makes it work reasonably well is the fact that the human characters are a likable bunch, each with their own quirks. I particularly like the fact that the crew includes a painter, an eccentric older woman. She's a refreshing change from the scientists, officers, and technicians aboard the exploratory starship.
Three stars.
Down to Earth
Coming back home after this imaginary voyage to other star systems was something like returning from a disappointing LSD trip. Some of the pieces were moderately diverting, but nothing was outstanding. Maybe it's time to turn to some other form of entertainment.

A recent children's book. It might be a safer way to travel than acid.

![[October 10, 1966] Let's Take A Trip (November 1966 <i>Worlds of Tomorrow</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Worlds_of_Tomorrow_v04n02_1966-11_0000-2-672x313.jpg)

![[October 6, 1966] One Trek, neat (<i>The Naked Time</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/661006title-672x372.jpg)















![[October 4, 1966] The Real Treasure Was The Friends We Made Along The Way (<i>Doctor Who</i>: The Smugglers)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/6601004kidnap-672x372.jpg)


![[September 30, 1966] Return to Base (October 1966 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/660930cover-672x372.jpg)























![[September 22, 1966] True Idols (the Isaac Asimov issue of <i>Fantasy and Science Fiction</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/660920cover-659x372.jpg)





![[September 20, 1966] In the hands of an adolescent (<i>Star Trek</i>'s "Charlie X")](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/660920a-672x372.jpg)

![[September 14, 1966] All the Old Familiar Places (October 1966 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/660912cover-672x372.jpg)






![[September 10, 1966] Bon appetit! (this month's Galactoscope)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/660910covers-672x372.jpg)







![[September 8, 1966] The Bare Hardly-Essentials (October 1966 <i>Amazing</i>)</big></b>](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/amz-1066-cover-491x372.png)




