by Gideon Marcus
At long last, it's holiday season again—and that means offering up our choices for the best science fiction of 1968.
These recommendations represent the culmination of a year's work: reading virtually every English-language (and some translated) work of science fiction and fantasy, regardless of where it's published; reviewing them; rating them; nominating them; and finally, assembling this article.
In many ways, 1968 has been a banner year, with plenty to enjoy from a variety of subgenres and moods. You could spend a good many weeks just enjoying the best of what this rather fraught year had to offer.
And after the last 363 days you've had to endure, haven't you earned a break?
——
Best Poetry
——

Report On A Supermarket, by Michael Hamburger
Dance Music for a Gone Planet, by Sonya Dorman
Two Voices, by D. M. Thomas
Instructions for Visiting Earth, by Christopher Logue
–
Poetry is the most subjective of the literary arts, so we won't offer a "Best". Instead, here is a nice cross-section of pieces we found moving. And remember that a lot of the best stuff can be found in the fanzines, so don't restrict yourself to the pros!
——
Best Vignettes (1-8 pages)
——

Sublimation World, by John Sladek
If you're a fan (or not a fan) of J. G. Ballard, then you must read "Sublimation World". It's an in joke, but one whose time has come.
ㅤ
Crazy Annaoj, by Fritz Leiber
A galaxy-spanning romance that you will fall in love with.
I Have My Vigil, by Harry Harrison
A poignant who, or what, am I story.
Segregationist, by Isaac Asimov
Organ transplants and artificial organs are the topic of the day, and this story explores the concept most fully.
Honorable Mention
The Deceivers, by Larry Niven
The Moving Finger Types, by Henry Slesar
The Tell-Tale Heart-Machine, by Brian W. Aldiss
Lib, by Carol Emshwiller
The Story to End All Stories for Harlan Ellison's Anthology Dangerous Visions, by Philip K. Dick
—
From hellish to hilarity, this year's crop of short shorts does not disappoint.
——
Best Short Stories (9-19 pages)
——

Wednesday, Noon, by Ted White
The Rapture comes to New York—time for dancing in the streets.
ㅤ
The Two Best Thieves in Lankhmar, by Fritz Leiber
Fahfrd and The Gray Mouser cross paths with Joanna Russ' Alyx in this sword and sorcererial adventure. What's not to love?
Shattered Like a Glass Goblin, by Harlan Ellison
Harlan's anti-drug polemic, done in horrific, uniquely Harlan style.
Honorable Mention
The Ajeri Diary, by Miriam Allen deFord
The Eye of the Lens, by Langdon Jones
The People Trap, by Robert Sheckley
All the Myriad Ways, by Larry Niven
The Meddler, by Larry Niven
Kyrie, by Poul Anderson
The Dance of the Changer and the Three, by Terry Carr
The Ferryman on the River, by David A. Kyle
One Station of the Way, by Fritz Leiber
The Dead Astronaut, by J. G. Ballard
Here Comes John Henry!, by Ray Russell
–
When you've got a three-way tie for a category, you know it's a good year. Even better when there are ten tales that get Honorable Mention, too. The subject matter is more serious, on the whole, than the vignettes, though the Niven, the Sheckley, and the deFord are not without their amusing qualities.
——
Best Novelettes (20-40 pages)
——

Time Considered As a Helix of Semi-Precious Stones, by Samuel R. Delany
A tale of art, crime, and hepcats in 21st Century New York—a quintessential Chip Delany story.
ㅤ
Total Environment, by Brian W. Aldiss
Inside an Indian city-skyscraper, but it's not the overpopulated Earth story you think it will be…
High Weir, by Samuel R. Delany
The Martians had an unique way of recording history—but unlocking it can destroy the unstable mind…
Honorable Mention
The Wall to End The World, by Vincent King
I See a Man Sitting on a Chair, and the Chair Is Biting His Leg, by Harlan Ellison and Robert Sheckley
There is a Tide, by R. C. FitzPatrick and Leigh Richmond
The Egg of the Glak , by Harvey Jacobs
The Barbarian, by Joanna Russ
Eeeetz Ch, by H. H. Hollis
The Sharing of Flesh, by Poul Anderson
–
A good suite of stuff, although I think the novelette category is not as strong as it has been in previous years. Also, how much you like our picks is strongly dependent on how much you enjoy Delany, who has a distinct flavor (although "High Weir" is the least Delany-ish story I've read by him in a while.)
——
Best Novella (40+ pages)
——

Lines of Power, by Samuel R. Delany
A "Wichita Lineman" of the future tries electrifying a gang of Canadian Luddite hippies. Culture clash ensures.
ㅤ
A Tragedy of Errors, by Poul Anderson
On an imperial planet reverted to savagery, the crew of a crashed starship attempt to effect repairs.
Grimm's Story, by Vernor Vinge
The world of Tu is another world that has become an interstellar backwater, but it is slowly clawing its way back to industrialization—in no small part thanks to Fantastique, the magazine of "contrivance fiction". When an astronomer with a psionic cat is tapped to rescue the one complete set of the magazine from destruction, it turns out far more is at stake.
The Consciousness Machine, by Josephine Saxton
WAWWAR, a psychotherapy machine, heals the mind by providing hallucinatory trips. But in this tale, just who is being healed, and how is the human therapist, who controls WAWAR, involved?
Honorable Mention
Hawk Among the Sparrows, by Dean McLaughlin
Perris Way, by Robert Silverberg
The Custodians, by James H. Schmitz
Grendel, by Larry Niven
I just discovered this terrific story in Niven's Neutron Star, a collection of Known Space stories. This one features Bey Schaeffer, a retired hyperspace pilot who gets entangled in a kidnapping plot. I'm not sure why it didn't get published in a magazine, but it's well worth your time.
–
In contrast to novelettes, the novella category is quite healthy, in part thanks to the rise of the paperback anthology. Lots of hard choices here, and some really excellent work across a range of genres. I'd say the novellas are the most universally SFnal of the pieces this year.
——
Best Novel/Serial
——

Stand on Zanzibar, by John Brunner
An overcrowded, 21st Century Earth depicted with New Wave, psychedelic sensibilities. A huge, unprecedented work.
Picnic on Paradise, by Joanna Russ
Ancient Mediterranean swashbuckler Alyx is now part of a far-future team of troubleshooting adventurers. Somehow, it works.
ㅤ
Rite of Passage, by Alexei Panshin
Young Mia Havero, who lives on a galaxy-faring trade ship, finds herself on a hide-bound, hostile colony world. Can she survive her rite of passage—her trip to the planet?
A Wizard of Earthsea, by Ursula K. LeGuin
The fantastic adventures of Ged, young sorcerer, on LeGuin's island world that has been featured in several stories to date.
Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?, by Philip K. Dick
San Fran bounty hunter on a denuded Earth is tasked to kill five androids. What does it mean to be human? What does it meant to live a robotic life?
Honorable Mention
The Jewel in the Skull, by Michael Moorcock
The Swords of Lankhmar, by Fritz Leiber
Synthajoy, by D. G. Compton
The Two Timers, by Bob Shaw
Nova, by Samuel R. Delany
The Spawn of the Death Machine, by Ted White
—
Another great year for paperbacks. In addition to the usual suspects (Delany, Dick, Leiber, Brunner), it's neat to see some newer names hit the charts: Russ, LeGuin, Shaw, White. The field is only getting bigger and better!
——
Best Science Fact
——

Heinlein in Dimension, by Alexei Panshin
The first more-or-less complete analysis of one of the titans of science fiction.
ㅤ
Into the Media Web, by Michael Moorcock
For Your Information: My Friend, the Nautilus, by Willy Ley
Andy Warhol: Portraits, Still Lifes, Events, by Andrew Lugg
Honorable Mention
The Seventh Metal, by Isaac Asimov
Barbarella and the Anxious Frenchman, by Michael Moorcock and Charles Platt
For Your Information: Mission to a Comet, by Willy Ley
If … and When, by Lester del Rey
—
It's nice to see Willy Ley's name ascendant again, and of course, Lexy Panshin earned his Best Fan Writer Hugo this year largely on the strength of his book on Heinlein (originally published serially in fanzines). If the appearance of a piece on Warhol surprises you, read it—after all, why shouldn't art be a cutting edge technology, too?
——
Best Magazine/Collection
——

The Farthest Reaches: 3.40 stars, 2 Star nominees (just one anthology)
Galaxy: 3.22 stars, 12 Star nominees (nine 1.5x size issues)
New Writings 11-13: 3.08 stars, 2 Star nominees, (three anthologies)
F&SF: 3.06 stars, 10 Star nominees (12 issues)
IF: 2.96 stars, 2 Star nominees (12 issues)
New Worlds: 2.90 stars, 5 Star nominees (seven issues)
Famous Science Fiction 2.889 stars, 0 Star nominees (four issues)
Analog: 2.75 stars, 3 Star nominees (12 issues)
Amazing: 2.60 stars, 1 Star nominee (six issues)
Orbit 3 and 4: 2.50 stars, 3 Star nominees, (two anthologies)
Fantastic: 2.44 stars, 1 Star nominee (six issues)
Worlds of Fantasy: 2.32 stars, 0 Star nominees (one issue)
Beyond Infinity: 1.46 stars, 0 Star nominees (one issue)
—
Tallying things this way, it looks like Galaxy remains the front-runner. It's certainly the magazine I look forward to the most. Fan favorite and subscription juggernaut Analog is near the bottom of the back, and the Orbits, while they provide some excellent stuff, fare even worse. A bit surprising.
——
Best Publisher
——

Ace: 3 Star nominees
Doubleday: 3 Star nominees
Lancer 1 Star nominee
Paperback Library 1 Star nominee
Parnassus Press 1 Star nominee
No surprises here. Ace puts out 24 books a year just in the Doubles format, not to mention all its single titles. Still, Doubleday brings the goods when it comes to "serious" SF.
——
Best Artist
——

Jeff Jones

Kelly Freas

Leo and Diane Dillon
Honorable Mention
Frank Frazetta
Gray Morrow
Russell Fitzgerald
Virgil Finlay
–
Lots of familiar names on the list, but also some new ones, and the first time a woman has been prominent in a while.
——
Best Dramatic Presentation
——

2001: A Space Odyssey, Stanley Kubrik, director

Planet of the Apes, Franklin J. Schaffner, director

Doctor Who: The Enemy of the World, by David Whitaker

Star Trek: The Tholian Web, by Judy Burns and Chet Richards
Honorable Mention
Hour of the Wolf, by Ingmar Bergman
The Prisoner: Hammer into Anvil, by Roger Woddis
Rosemary's Baby, Roman Polanski, director
Star Trek:Is There in Truth no Beauty?, by Jean Lisette Aroeste
Star Trek: "The Trouble with Tribbles"
Theatre 625: The Year of the Sex Olympics, by Nigel Kneale
Wild in the Streets, Robert Thom, writer; Barry Shear, director
The Witchfinder General, Michael Reeves, director
–
With so much to choose from, the Hugos next year are going to be a mess. The Trek episodes, with the exception of "Tribbles", will be rerun this summer, and most of these movies are still in the cinema. In short, you still have time to appreciate these instant classics!
——
Best Comic Book
——

Deadman

The Trigan Empire

Nick Fury, Agent of SHIELD
Honorable Mention
The Incredible Hulk
The Silver Surfer
Valerian et Laureline
–
Deadman doesn't have a book of his own, but ever since his introduction last year, he has been a National (DC) fan favorite. Or, as fellow traveler Kris puts it:
Deadman is so great. It is like Arnold Drake went:
"So this comic is like The Fugitive…"
"Great"
"…except he's a trapeze artist…"
"Sure"
"…and dead…"
"Erm"
"…well a ghost who can possess people's bodies…"
"what?"
"….where the murderer is trying to get inducted into a Society of Assassins run by an ancient martial artist."
"…….."
——
Best Fanzine
——

Algol
Trumpet
Riverside Quarterly
Science Fiction Times
Amra
–
The winning entry speaks for itself. Trumpet has terrific production values with its pro-style offset printing, but only one issue came out this year. Riverside Quarterly continues to be scholarly and excellent. The new incarnation of Science Fiction Times is the best way to keep up to date on the goings on in the fan world.
——
Best Fan Writer
——
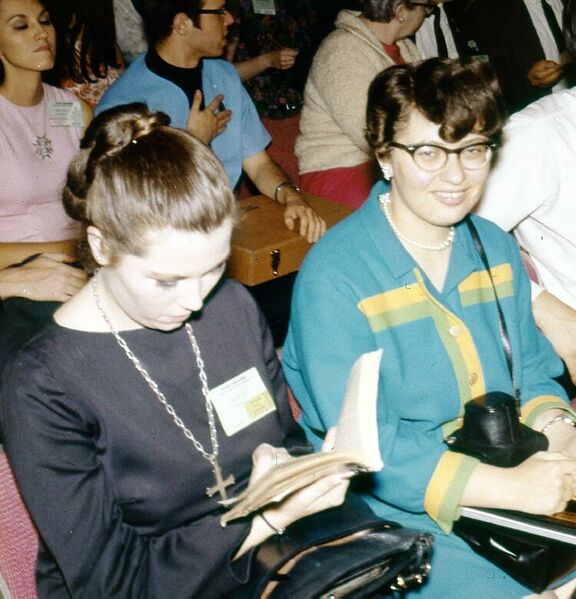

Ruth Berman (on the right)
There are lots of terrific fan writers out there maintaining a myriad of 'zines for our enjoyment. It's difficult to pick just one, so I'm just going to play favorites. I met Ruth this year. She is big in Star Trek fandom, editing the 'zine Inside Star Trek. She also covers conventions, is incredibly literate and sharp, conducting interviews of various luminaries in addition to her writing, and is an all around superfan. I would not be surprised if she has a big pro career ahead of her.
She was also a nominee for Best Fan Writer Hugo this year, so I'm not the only one who loves her!

Whew! That's some list. And no rest for the wicked—we're already reading 1969's offerings. But with entries like those above, there's plenty of wind in our sails. Sure, we run into shoals every so often (ahem Piers Anthony, John Norman, Lin Carter) but the great discoveries keep our momentum going.
So enjoy…and let us know which of these you particularly liked!




![[July 26, 1969] California Dreams…and Nightmares ("The Late, Great State of California")](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/690726cover-672x372.jpg)
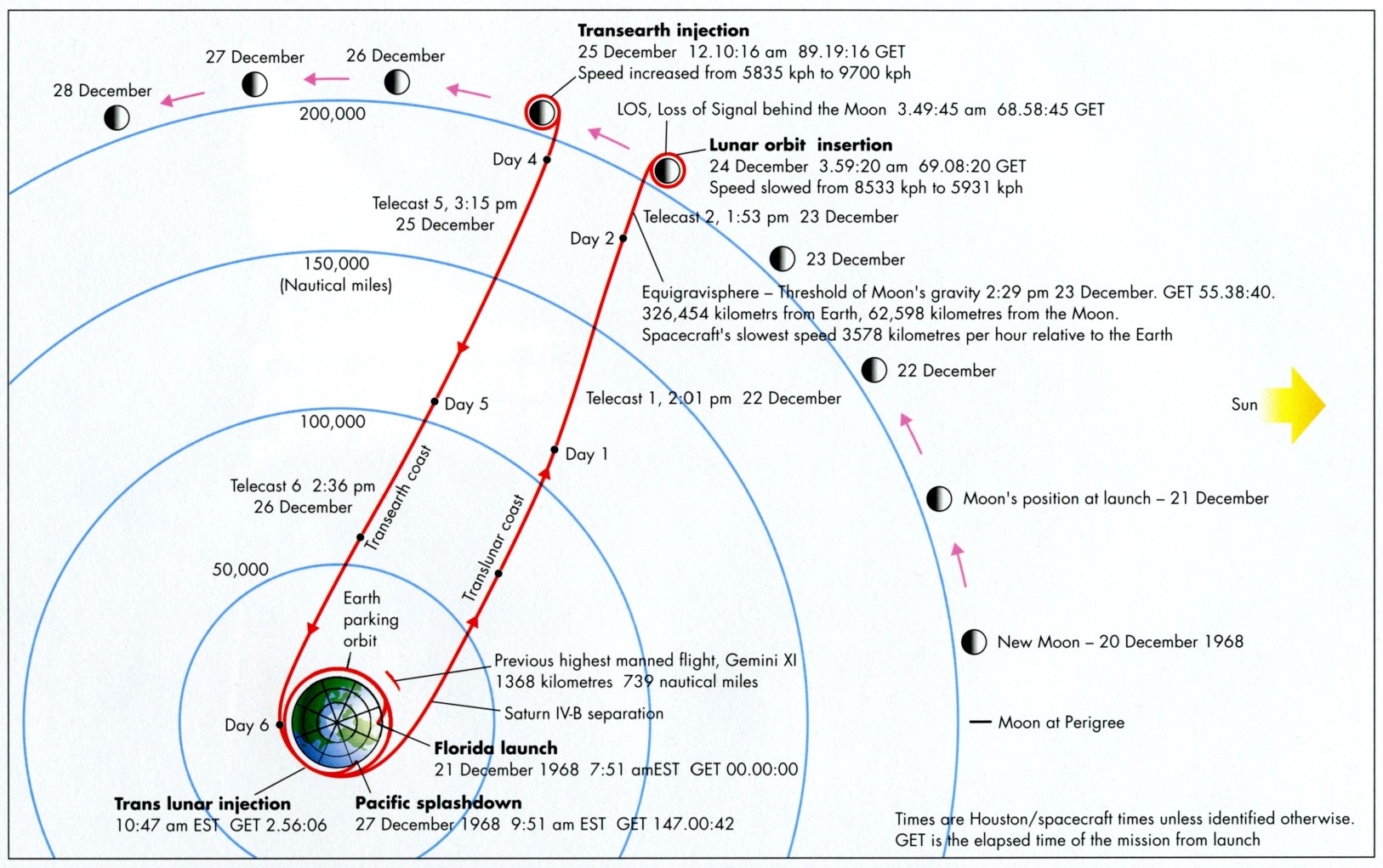
![[January 22, 1969] NASA’s Christmas Gift to the World Part 2 (Apollo 8 continued)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Apollo-8-Earthrise-672x372.jpg)
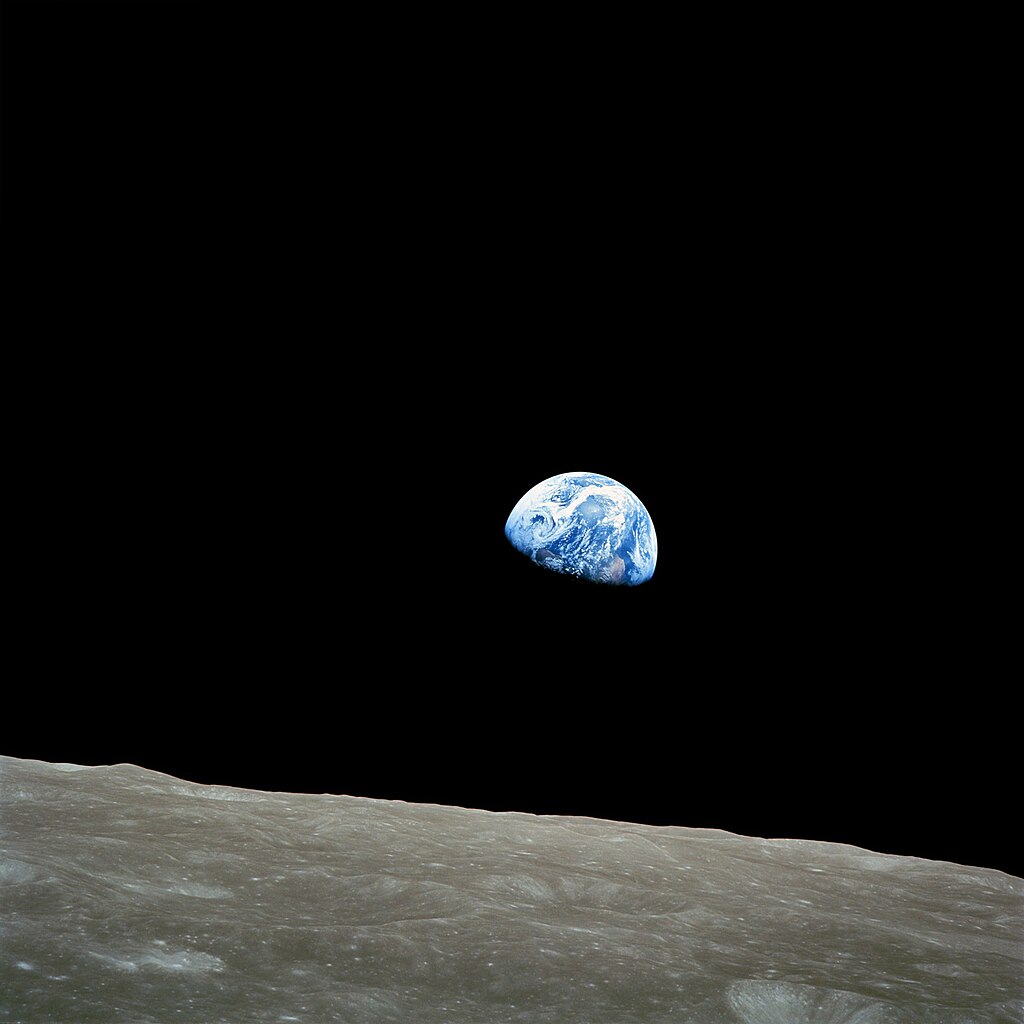
 "Oh my God!" is what Astronaut William Anders said just before he took this awe-inspiring photograph of the Earth rising over the Moon, as seen from lunar orbit. That was my exact response – and yours, too, I expect – on first seeing this incredible sight. I confidently predict that this amazing view will become one of the defining images of the Space Age
"Oh my God!" is what Astronaut William Anders said just before he took this awe-inspiring photograph of the Earth rising over the Moon, as seen from lunar orbit. That was my exact response – and yours, too, I expect – on first seeing this incredible sight. I confidently predict that this amazing view will become one of the defining images of the Space Age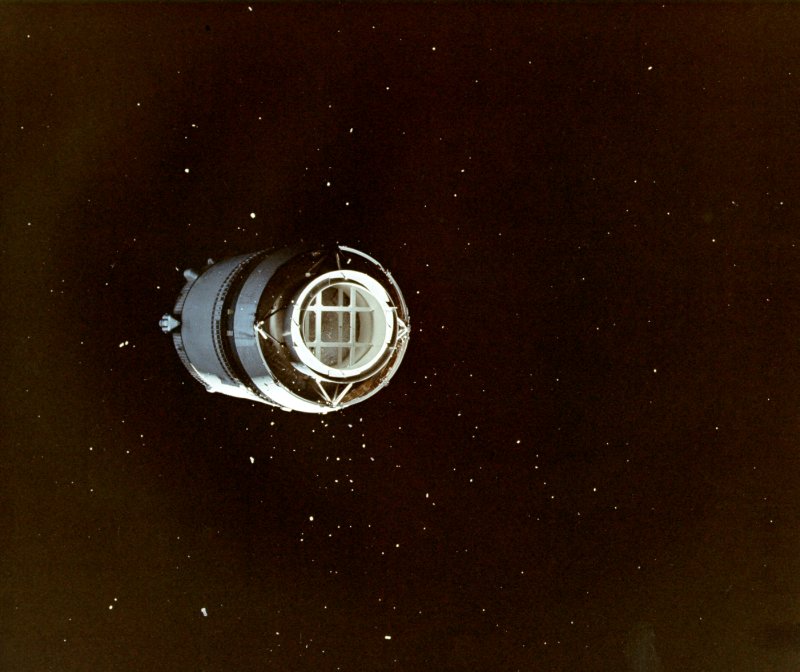 Fuel venting isn't visible in this image of the jettisoned S-IVB stage, but small debris from the separation can be seen floating around it. Although Apollo 8 carried no Lunar Module, this shot shows the LM test article contained in the S-IVB stage
Fuel venting isn't visible in this image of the jettisoned S-IVB stage, but small debris from the separation can be seen floating around it. Although Apollo 8 carried no Lunar Module, this shot shows the LM test article contained in the S-IVB stage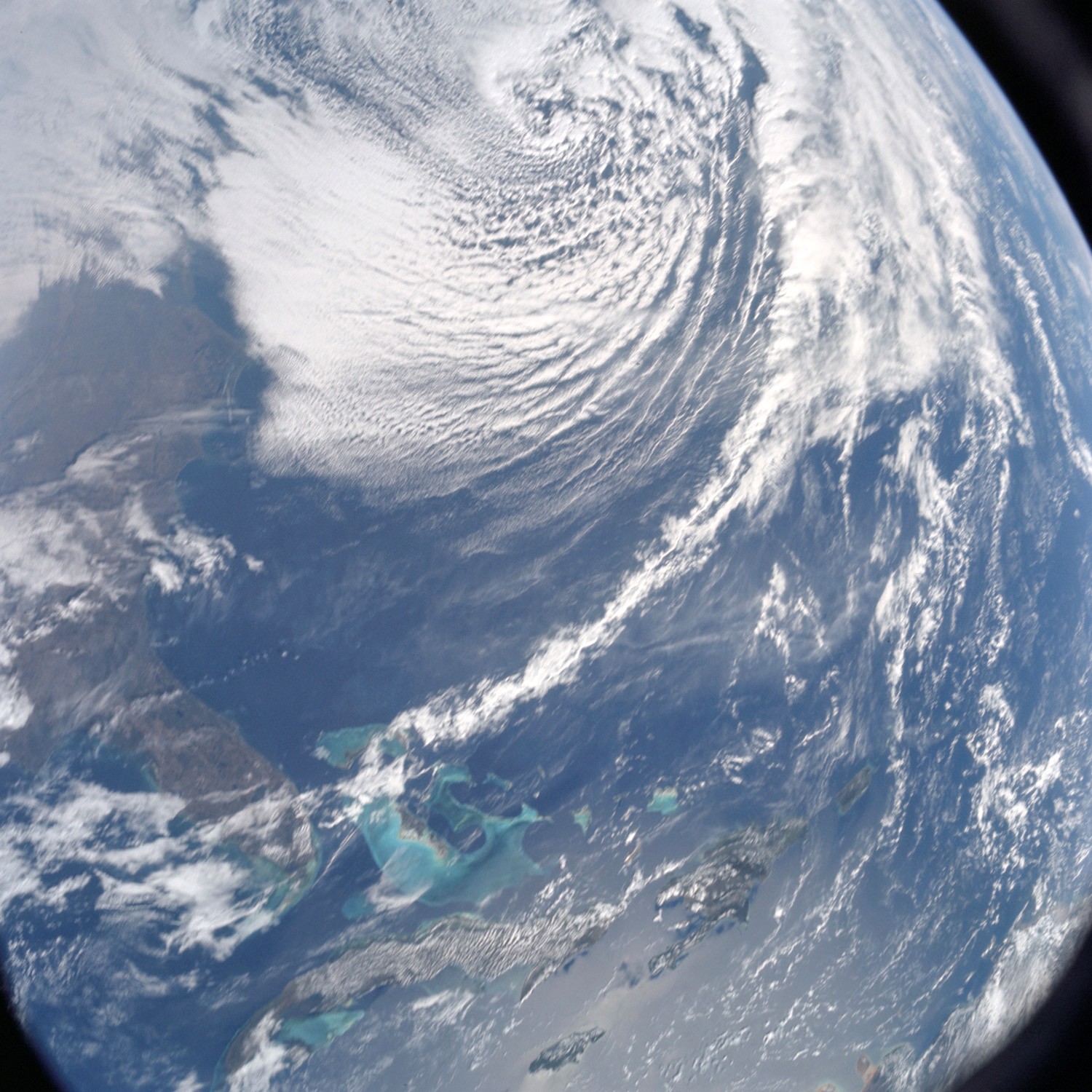 Taken just around the time of TLI, this view from high orbit shows the Florida peninsula, with Cape Kennedy just discernible, and several Caribbean islands
Taken just around the time of TLI, this view from high orbit shows the Florida peninsula, with Cape Kennedy just discernible, and several Caribbean islands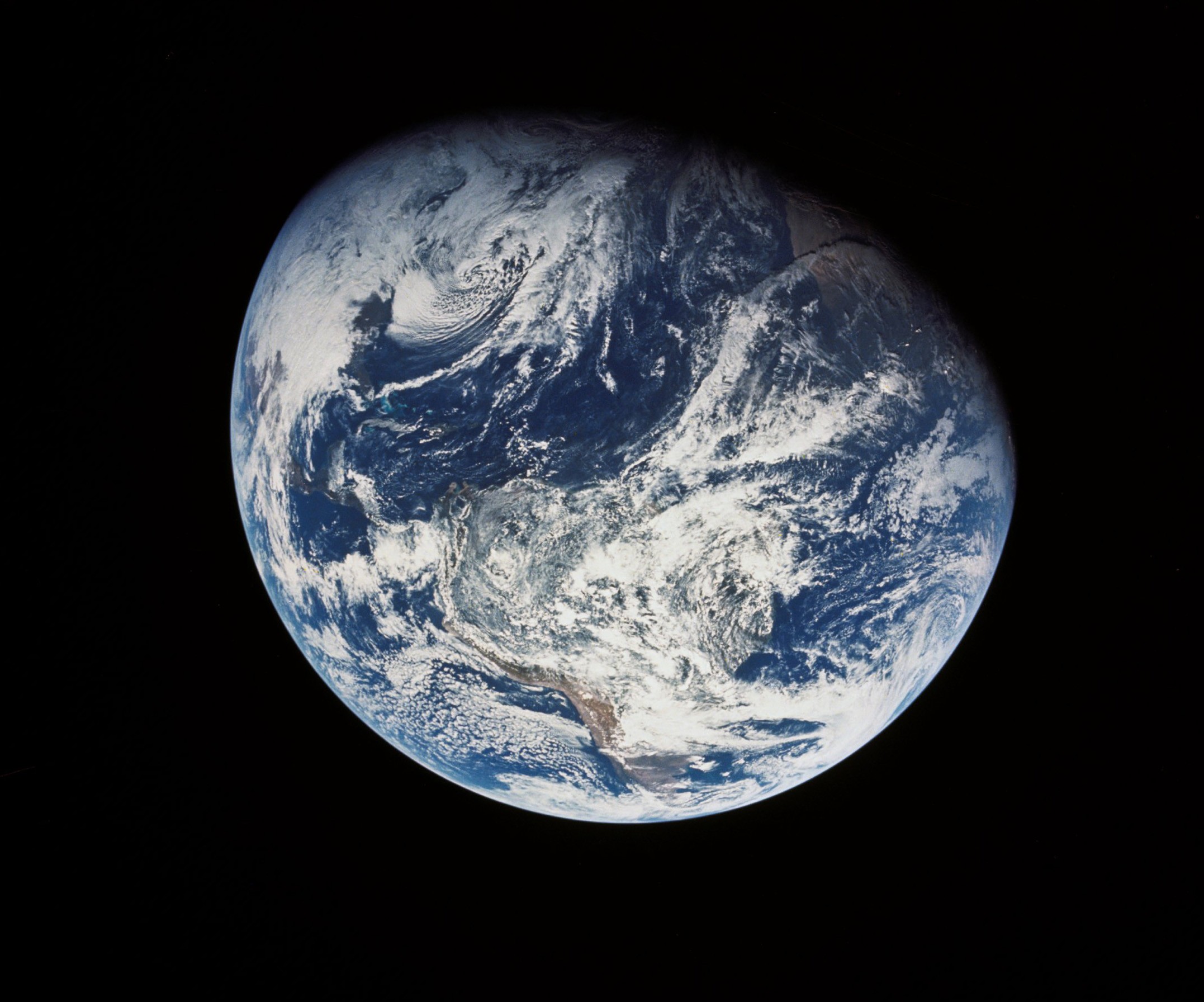 The view of Earth after S-IVB stage separation. From the Americas to west Africa, and from daylight to night, for the first time humans could see their entire planet at a glance!
The view of Earth after S-IVB stage separation. From the Americas to west Africa, and from daylight to night, for the first time humans could see their entire planet at a glance! The first mission status report for Apollo 8, sent to the NASA tracking stations around the world, for release to local media. Dated some 19 hours after launch, it outlines some of the activities of the early part of the coast to the Moon
The first mission status report for Apollo 8, sent to the NASA tracking stations around the world, for release to local media. Dated some 19 hours after launch, it outlines some of the activities of the early part of the coast to the Moon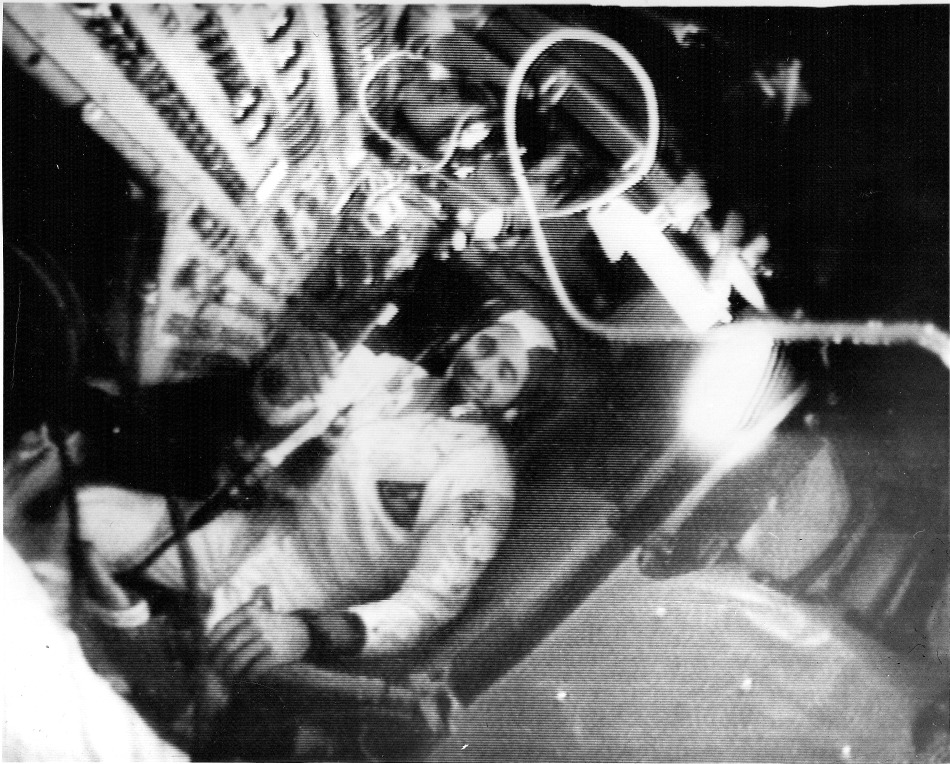
 Astronaut Anders shows us his toothbrush (top) and Jim Lovell wishes his mother "Happy Birthday" (bottom) during Apollo 8's first deep space broadcast
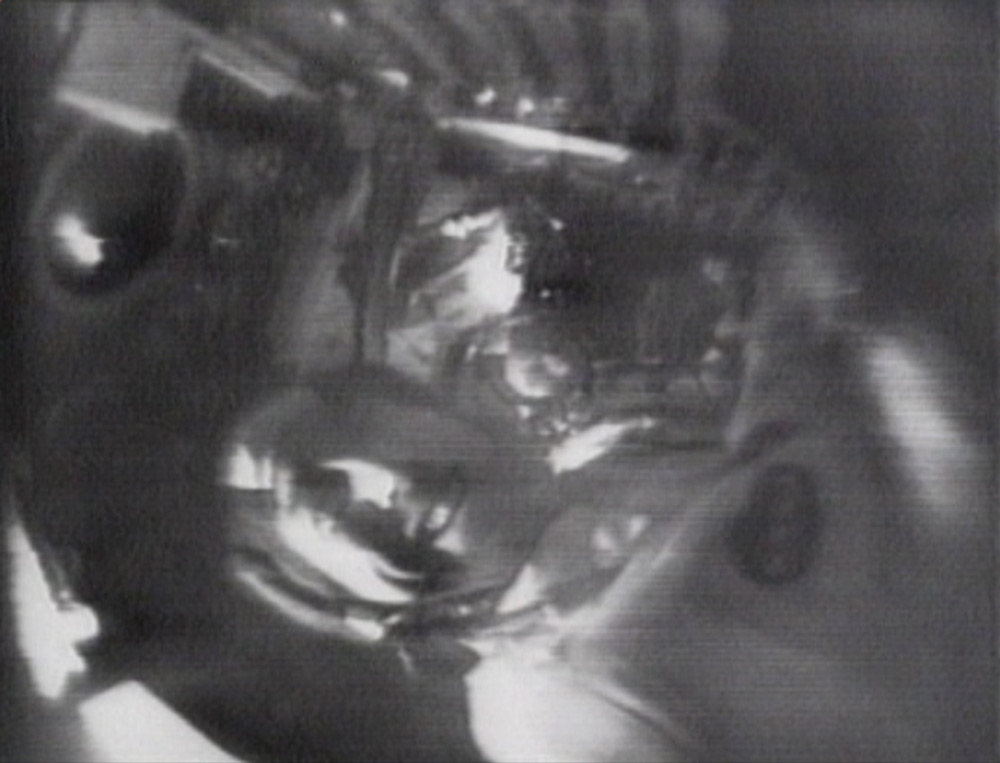
Astronaut Anders shows us his toothbrush (top) and Jim Lovell wishes his mother "Happy Birthday" (bottom) during Apollo 8's first deep space broadcast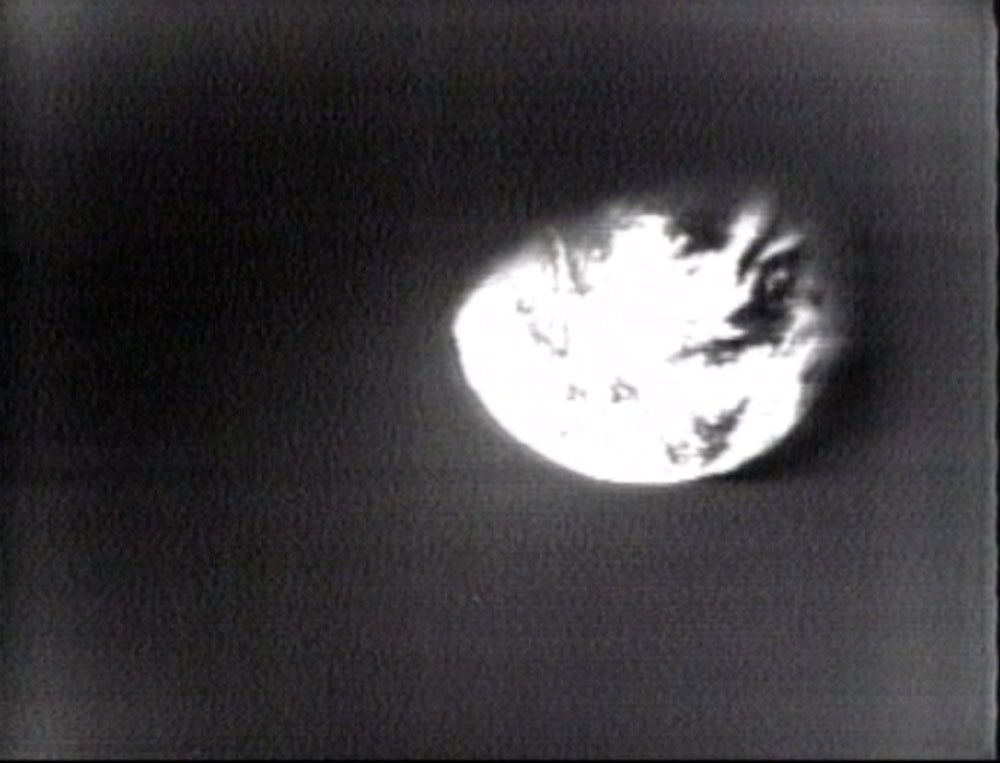 The Apollo 8 second broadcast view of the Earth as we saw it on television (above) and how Capcom Collins saw it on his monitors in Mission Control (bottom). Would alien visitors to our solar system think anyone lived there?
The Apollo 8 second broadcast view of the Earth as we saw it on television (above) and how Capcom Collins saw it on his monitors in Mission Control (bottom). Would alien visitors to our solar system think anyone lived there?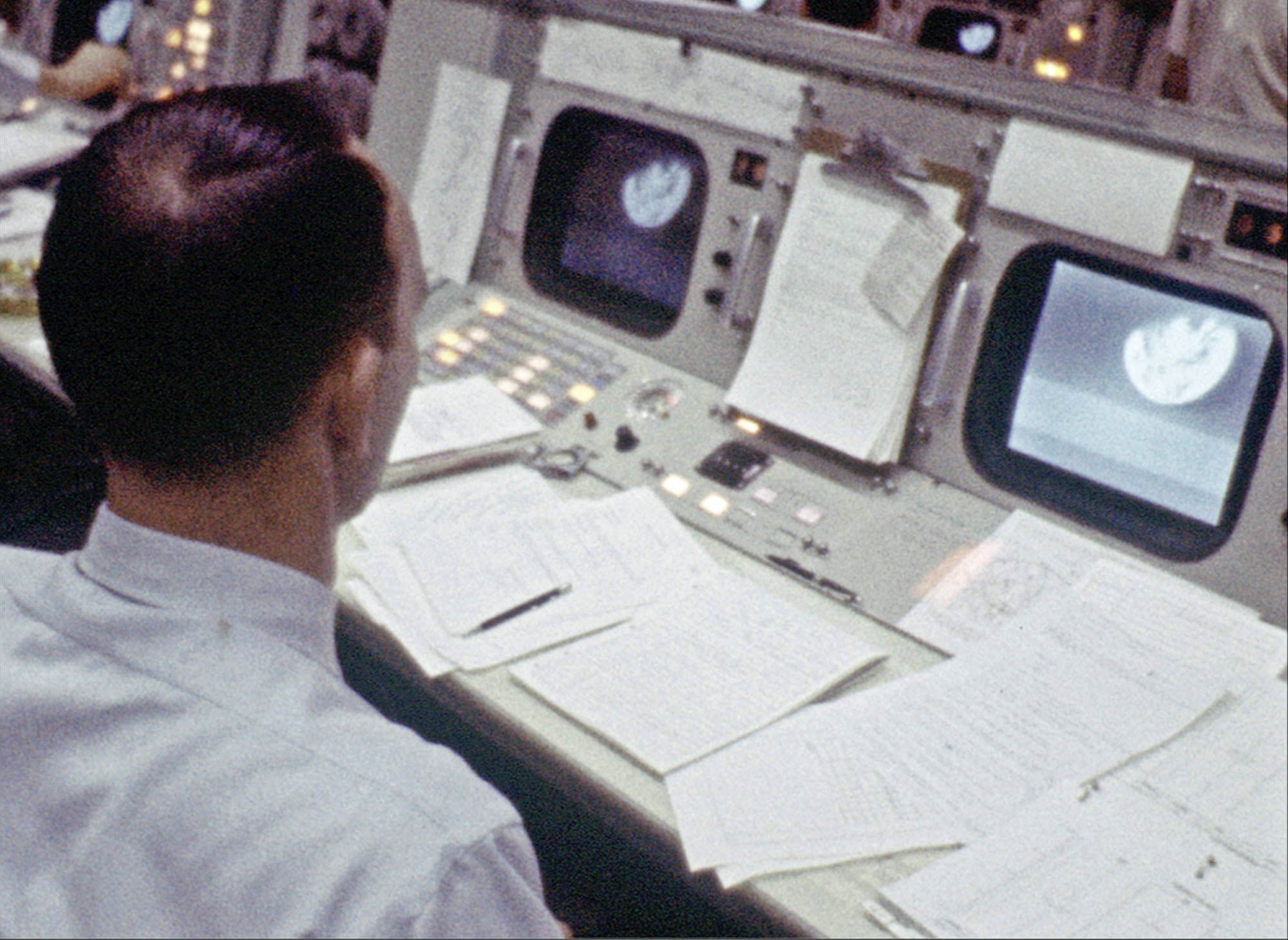
 A view of the Moon, finally visible as Apollo 8 approached and prepared to go into orbit
A view of the Moon, finally visible as Apollo 8 approached and prepared to go into orbit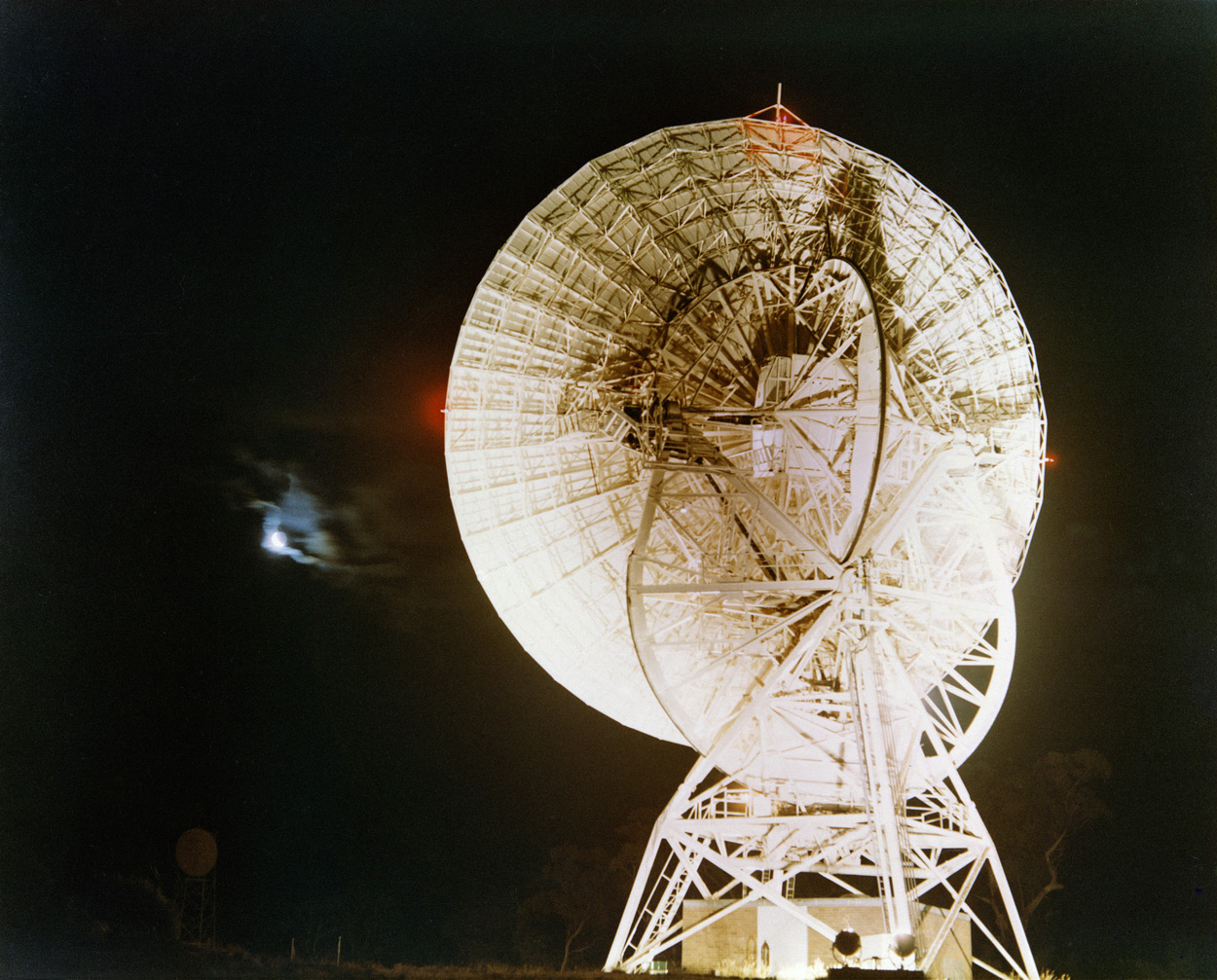 The Manned Space Flight Network station at Honeysuckle Creek, near Canberra, was tracking Apollo 8 as it went behind the Moon and received the first signals as it re-emerged, safely in lunar orbit
The Manned Space Flight Network station at Honeysuckle Creek, near Canberra, was tracking Apollo 8 as it went behind the Moon and received the first signals as it re-emerged, safely in lunar orbit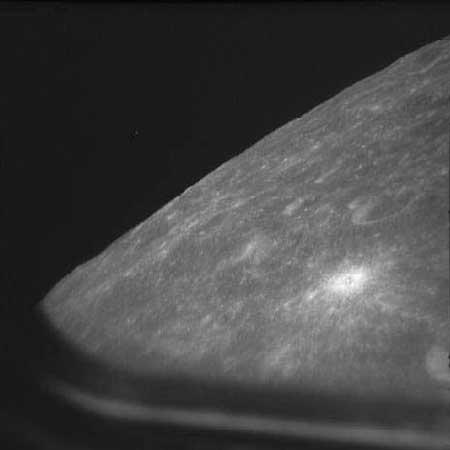
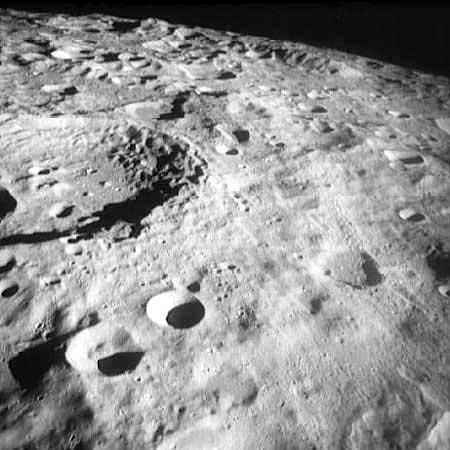 Jim Lovell's "sand pile" on the Moon!
Jim Lovell's "sand pile" on the Moon! View of the Moon's surface during the third Apollo 8 television broadcast
View of the Moon's surface during the third Apollo 8 television broadcast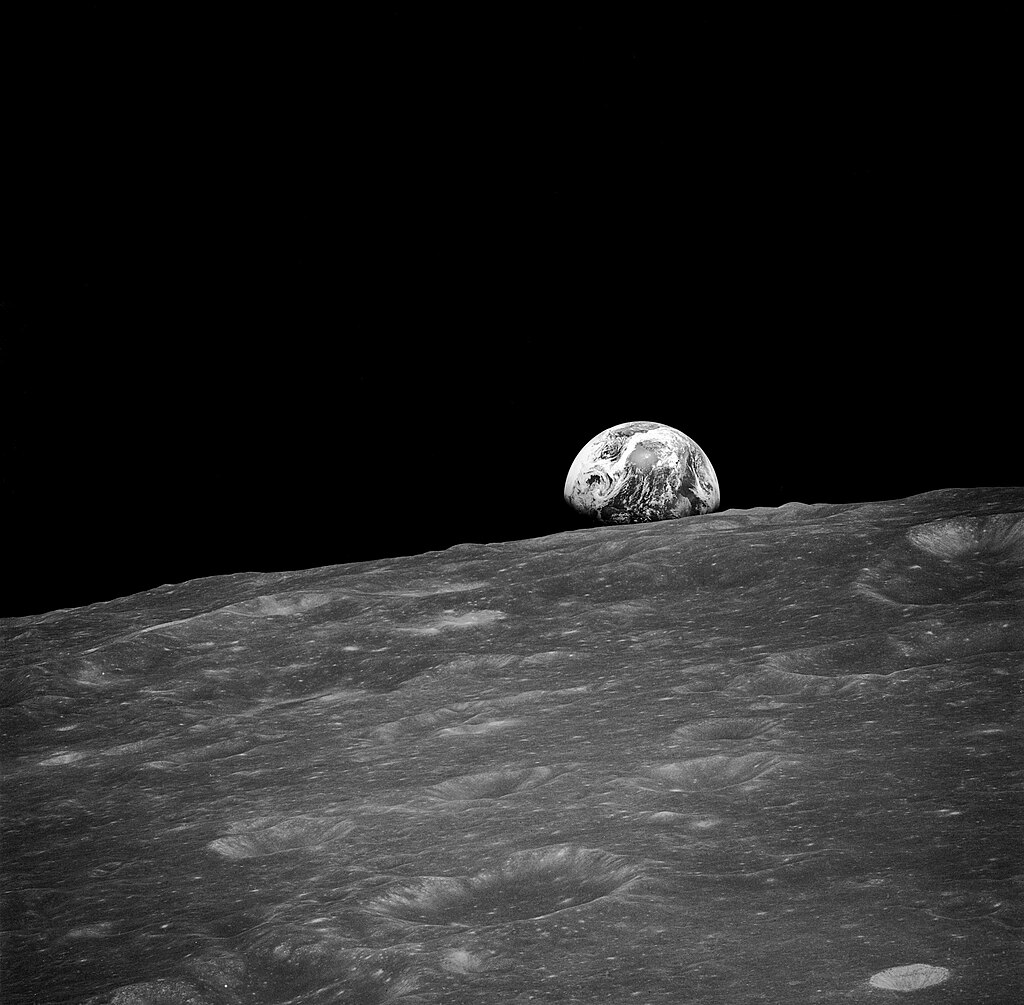 Awestruck, they scrambled so quicky to capture the vision that no-one is quite sure now who took which picture, although it seems that Col. Borman may have snapped the first black and white photograph, and Bill Anders a number of breathtaking colour images of the Earthrise.
Awestruck, they scrambled so quicky to capture the vision that no-one is quite sure now who took which picture, although it seems that Col. Borman may have snapped the first black and white photograph, and Bill Anders a number of breathtaking colour images of the Earthrise.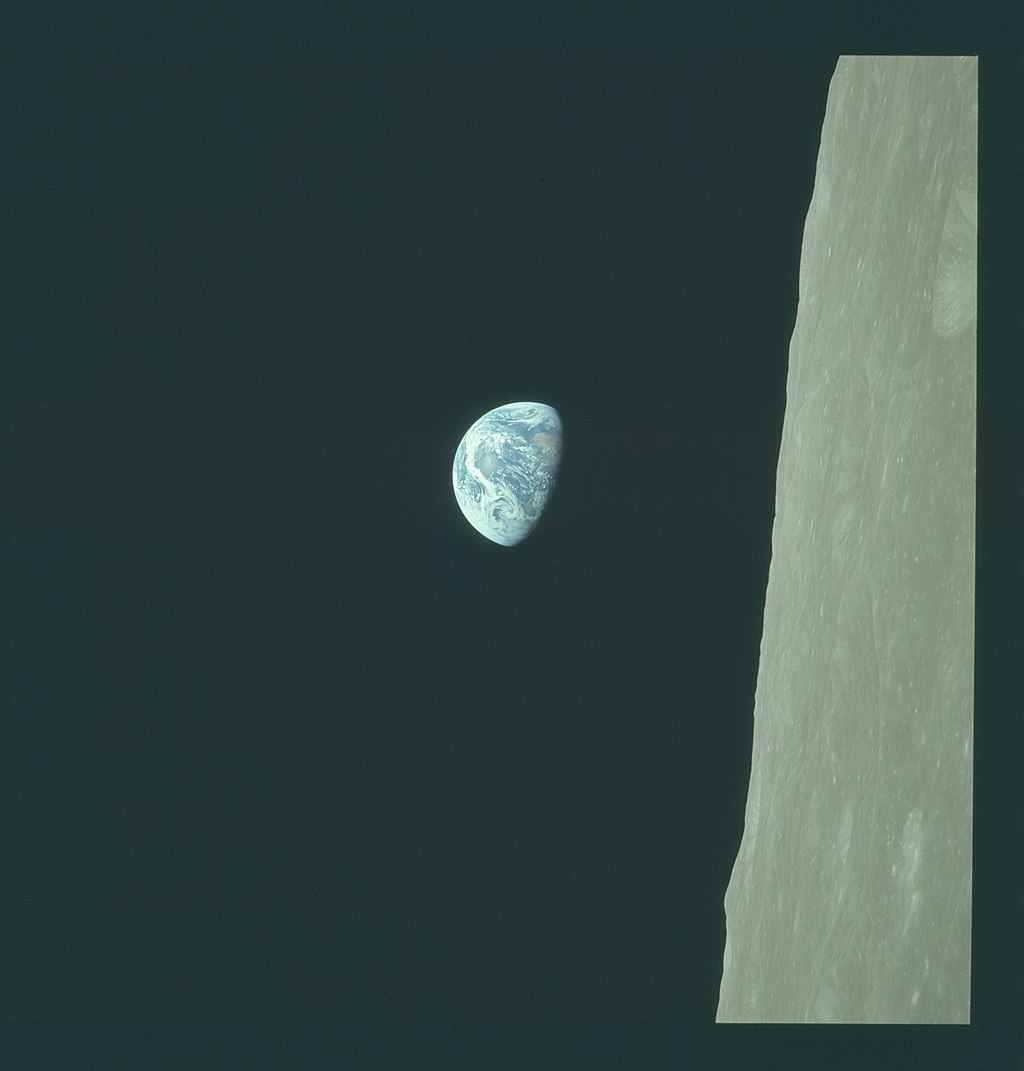 Apollo 8's Earthrise images are usually published oriented with the lunar horizon at the bottom, as that is how we are used to seeing the Moon rising over the horizon on Earth. But the orientation of astronauts' orbit meant that they actually saw the Earth appearing to rise 'sideways', as seen in this original version of Major Anders' photograph
Apollo 8's Earthrise images are usually published oriented with the lunar horizon at the bottom, as that is how we are used to seeing the Moon rising over the horizon on Earth. But the orientation of astronauts' orbit meant that they actually saw the Earth appearing to rise 'sideways', as seen in this original version of Major Anders' photograph This spread from the 15 January issue of the Australian Women's Weekly is just one example of thousands of magazine and newspaper articles already featuring the Earthrise photograph and Apollo 8's other amazing pictures
This spread from the 15 January issue of the Australian Women's Weekly is just one example of thousands of magazine and newspaper articles already featuring the Earthrise photograph and Apollo 8's other amazing pictures A view of the Moon seen by the audience on Earth while the crew of Apollo 8 read from the Book of Genesis
A view of the Moon seen by the audience on Earth while the crew of Apollo 8 read from the Book of Genesis Families around the world gathered on Christmas Eve/Christmas Day (depending on where you were!) to watch Apollo 8's broadcast
Families around the world gathered on Christmas Eve/Christmas Day (depending on where you were!) to watch Apollo 8's broadcast A view inside the Command Module, during the fifth Apollo 8 television broadcast
A view inside the Command Module, during the fifth Apollo 8 television broadcast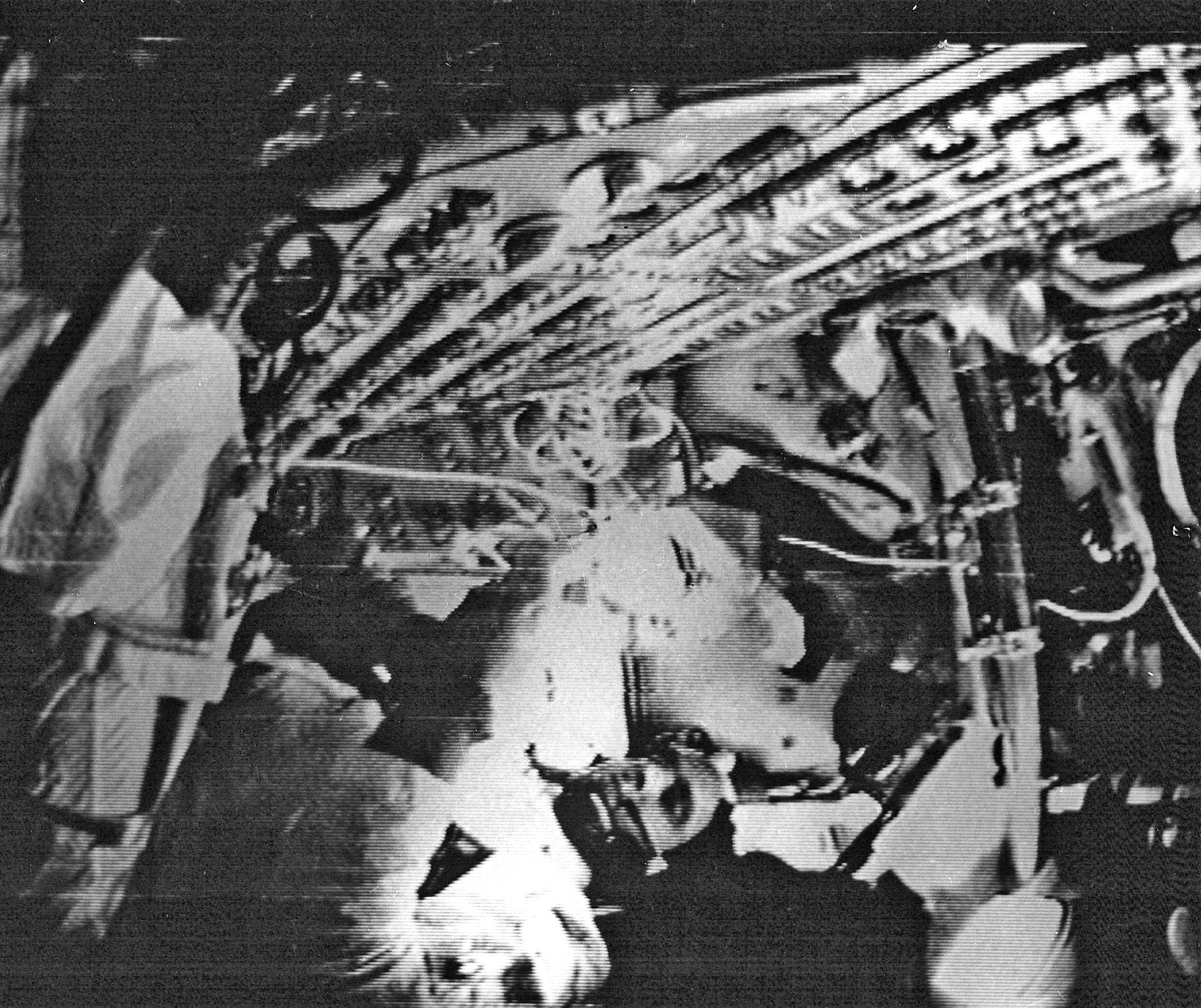 An image from the fifth broadcast taken directly from a monitor at the Honeysuckle Creek tracking station. It shows Bill Anders demostrating how to prepare a meal
An image from the fifth broadcast taken directly from a monitor at the Honeysuckle Creek tracking station. It shows Bill Anders demostrating how to prepare a meal Slayton also included three miniature bottles of brandy with the meal, although Borman decided that they should be saved until after splashdown!
Slayton also included three miniature bottles of brandy with the meal, although Borman decided that they should be saved until after splashdown!

 Apollo 8's re-entry, captured by one of NASA's Apollo Range Instrumented Aircraft that operate as airborne tracking stations
Apollo 8's re-entry, captured by one of NASA's Apollo Range Instrumented Aircraft that operate as airborne tracking stations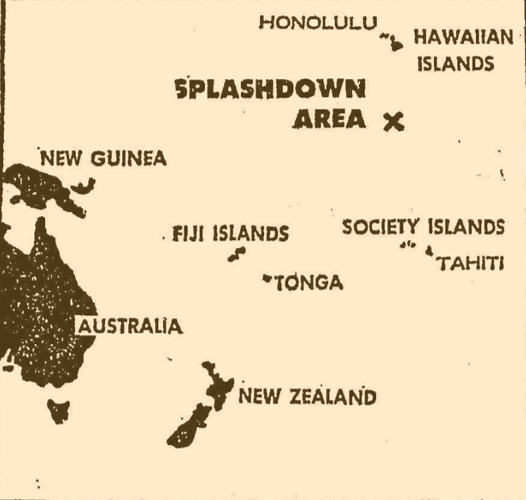 Map of Apollo 8's splashdown area
Map of Apollo 8's splashdown area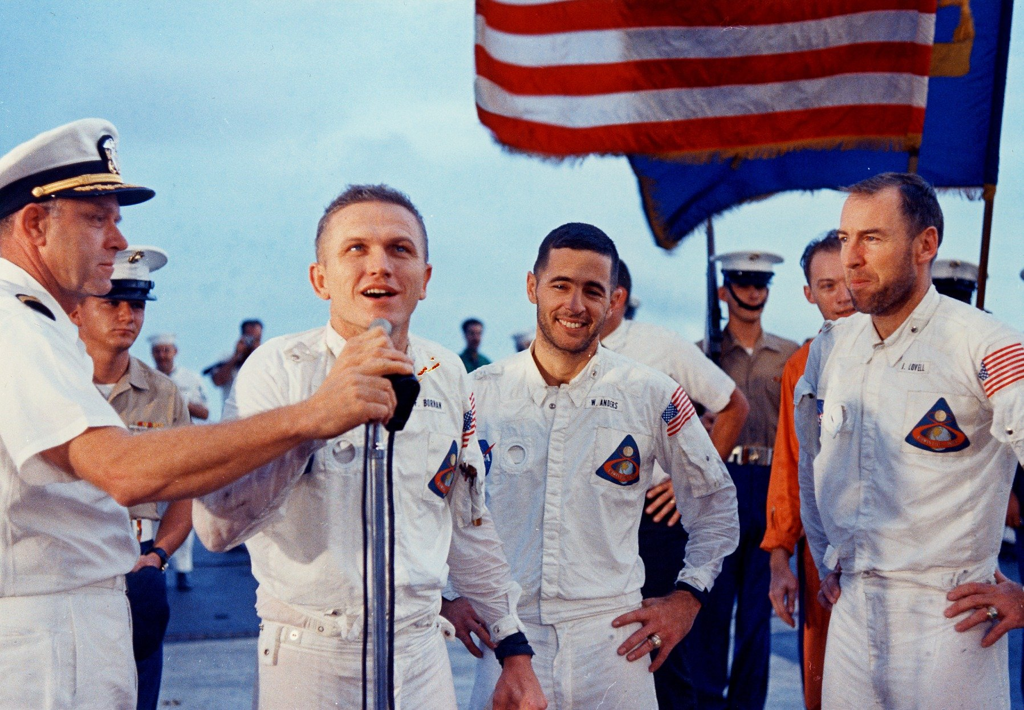  After their recovery, the Apollo 8 astronauts addressed the USS Yorktown's crew, very glad to be home!
After their recovery, the Apollo 8 astronauts addressed the USS Yorktown's crew, very glad to be home!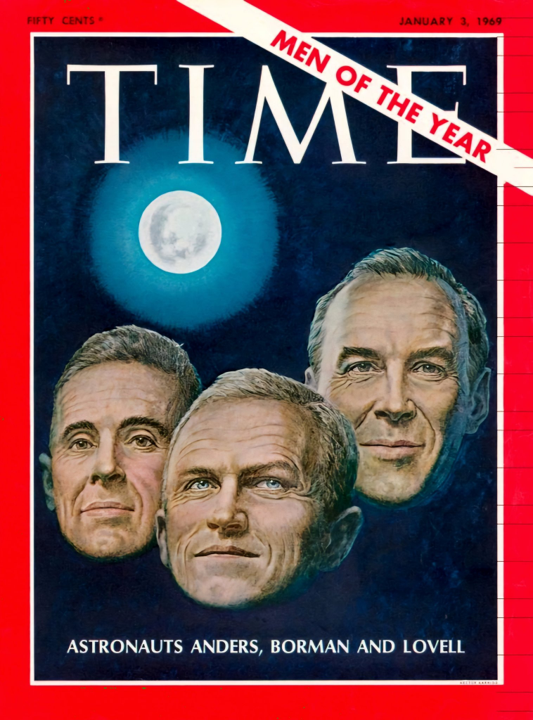 <
< For the influence and impact of their mission, Time magazine has chosen the crew of Apollo 8 as its Men of the Year for 1968, while Life has selected the post-TLI image of the Earth for the cover its 1968 retrospective issue.
For the influence and impact of their mission, Time magazine has chosen the crew of Apollo 8 as its Men of the Year for 1968, while Life has selected the post-TLI image of the Earth for the cover its 1968 retrospective issue.


![[January 12, 1969] Taking French Leave: Playtime (a movie) and The Green Slime (a flick)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/690112movies-672x328.jpg)





 The car carousel makes Paris playful again
The car carousel makes Paris playful again
![[December 31, 1968] Auld Lang Syne (January 1969 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681231cover-672x372.jpg)










![[December 30, 1968] Beautiful Downtown Starbank (the 1968 Galactic Stars)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681230stars-672x372.jpg)























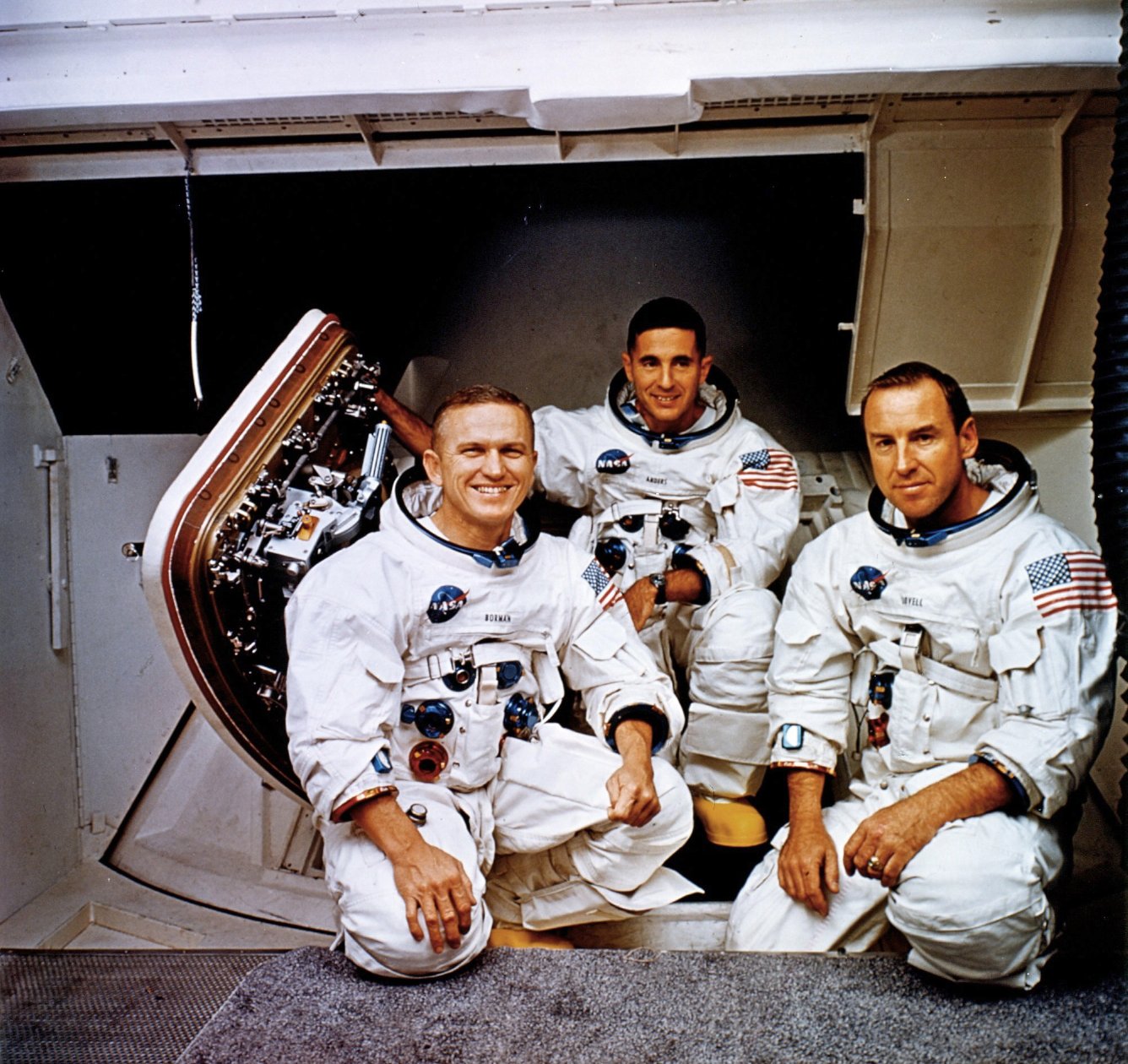
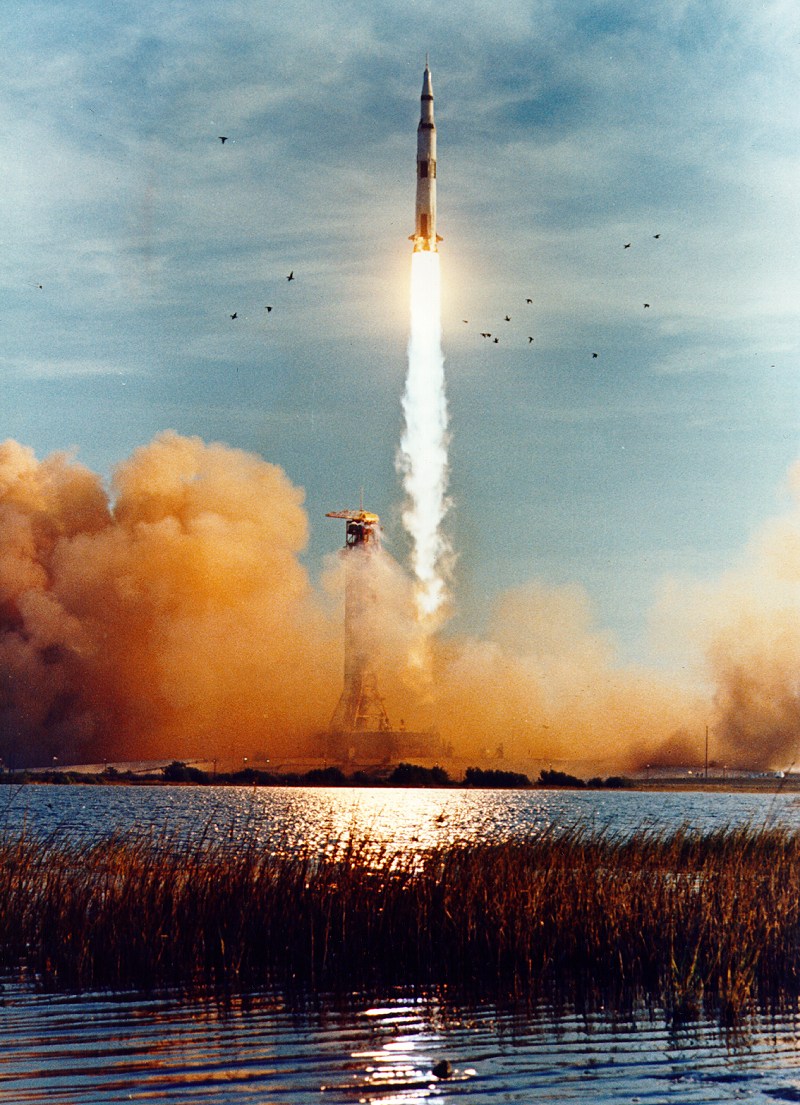
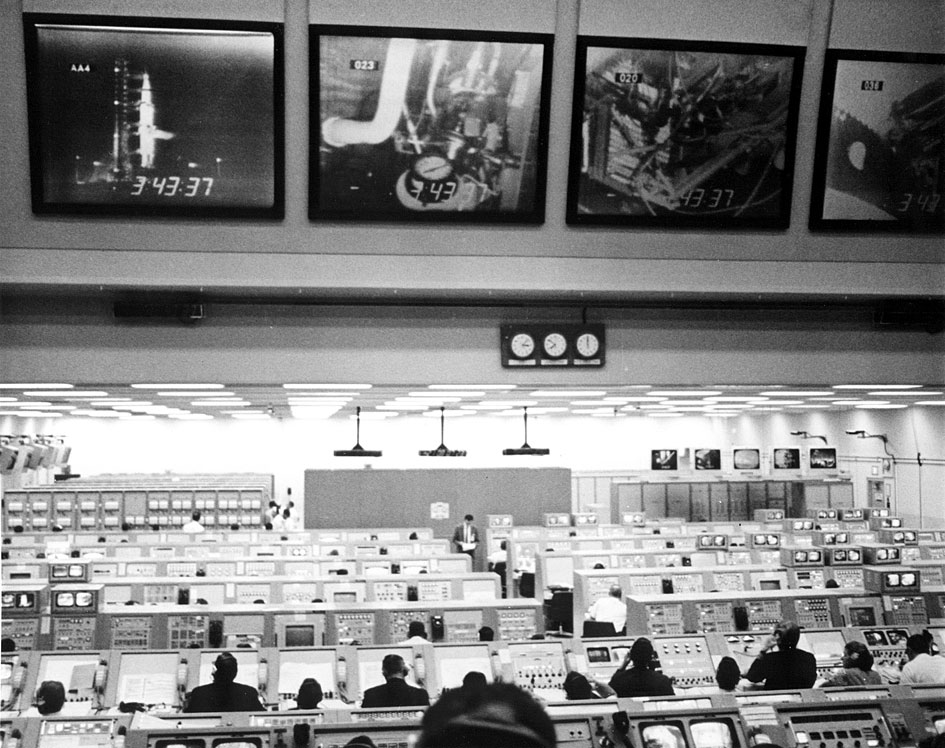
![[December 28, 1968] A Christmas Gift to the World – Part 1 (Apollo 8)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Apollo-8-patch-672x372.png)
















![[December 24, 1968] We Shall Fight Them In The Streets (<i>Doctor Who</i>: The Invasion [Episodes 5-8])](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681224stepsofstpauls-672x372.jpg)


![[December 22, 1968] What wonders await? (January 1969 <i>Fantasy and Science Fiction</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681222cover-672x372.jpg)




![[December 20, 1968] A failure to communicate (<i>Star Trek</i>: "The Empath")](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681220title-672x372.jpg)














![[December 18, 1968] Sex, Drugs and Boris Karloff: Curse of the Crimson Altar](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Curse_of_the_crimson_altar_poster.jpg)


 Another tedious sex party, ho hum.
Another tedious sex party, ho hum.
