
by Mx. Kris Vyas-Myall
Just as with the ancient Norse concept Ragnarök, it is inevitable the gods of music will fall. In America exciting new acts have been emerging to challenge the so-called British Invasion. The Grateful Dead appeared on an episode of documentary series Panorama, Otis Redding got a full dedicated special on Ready, Steady, Go and ? and the Mysterians have entered the top 40 with the bizarre Vox Organ sound of 96 Tears.
But none has been more dramatic than the dethroning of Eric Clapton by young James Marshall “Jimi” Hendrix.

Eric Clapton has become a central figure of the London Blues scene. Making his name with The Yardbirds, he has also recorded with John Mayall’s Bluesbreakers and The Powerhouse. He had become seen by many as the greatest guitarist in the world, with the phrase “Clapton is God” spray-painted in Islington.
When Former Animals Bassist-turned-Manager Chas Chandler brought Jimi Hendrix to England, he took the American guitarist to see Clapton’s new band Cream at the London Polytechnic. In the middle of their set, Hendrix went on stage and asked Clapton if he could play a couple of numbers. He then proceeded to play a fast-paced version of Killing Floor (A Howlin Wolf song Clapton has reportedly found difficult in the past) and then walked off stage—thereby managing to upstage this musical God at his own concert.
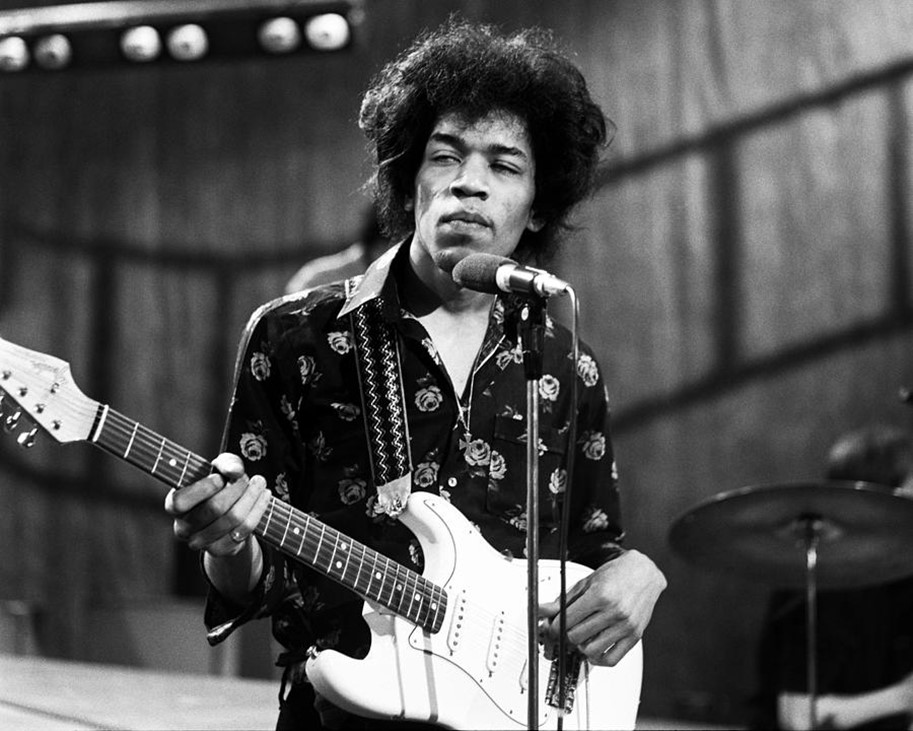

Since then, he has given a fiery performance on Ready, Steady, Go! and released his first single “Hey Joe”. Is this kind of Nietzschean destruction of the British musical gods to prove permanent? Only time will tell.
It is not just in music the old gods are being replaced by new ones. There are two books that have come out where scientists are forced to face new computer overlords:

Battle of the Computers
B.E.A.S.T. by Charles Eric Maine

Charles Eric Maine is one of the old hands of British SF, having begun publishing short fiction before the war and novels since the early 50s. However, he has never quite impressed me in the way others of his generation have, like Eric Frank Russell, John Wyndham or Arthur C. Clarke. His latest has actually managed to lower my opinion of his work further.
The first thing to note about B.E.A.S.T. is it is a pretty short novel. The print is rather large and the whole thing probably only amounts to around 50,000 words.
The author then proceeds to spend a large amount of time at the start of the book explaining in great detail what DNA is and how genetics works. Whilst Maine clearly delights in showing his knowledge it is largely extraneous (do we need to know the names of the nucleic acids for things to progress?)
The depiction of women is also appalling. The narrator spends his time dissecting the looks of each one he sees with an horrendous judgement on each. One extroverted woman is described as a “congenital nympho”; of an an introvert a few pages later: “If she wasn’t exactly fat, she was well turned. Her face wouldn’t have launched a dinghy, let alone a thousand ships…[yet] somewhere inside her was a woman waiting to get out.” This is proceeds throughout text whenever a woman is introduced and, even ignoring the tackiness of it, represents another waste of space.
What remains is a rather mediocre thriller where Mark Harland, a member of the Department of Special Services, is sent to investigate Dr. Gilley, a research director at a genetic warfare research division. It is discovered Gilley has been doing experiments in simulating evolution in accelerated fashion inside a computer and believes he has created a sentient machine. The whole thing is oddly paced, filled with long conversations, and it has an ending that is among the most cliched possible
B.E.A.S.T. is a jumble of the most fashionable current ideas in science fiction, sexual psychology and spy-craft, gene warfare and computer control, thrown together in an attempt to appeal to the current reader. But it is done so poorly, it comes off as amateurish and cynical.
One star for this mess.
Colossus by D. F. Jones

From an old hand to a new writer. To the best of my knowledge this is the first SF work of DF Jones, and little seems to be known about him from the people I have spoken to. However, this novel makes it seem like he will have a bright future in science fiction.
The plot: Forbin has spent years devoting himself to the project of making a computer powerful enough such that it can be trusted to control the USNA nuclear weapons systems, thereby removing the dangerous threat of someone launching an unnecessary strike. However, as the launch of this computer (named Colossus) approaches he becomes nervous of its power, worried they will have no way to stop it if something goes wrong. The USNA president dismisses this and sets it to activate, then putting it in an impenetrable location so no one can tamper with it.
Two unexpected things happen however:
1. Colossus proves to be even more intelligent than Forbin had predicted;
2. It turns out the Soviet Union have also been building their own computer system, and now both sets of nuclear weapons are in electronic hands.
Most fans of science fiction may well be able to guess where this story was going, I myself was particularly reminded of Doctor Who: The War Machines (albeit with more nuclear missiles and fewer giant plastic boxes roaming the streets of London).
However, Jones is a very capable writer and manages to keep the tension up even as we are just reading Colossus reel off simple sums or instructions. One of the least discussed truths of our world is that the most important decisions in life are just made by people talking in rooms and calculations being made. Yet this will rarely be shown in films in this manner as it is hard for even a skilled director to keep you engaged. This is one advantage that the written word has over the screen, which Jones puts to excellent use (and I fear what would happen if this was made into a movie: presumably a lot of noise and gunfire signifying nothing).
In a recent interview with New Worlds, Kingsley Amis criticizes Colossus for spending some of the early part of the book explaining how the computer works, on the grounds that the concepts would be well known to the average science fiction reader. As much as I respect Mr. Amis, I would like to disagree at the most basic level with his argument. Firstly, unless something has truly entered popular culture enough that it would not need to be explained to one's grandfather (e.g. the presence of a gun in a western) the facts should be laid out for the reader that will be pertinent to a later understanding. And in this case I believe what Jones laid out is necessary to the reader's comprehension of future plot points, (not merely the explanation for its own sake we get from Maine). Secondly, and relatedly, I think we should be careful not to make SF books opaque to the mainstream reader. Particularly with those being released by a mainstream publisher, one never knows when a book will be the first science fiction novel a reader will pick up. If we simply assume they will know what a given term means because A. E. van Vogt used the term in a novelette in 1948 the genre will become increasingly insular.
In spite of just being a computer who largely communicates in curt typed instructions, Colossus must rank among the more memorable of science fictions villains. It is at once both coldly utilitarian and has its own god complex. Based on its own assessment of the facts and a belief that its mission is to prevent war, it cannot understand why it should not control the world, be worshipped as a deity and kill millions of humans in order to achieve greater aims.
Unfortunately, something this book shares with B.E.A.S.T. is the poor treatment of women. Whilst it is nowhere near as bad as what Maine has published, we still get Dr. Cleo Markham, one of Forbin's team, having a scene where she is naked for no apparent reason other than to titillate the reader, and we hear more about her “female intuition” than her actual skills at her job.
In contrast to B.E.A.S.T. which feels complete, Colossus feels open-ended. I have not heard if Jones has plans for a sequel or if it is meant to simply suggest the horror of what might come (ala Asimov’s The Evitable Conflict) but in either case it finishes the book on a high note rather than a damp squib of an ending that Maine gave us.
A high three stars
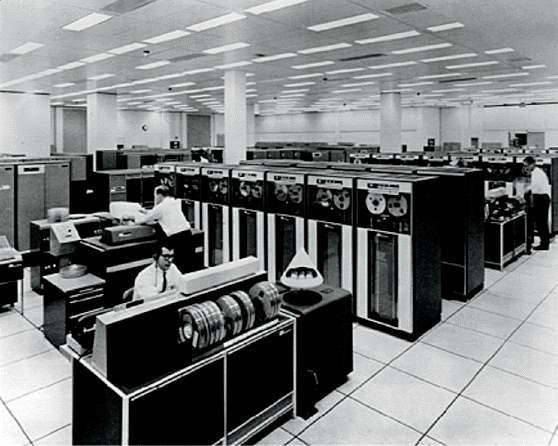

To The Victor…
So, in the future cybernetic war of who will control us, it definitely appears Colossus is going to win out over B.E.A.S.T. Whether we wish to accept their dominance is another matter…
[Having read about two fictional computers, you might enjoy reading about the state of the art in real computers. The Journey has a great many articles devoted to the subject. Stay up to date and give them a read!]

![[December 16, 1966] The God Slayers (two computer-themed novels)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/661216covers-672x372.jpg)

![[April 22, 1966] No Man's Land (<i>Women of the Prehistoric Planet</i> and Further Female Filled Fantasy Films)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/women_of_prehistoric_planet_1966-3.jpg)




























![[May 24, 1964] The Darkest of Nights… ( <i>June 1964</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/640528Darkest-book-club-1964-423x372.jpg)


