
by John Boston
The August 1967 Amazing looks out on the world through one of Frank R. Paul’s later and less interesting works, trimmed of course from its original pulp size. This one, titled A City on Uranus, is from the back cover of the April 1941 Amazing, as usual cropped to fit the lower half of this smaller magazine. The issue’s overall contents and presentation are also as usual: one new story and a bunch of reprints, with Harry Harrison’s intelligent book reviews taking a few pages.

by Frank R. Paul
La de da de de.
The Man from Zodiac, by Jack Vance
Once more I say—at the risk of repeating myself repeating myself repeating myself—when a first-rate author shows up at the bottom of the market, there’s a reason for it. The one non-reprinted piece of fiction here is Jack Vance’s “Great New Short Novel,” as the table of contents has it, The Man from Zodiac. Zodiac Control, Inc., is a corporation that sells government services to colony planets across the galaxy, or galaxies (there is ambiguous reference to Andromeda), with competitors like Aetna, Fidelity, and Argus.

by Gray Morrow
The eponymous Man is Milton Hack, a Zodiac employee (and also a minority shareholder, a fact which ultimately has little significance), who is charged by the main owners with getting and supervising a contract with the Phrones of Ethelrinda Cordas. The Phrones are cartoon barbarians who have (or whose elite has) little interest in schools, sewer systems, and the other usual appurtenances of government; they wish only to obtain weapons with which to smite their neighbors and enemies, the equally cartoonish Sabo.
Hack engages in a course of bamboozlement and chicanery and ends up representing both the Phrones and the Sabos with identical contracts, and persuading them to live in something resembling peace, outsmarting everyone in sight at every opportunity since they are all utterly stupid. It’s frankly pretty crude, devoid of Vance’s usual sharp satirical wit; worse, it’s thoroughly boring, and gives the impression that the author is as bored as the reader. Or maybe he is attempting to emulate the literary and commercial success of Christopher Anvil. Two stars.
Martian and Troglodyte, by Neil R. Jones
The reprints are the usual mixed bag, slightly better mixed than in some issues. The longest and oldest—a “Special—Short Novel” per the contents page—is Neil R. Jones’s Martian and Troglodyte, from the May 1933 Amazing. Jones is best remembered for his protracted “Professor Jameson” series, about a scientist who is revived from his orbiting tomb and who goes chasing around the universe for a couple of dozen stories with the robot-bodied Zoromes. In this one, Thrag, a cave guy who has been chased out of his tribe in a dispute over possession of the winsome Tua, is saved from becoming lunch for a cave bear by visiting Martians on a voyage of discovery. (Jones’s Earth has many perils. In addition to cave bears and saber-tooth tigers, tyrannosaurs and pterodactyls are still around.) Thrag learns not to be afraid of the Martians and they help him out in his quest to recover Tua from her brutal usurper by lending him lethal Martian technology. Thrag’s and the Martians’ efforts to figure each other out are surprisingly well done.
by Leo Morey
Overall, this is a pleasant antique, though Jones’s peculiar verbosity is sometimes a distraction. (Any resemblance to the present commentator is entirely illusory.) A sample:
“In the depths of space between the earth and its contemporary planet, known to present day man as Mars, a small space ship sped at an inconceivable speed across the millions of miles of space towards the earth. It was now very close, having been upon its journey through the stellar void for the period of time in which it had taken the great globe it was approaching to turn upon its axis forty times. Forty times the topographical features of the planet earth had swung lazily before the eager eyes of the two space navigators within their interstellar craft as day by day, according to the rotation of the cosmic sphere, the planet grew larger in proportion as they drew near.”
Two stars; it probably would rate higher by the standards of its time.
Blabbermouth, by Theodore Sturgeon

by Malcolm Smith
Theodore Sturgeon’s Blabbermouth, from the February 1947 Amazing, is about a captivating woman who is telepathic and compulsively blurts out people’s secrets to those from whom they are being kept secret. This brings ruin to her husband’s career as a prominent New York radio emcee, but by the end he figures out how to make lemonade (i.e., money) from this particular lemon. The story is told in an affected semi-Damon Runyonesque style that bespeaks a writer trying to execute the cliches he thinks his market requires. And maybe it did. Or not. This is only the second published story Sturgeon sold to an SF or fantasy editor other than John W. Campbell, and maybe he didn’t have much confidence about following his own bent anywhere else. Two stars.
The Roller Coaster, by Alfred Bester

by Bernard Krigstein
There are two stories here from the magazine’s brief high-word-rate renascence of 1953-54. Alfred Bester’s The Roller Coaster, from the May-June 1953 Amazing, is also told in an affected style, but it’s Bester’s own affectation, so it’s a lot more convincing than Sturgeon’s off-the-rack costume in Blabbermouth. It starts with a slap to the reader’s face of Spillaneish violent sadism—quite appropriate in context, as it turns out—and continues without letup or wasted words to retell a familiar SF story. It’s as if somebody said, “You read Vintage Season? Here’s how it really goes.” Four nasty stars.
One Way Street, by Jerome Bixby

by Augusto Marin
In the other renascence item, Jerome Bixby’s One Way Street (Amazing, December 1953-January 1954), the protagonist has a split-second blackout, drives off the road, and wakes up in a wrecked car and a slightly different world—phone numbers are different, his dog is different, there’s no Hamlet, Shelley, Keats, or atomic power, and Stalin’s alive. His wife’s a little different too, but he likes the differences and is trying to make a life in this new world when he gets a chance to try to go home via an experimental procedure. The surprise ending is about as surprising as the sun rising in the morning, but overall the story is sharply and economically done. Three stars, pushing four.
North God’s Temple, by Henry J. Kostkos
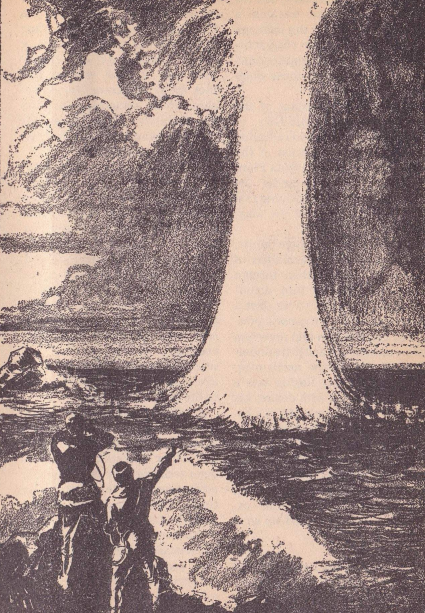

by Leo Morey
We dip back into the archaic with Henry J. Kostkos’s North God’s Temple (Amazing, August 1934), in which a Professor Challenger-type blowhard, Professor Norton of the Cosmopolitan Museum, receives a telepathic summons from the historians of the People of the Magnetic God, who live undersea near the North Pole. So he fakes up a pretext for an expedition to seek out the magnetic pole. Once there he is summoned alone and sucked underwater and then underground in a rowboat, and finds the Temple of the Magnetic God (it must be, since he’s pinned to the wall until he manages to work his steel revolver out of his pocket). This Temple landed on Earth after the breakup of the former fifth planet that became the asteroids. Then Norton gets sucked back underwater in a contretemps that apparently is intended to explain the migration of the magnetic poles. Two stars for this tiresome period piece.
Vis Scientiae, by Miles J. Breuer, M.D.
But there’s still one more piece of archaic to eat: Vis Scientiae, a poem by Miles J. Breuer, M.D. (Amazing, May 1930), which seems to be a lament by the ancient gods that they’re no longer in charge of those pesky humans. It must speak for itself:
“They have chained the livid lightning that goes hurtling down the sky,
Made it slave for them and pass them scatheless as it hurtles by;
They have trapped the furious tempest at whose breath the forest reels,
And the angrier it rages all the merrier turn their wheels; . . .”
Et cetera, though the meter varies. The substance of Tennyson and the accidents of Robert W. Service? The best to be said for it is that it could have been worse. Two stars.
Summing Up
A couple of stories well worth reading, a couple more at least readable, and a couple of wastes of time. La de da de da.

![[July 14, 1967] The Beat Goes On (August 1967 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/amz-0867-cover-383x372.png)

![[May 6, 1967] Stirred? Shaken? (June 1967 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/amz-0667-cover-504x372.png)




![[March 14, 1967] Family Matters (April 1967 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/amazing-apr-1967-cover-489x372.png)







![[January 14, 1967] First batch (January Galactoscope)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/670114covers-672x372.jpg)







![[January 6, 1967] Happy Anniversary (February 1967 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/amz-0267-cover-465x372.png)







![[November 24, 1966] Middling (December 1966 <i>Amazing</i>)</big></b>](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/amz-1266-cover-503x372.png)






















![[September 8, 1966] The Bare Hardly-Essentials (October 1966 <i>Amazing</i>)</big></b>](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/amz-1066-cover-491x372.png)





![[July 22, 1966] Ridiculous! (August 1966 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/amz-0866-cover-665x372.png)






![[July 14, 1966] October's Judgment (July Galactoscope)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/660714coversjpg-672x372.jpg)

