by Lorelei Marcus
What Ever Happened to Commissioner Nancy?
The tomfoolery of "I, Mudd" was a delight, but I'm personally more of a fan of the serious episodes that delve deeply into the drama and science. The preview for this week's episode presented a new planet, mystery, and even new characters–how exciting!

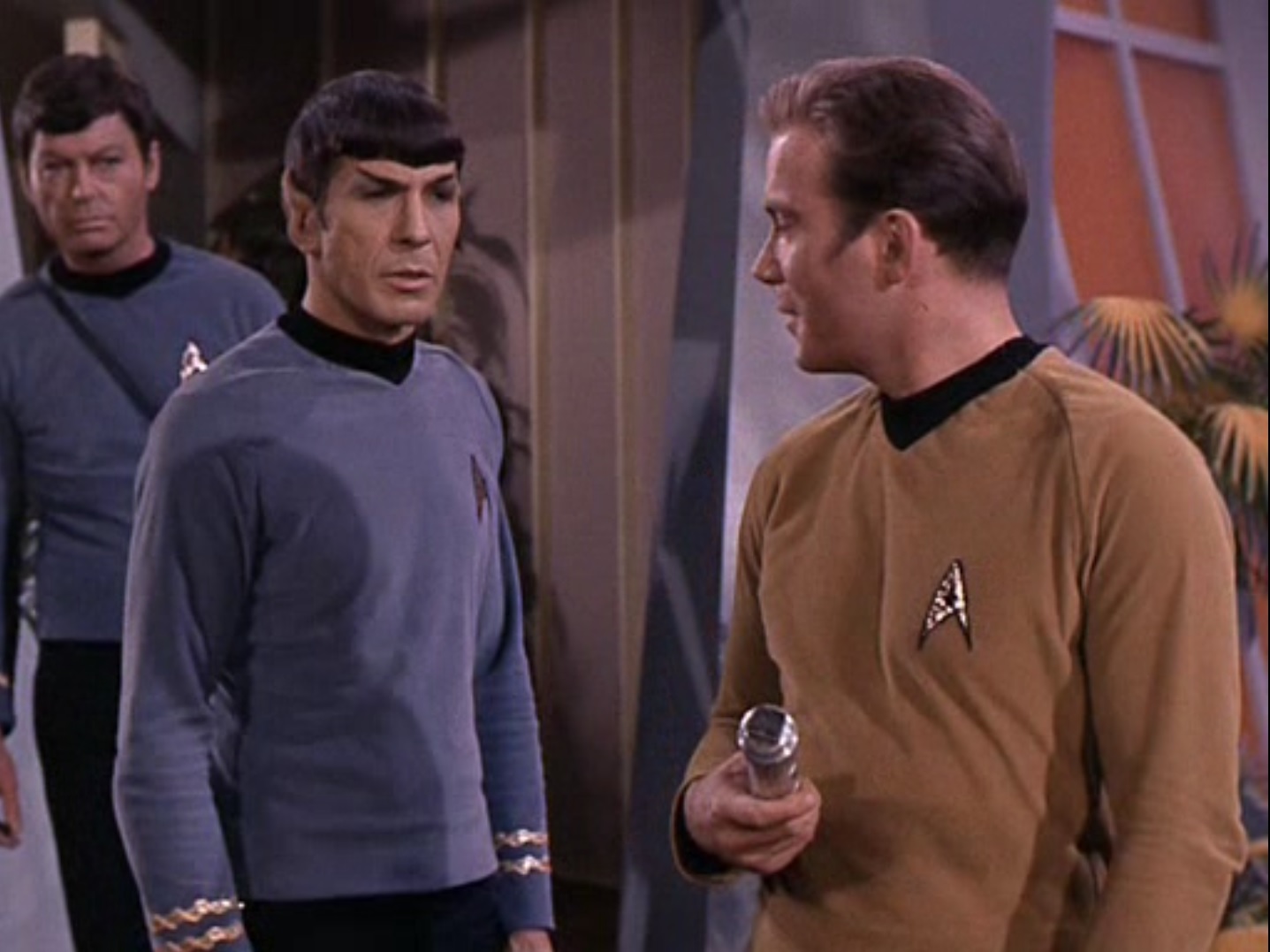
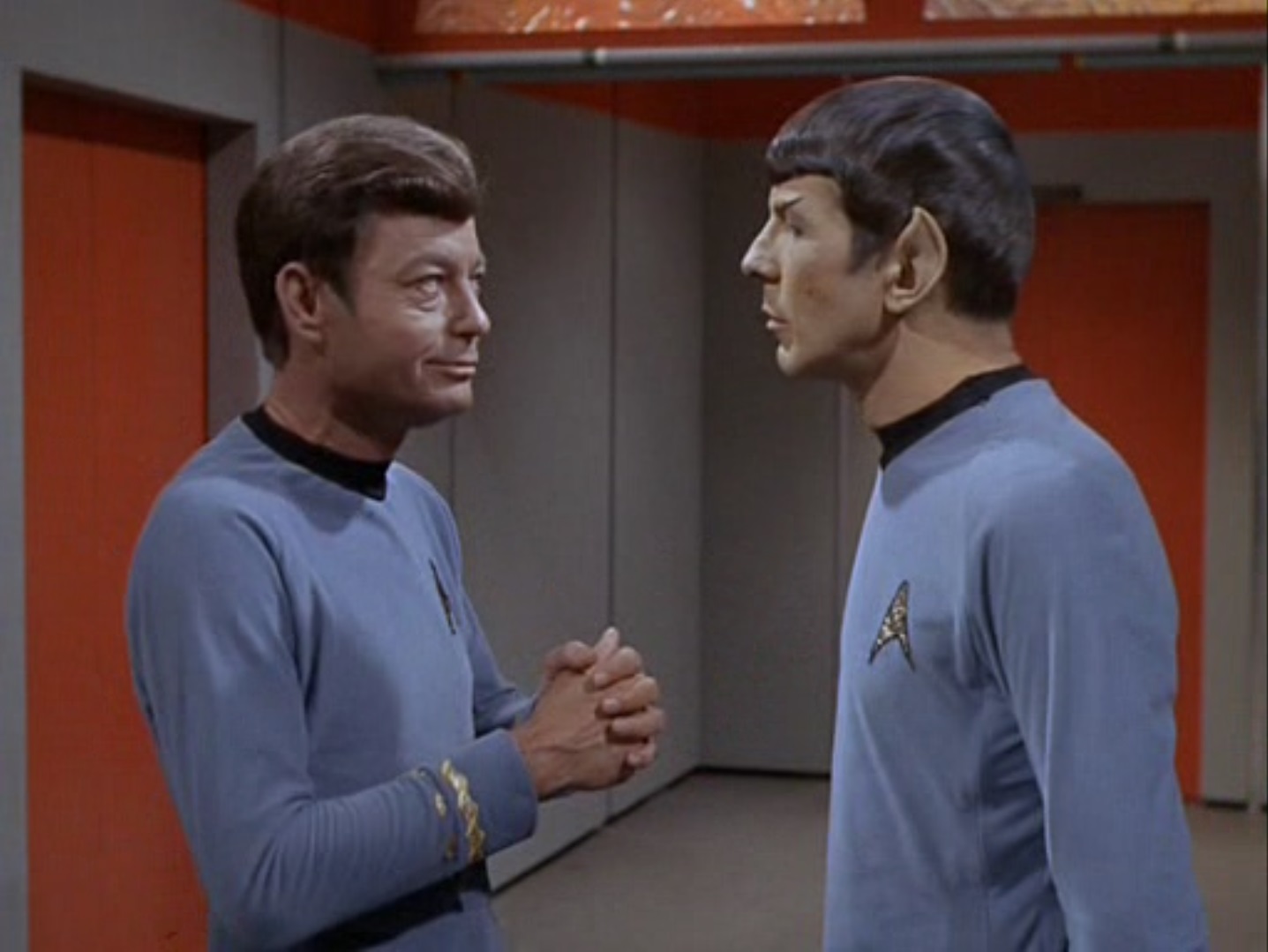
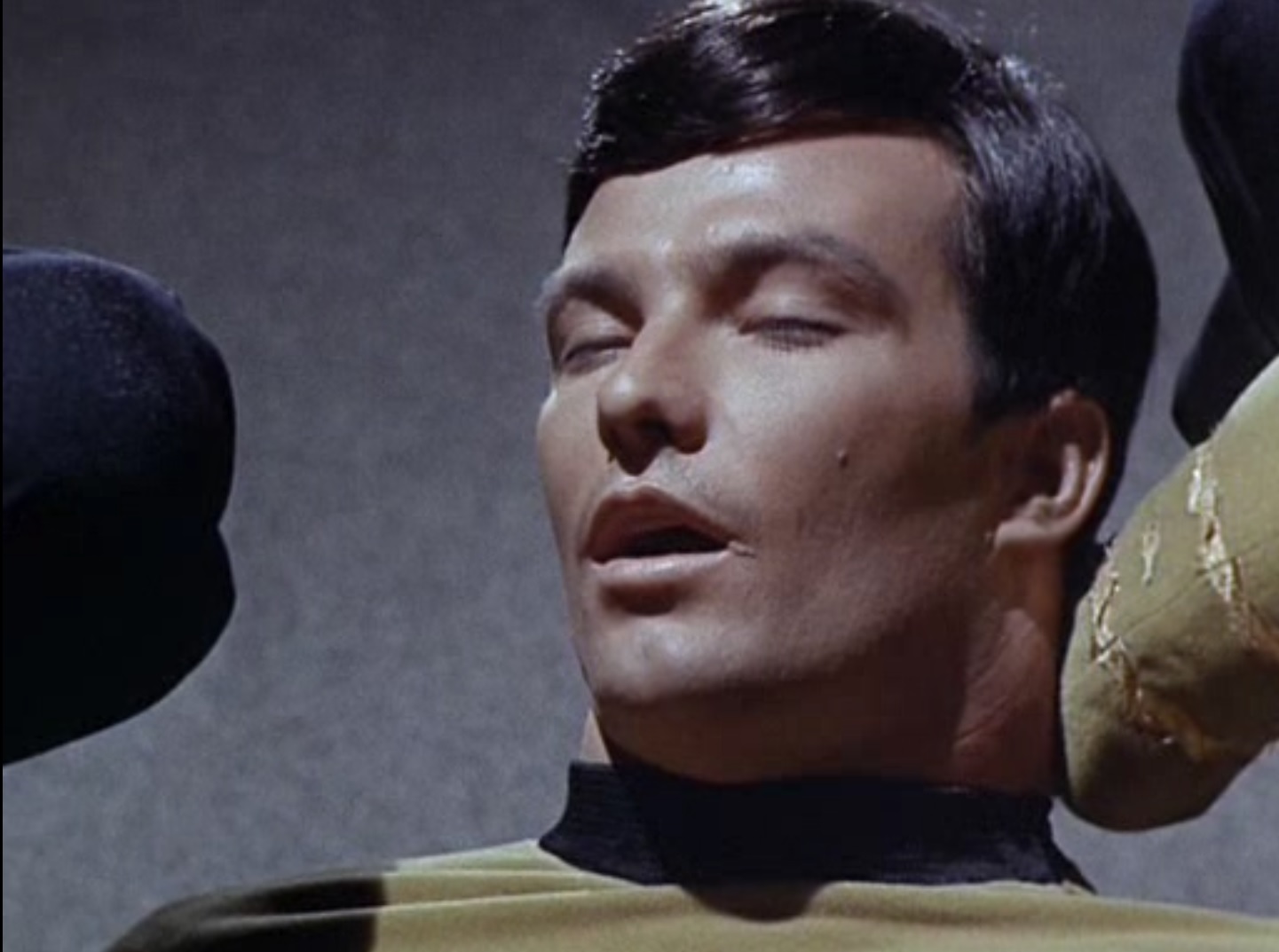
"Metamorphosis" begins with Kirk, Spock, and McCoy on a Galileo shuttle craft, escorting a civilian woman back to the Enterprise. The woman is Nancy Hedford, Commissioner for the Federation, who was acting as a diplomat to prevent war between two colonies before she was pulled from her task after contracting a rare but deadly disease. She must be treated within the next twenty-four hours or she'll die.

Commissioner Hedford, after her promotion from the city council of Mayberry
I'm always pleased to see new competent female characters on Star Trek, and here's one that isn't set up to be a love interest for Kirk. Unfortunately it doesn't seem like her character is going to last long. Almost immediately, the shuttle craft is hit by a strange energy beam and is pulled towards an asteroid with its own atmosphere, almost exactly like that of Earth's. Spock theorizes that the planetoid is a fragment from a larger planet that's been split apart. That still doesn't explain how such a small celestial body could retain its own atmosphere, but perhaps there's some supernatural reason for it that they will explain later.
Hedford understandably begins panicking and orders Kirk to put the craft back on course. It's a fascinating contrast to see her civilian reaction compared to the coolheaded and seasoned Enterprise crew. Unfortunately, despite Kirk's best efforts, the craft is still forced to land on the asteroid, and thanks to a powerful dampening field, cannot take off again.

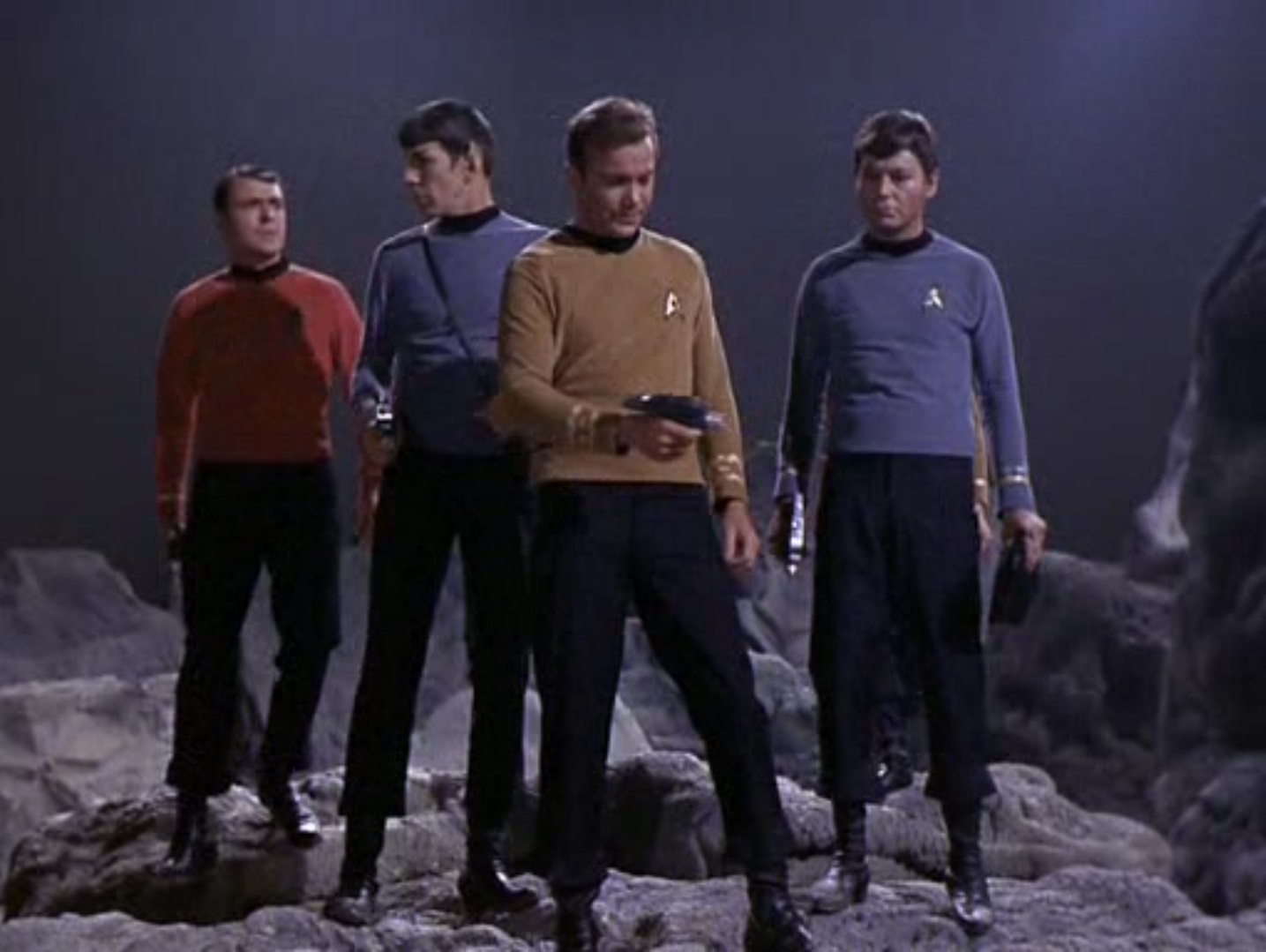
The Galileo Four
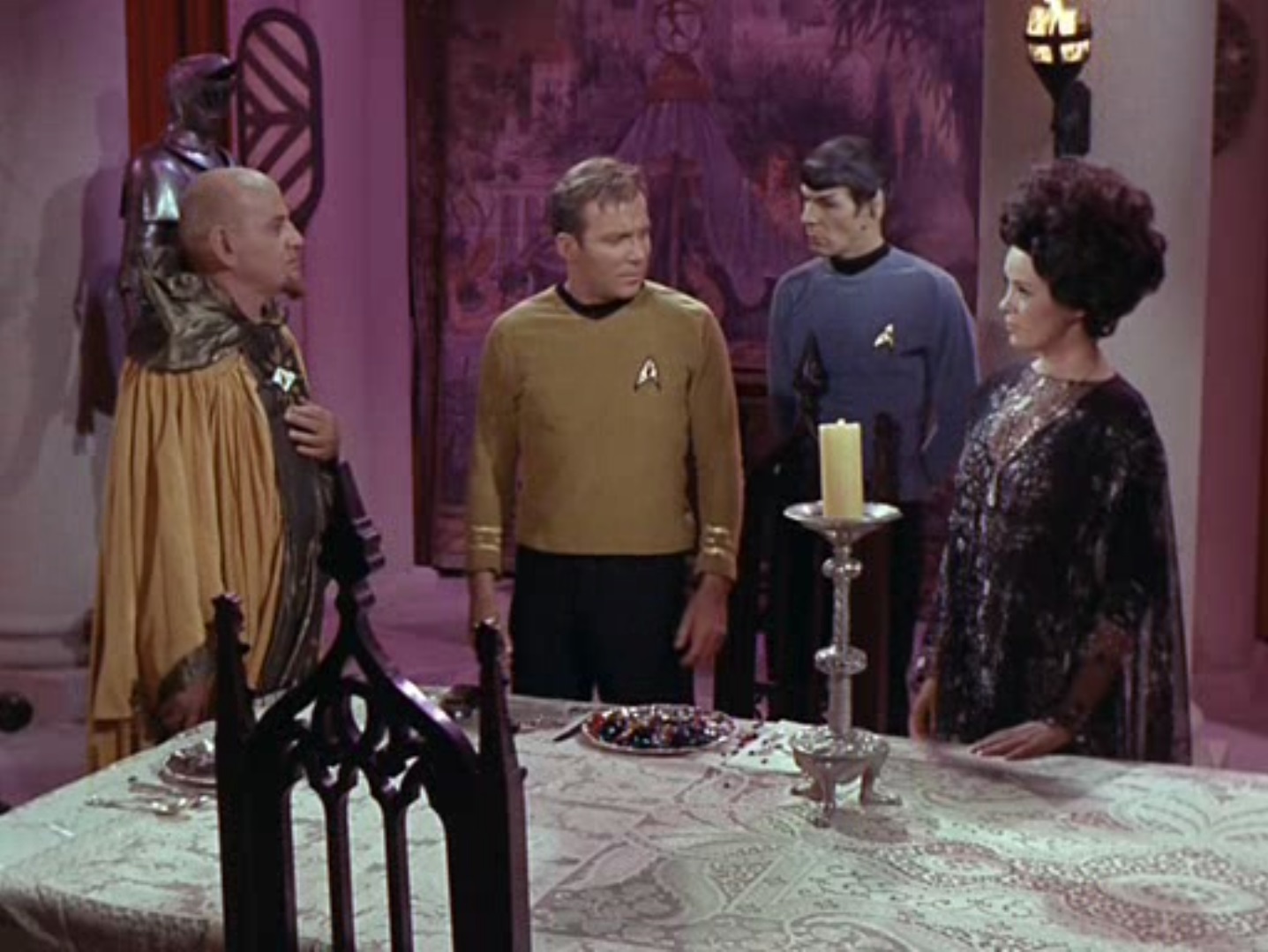
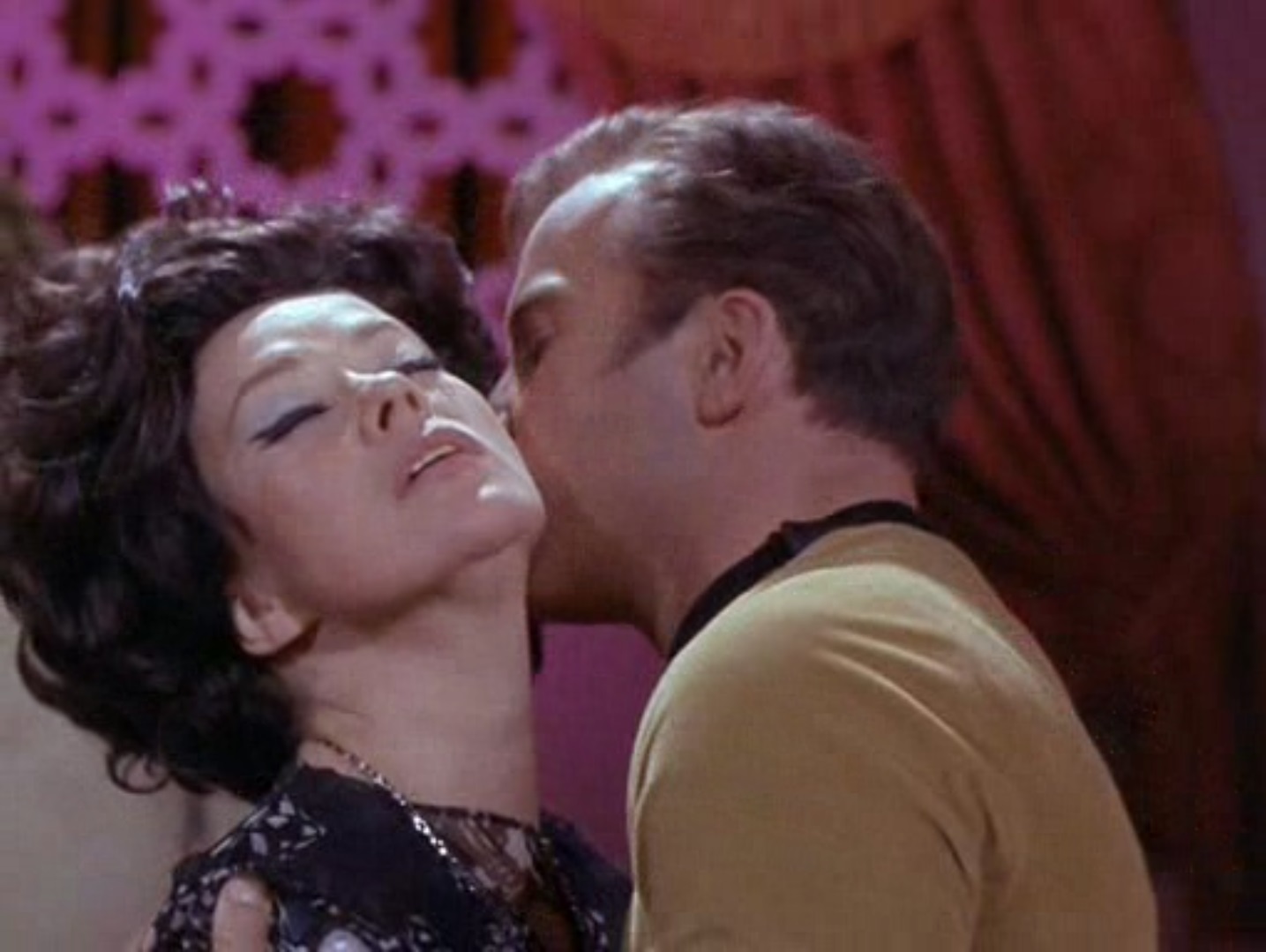
Soon after they land, something – or someone – calls to the party and begins to approach them. It turns out to be a young man in a jumpsuit, reminiscent of the Federation uniform, but clearly older in style. The man is amiable, and he seems relieved to see other people again. He recognizes Spock as a Vulcan, but he takes particular interest in Hedford because she is a "beautiful woman". Hedford, twenty-three hours away from death and stuck on an asteroid in the middle of nowhere, brushes off the advance irritably.

Disdain at first sight
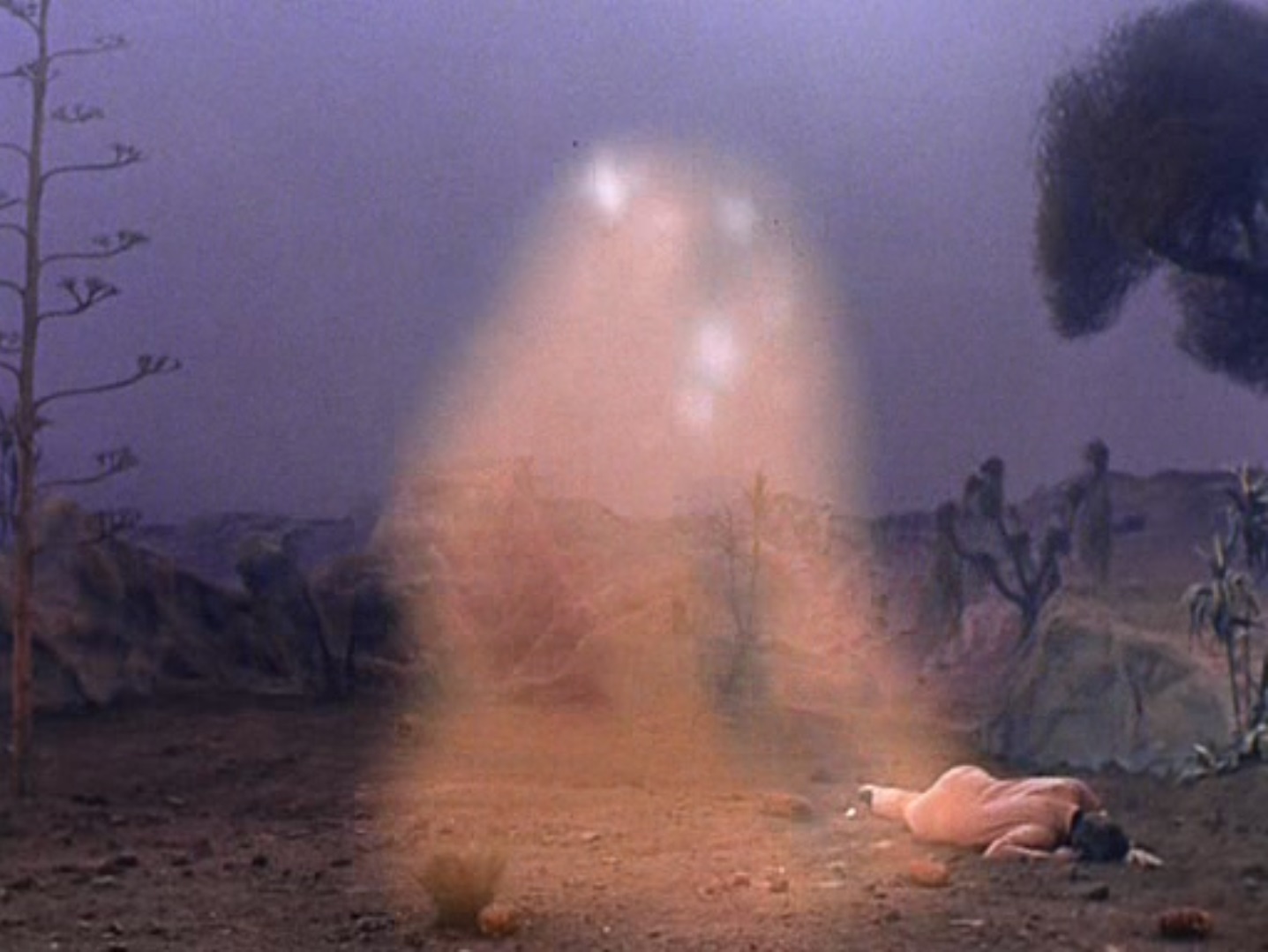
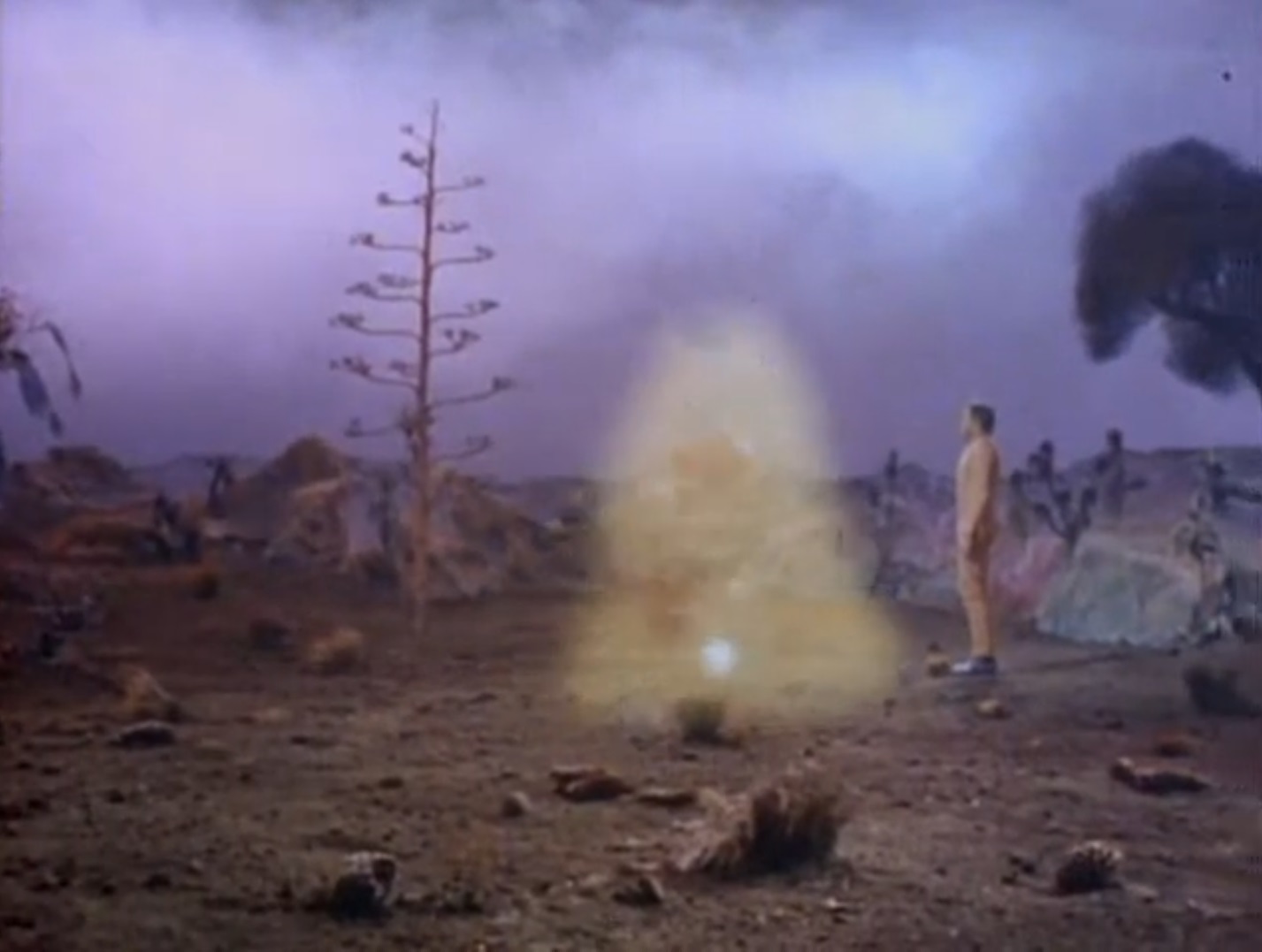
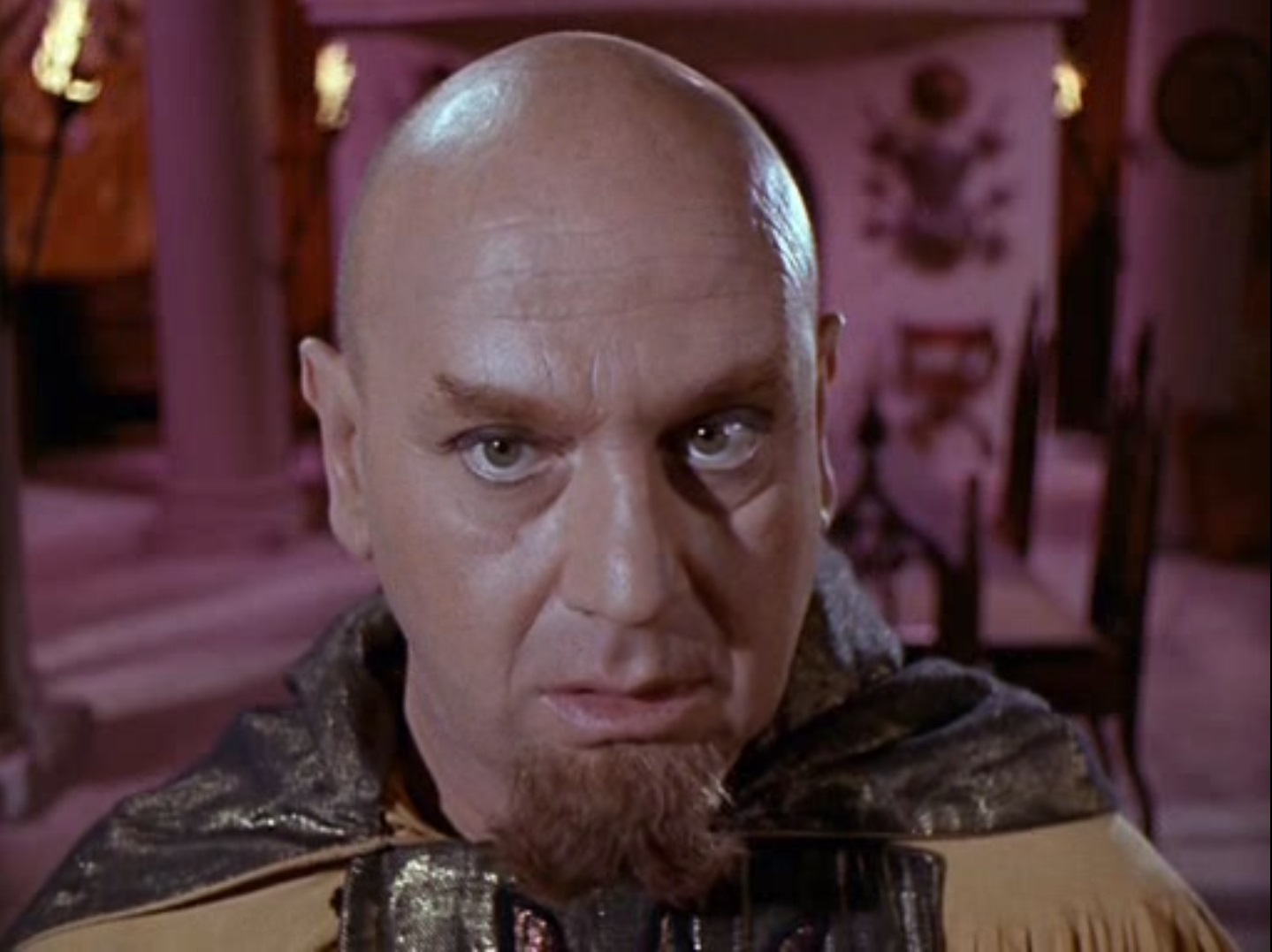
The man takes the party to his home, a building he apparently built with the scraps of his ship which was pulled to this planetoid like the Galileo craft. Except, it's revealed, that his ship crashed 150 years ago and he's actually Zefram Cochrane, the original inventor of warp drive! Cochrane explains that at age 87 he took a ship into space to die, but he was discovered by an alien being which drew him to this asteroid and forced him to live there with it. The alien, which he calls the Companion, restored his youth and stopped him from aging, and he's since built a life here with his newfound immortality. (And he was able to grow crops to sustain himself, despite the asteroid's soil comprising almost entirely nickel and iron, but perhaps the Companion had something to do with that).
Kirk's craft was brought here because Cochrane told the Companion he would die of loneliness without other humans in the hopes of being freed. Instead the Companion brought the humans to him, and now refuses to let them leave. Hedford's fever worsens, and she breaks down hysterically, disgusted by the idea of being trapped and forced to be someone's consort.
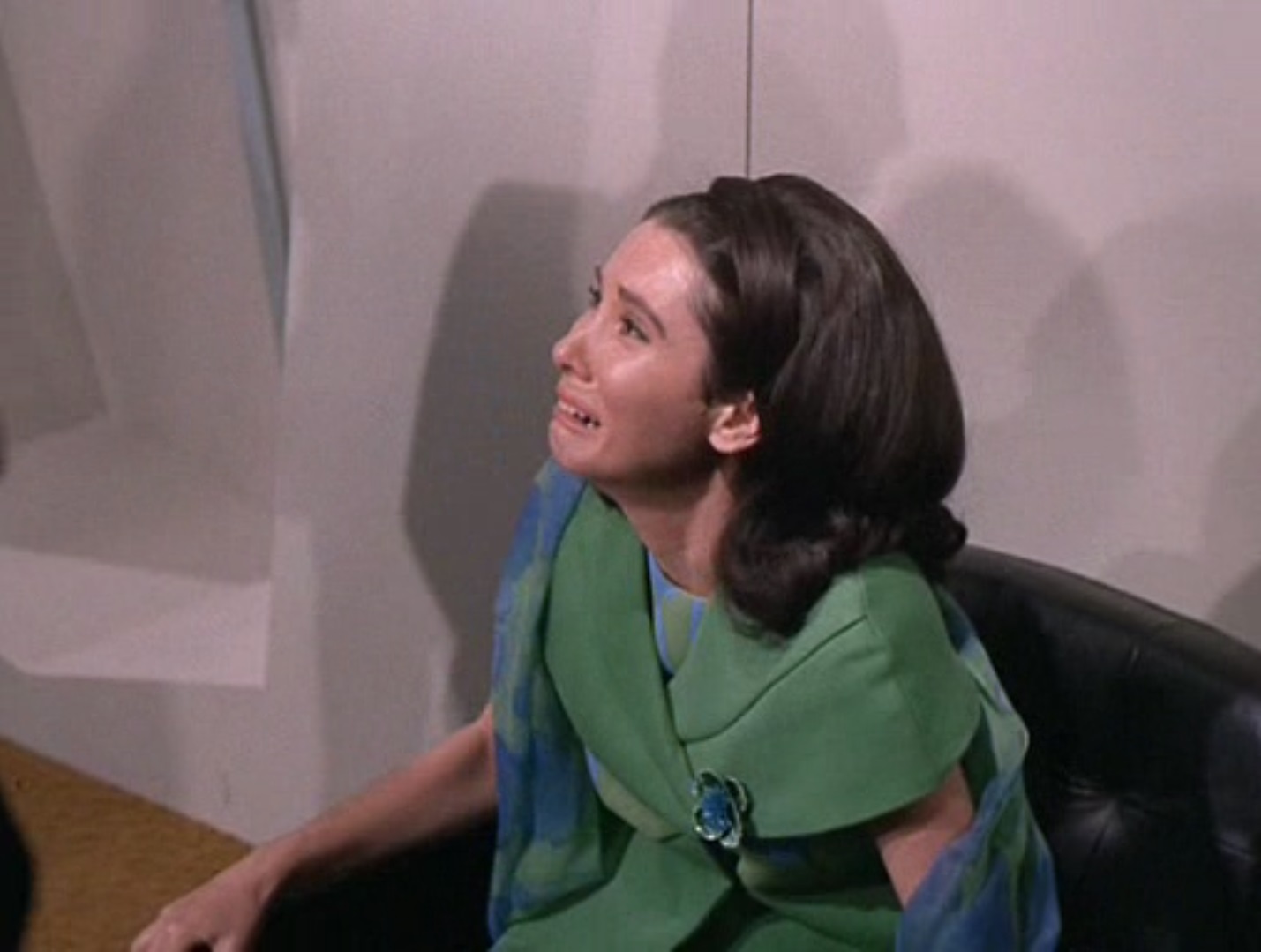

I wouldn't be too happy, either.
Forced into action by Hedford's deteriorating condition, Kirk begins to think of a plan. The Companion is intelligent and can communicate with Cochrane fairly fluently. It also appears to be composed of raw electricity, and possesses great healing properties if Cochrane's de-aging is any example. Of course the only way to deal with a one-of-a-kind, sentient, all-powerful creature like that… is to kill it! (What is that speech that Kirk gives in the intro? Something about seeking out and exterminating new life and new civilizations? I can never remember.)
Spock conveniently pulls out his electric impulse scrambler (I can only guess where he keeps it), and their attack on the Companion goes about as well as you might expect. Kirk and Spock almost die and are saved only by Cochrane's intervention. McCoy gently suggests to Kirk that perhaps they could try negotiating with the alien instead of hurting it. Kirk agrees that the negotiation sounds like a good idea, and he orders Spock to adjust their universal translator to work on incorporeal beings.

Yes, maybe talking is the better option.
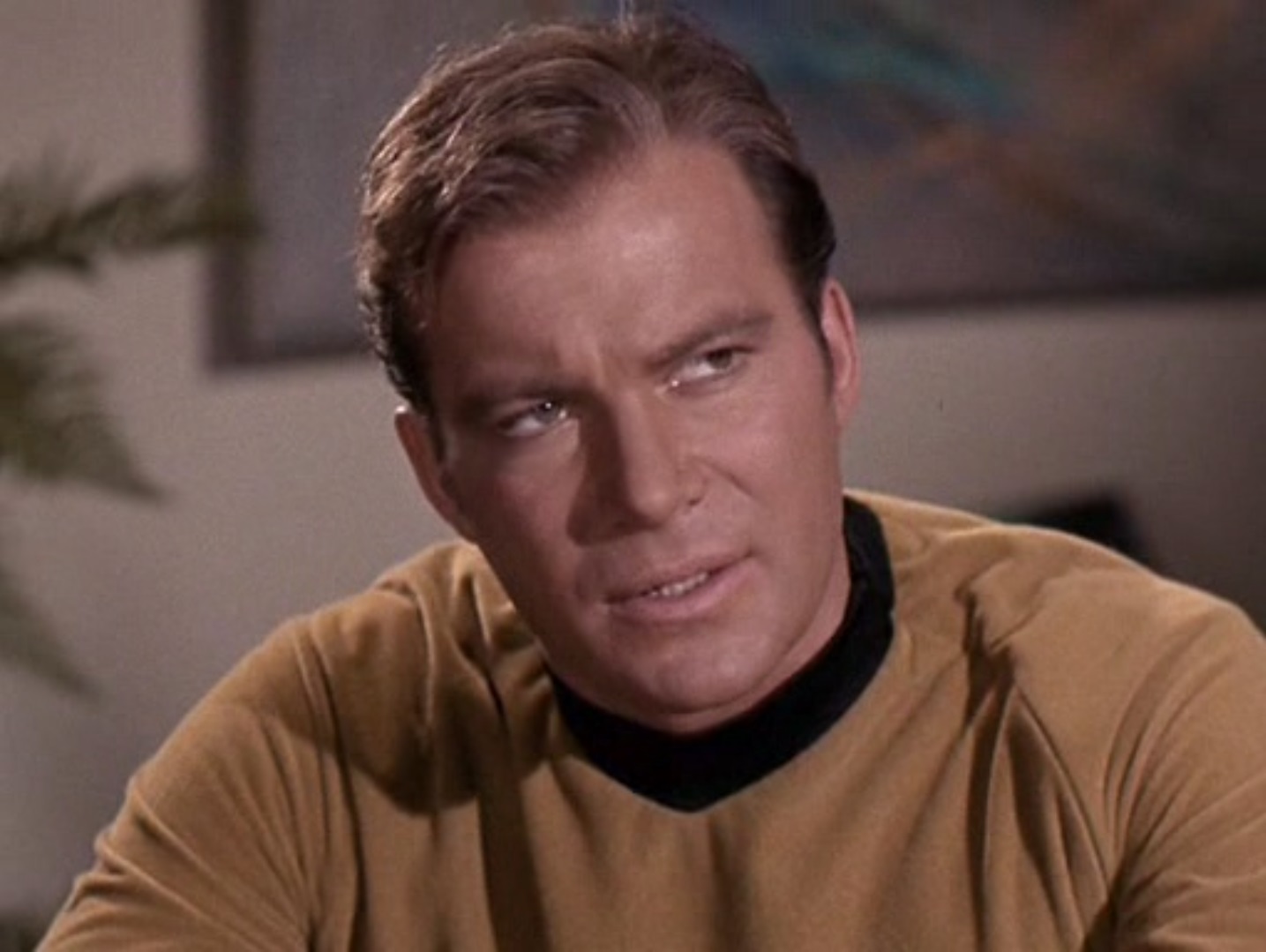
One cut later, and Spock's magically gotten the translator to work. Kirk explains that the alien's voice from the translator will be interpreted as however the creature perceives itself; what a surprise when the voice that comes out is female. Cochrane is dumbfounded, "how can that be possible?"
Kirk makes the point that male and female are universal concepts that apply to all living creatures, and obviously this creature is just female. (I guess he forgot about his basic biological studies and the numerous asexually reproducing living creatures: single celled organisms, plants, certain lizards, Talosians…)
Anyway, because of the Companion's newly discovered sex, Kirk makes the completely baseless assumption that the creature is romantically in love with Cochrane and that is why it sustains him. Cochrane, despite having the wisdom of two entire lifetimes, and living the better part of that time with this creature, finds the possibility of being loved by an alien absolutely disgusting, and he completely rejects the Companion.
Just then, Hedford cries out, and everyone remembers that she exists. On the verge of death, she makes a moving speech lamenting that though she lived an accomplished life with a successful career, she will never get the chance to love romantically or be loved. How selfish Cochrane is, for receiving such a pure form of love and then rejecting it because of his own biases.
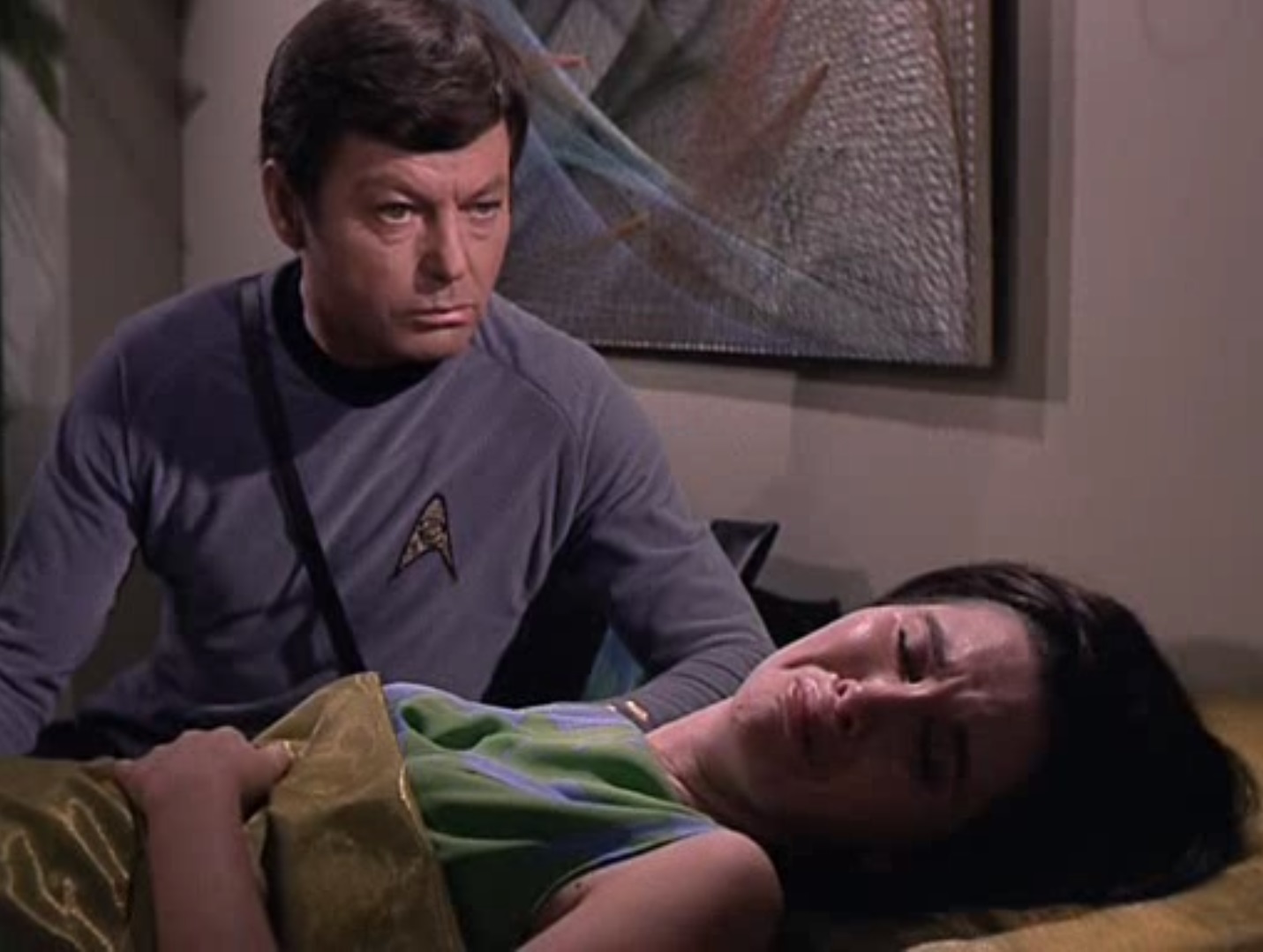

I never had time for love because I stop wars for a living. What's his excuse?
Kirk tries to negotiate with the Companion one last time, in the hopes that it might possibly free them to save Hedford's life. Except, instead of actually discussing a deal and offering the Companion literally anything, Kirk pulls his Kirk logic on the alien and convinces it that the only way for the Companion's love and Cochrane to coexist is for the Companion to be human. I think it would've been simpler to ask if the Companion could just let McCoy and Hedford go so they could save her life, and then he and Spock would stay behind to keep Cochrane company until the Enterprise could return and sort things out. Just me?
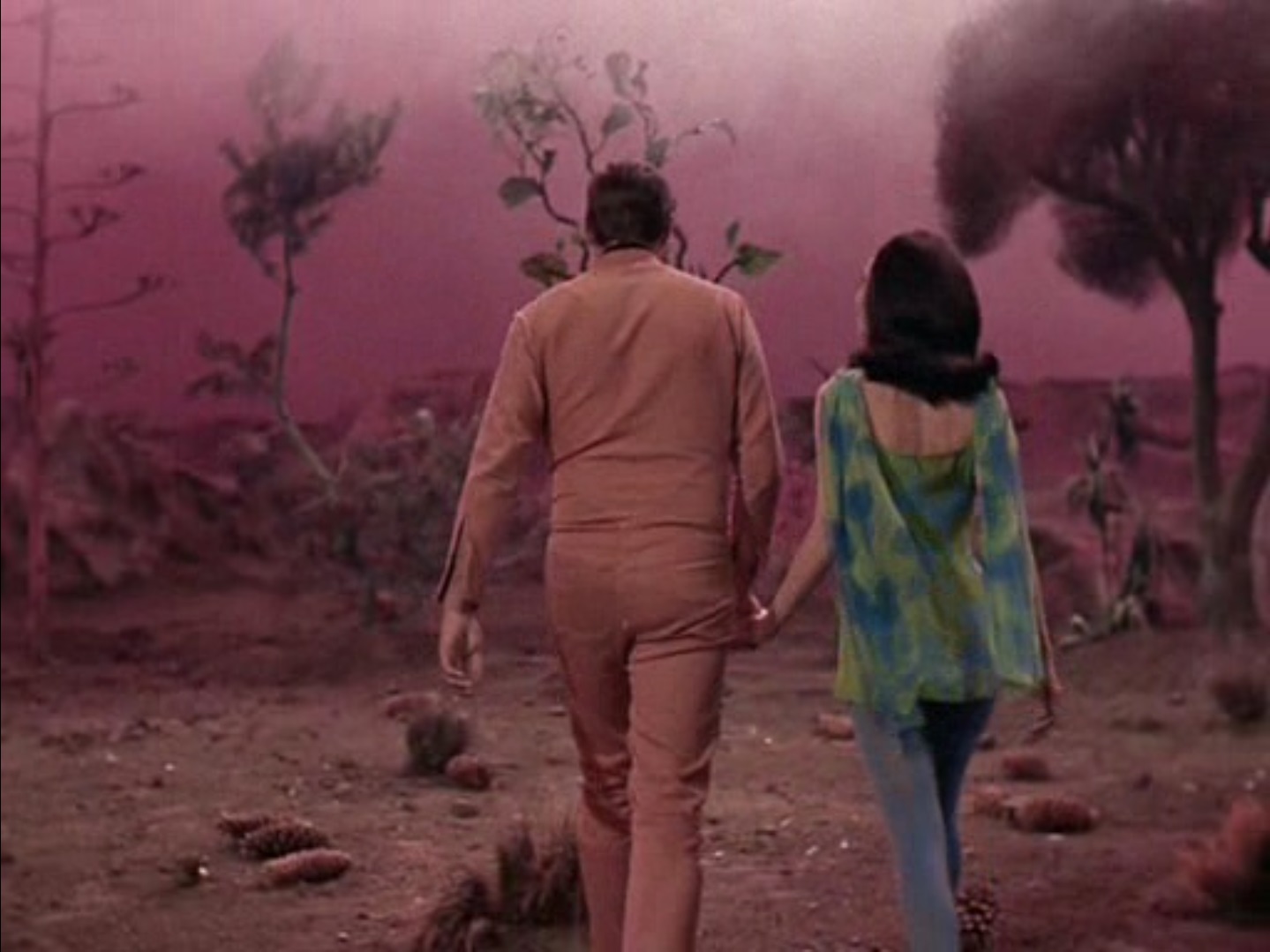

The Garden of Zephrem.
Of course the Companion disappears, and then shortly after a completely healed Hedford appears, restored by the Companion who has now occupied her body. Hedford walks towards Cochrane and explains with the Companion's voice that if not for the alien's intervention, Hedford would have ceased, but now they coexist inside her body and are both there, and are both in love with Cochrane. Cochrane instantly gets over his xenophobia now that his lover has a female body, and they decide to stay on the asteroid and live happily ever after together. Oh yeah, and by possessing Hedford's body, the Companion gave up her immortality and Cochrane's with it, and also she can't leave the asteroid because it's the source of her life force, so they are actually stuck there for the rest of their lives. But now they can spend the next 100 years planting fig trees and having sex, so it all works out.
And what about the intergalactic war that Hedford was supposed to stop? Well, in the words of Captain Kirk, "I'm sure the Federation will find some woman, somewhere to stop it."
This episode was so frustrating because it started with so much promise, and then failed in every regard at the ending. I was intrigued to see how they would handle the psyche of a 200-year-old man, and also the relationship between a human and a non-humanoid alien. The writer and Glenn Corbett's performance did neither of these subjects justice. Shatner's performance was particularly stilted, to the point where I had trouble following what he was saying at many points. The pacing started off sharp, but began to meander as the characters made stupider and stupider decisions, and the focus jumped to fun but unnecessary scenes on the Enterprise. But what bothers me most of all is the tragedy of Hedford's character framed as a happy ending.

Not necessarily a happy ending.
The companion speaks for Hedford at the end, and while it claims that both of them are there in consciousness, there is no evidence to justify it. All of Hedford's personality, her tenacity, her drive to complete her duty, and her anxiousness to return to her very pressing work, are gone after she is possessed. Presumably, she really did die on that asteroid, and all that remains are her body and her memories, which the companion takes advantage of to its own end. Or perhaps more horrifyingly, Hedford is still there, but so overpowered by the Companion that she is imprisoned in her own body, doomed to be the slave of this alien and its lover.
I can only hope that this type of story is a fluke, and will not become a standard for Star Trek.
Two stars.

by Joe Reid
Who’s Fooling Who?
It is often the case that at the end of an episode you are left with all of the answers to the questions that were posed in the show and a reasonable conclusion to the adventure of the week. The intelligent heroes are drawn to a place. In that place they discover a mystery. They use the powers and abilities at their disposal to solve that mystery and are rewarded. The rewards are treasure, or freedom, or their own safety, or that of the ship. It’s been a reliable formula that I’ve never had reason to doubt, until this week’s episode.
We never doubt what we have seen, because Kirk and Spock directly tell us exactly what is or has happened. In “Mirror, Mirror”, Kirk told us that the crew has traveled to a parallel universe. In “The Changeling”, Spock told us the origins of the space robot named Nomad. “The Doomsday Machine” had Kirk telling us that the giant space funnel was an ancient planet killing weapon that got out of control and destroyed its creators. How in space did he know that? More importantly, what if Kirk was wrong in some of his musings?
We ascribe superior intelligence to characters in sci-fi: they are smarter than us, and smarter than whatever baddy they face. What if this time, instead of our heroes understanding, and outsmarting the baddy, it was the creature who outsmarted the members of the crew?

One smart lady.
“Metamorphosis” featured a powerful entity. “The Companion” finds an 87-year-old man, Zefram Cochrane, who may or may not have been dead when she found him. She rejuvenates him to the prime of youthful manhood, feeds him, and keeps him from going insane for 150 years. She communicates with him in a physical way, enmeshing herself among his very cells. She must have been pretty advanced to do that.
When the Companion discovered that “the man”, Cochrane, needed female companionship, she reached millions of miles into space and located a vessel containing a dying human woman which would provide the means for her to personally meet the needs of the man. She grabbed the moving shuttle craft, and by power of force drew it several millions of miles to be stranded on her little asteroid. If that wasn’t powerful enough, when the Enterprise started to search for the lost shuttle, they discovered a trail from the shuttle to follow. The Companion, millions of miles away, made the trail vanish. This creature possessed the ability to manipulate living and inanimate matter on a cellular level from a vast distance.
As our heroes attempted to communicate with the companion, we thought we were shown a creature that demonstrated the intelligence of a child in her understanding of humans. A creature that they had to guide to an understanding of humanity using their superior intellect. What we really saw was a creature so smart that it guided the heroes down a path where they felt accomplished, but it met its own agenda. All without threatening the Enterprise or killing anyone.
In the end the Companion was able to convince a 230 year old man to love her, everyone else that she was not a threat, and she convinced a dying, love-starved woman to allow her to possess her body. This episode posed a challenge to the assumption that we understand the story as it is portrayed on the screen. “Metamorphosis” gave me the satisfaction of doubt at the conclusion. I liked it.
Four stars.
Boring Sex(es)

by Jessica Dickinson Goodman
As I watched "Metamorphosis," I found myself thinking of fig wasps. In my evenings and weekends, I run a small community garden on a church campus; a volunteer fig tree grows long and tall between the fence and the tool shed. When Mr. Cochrane mentioned wanting to plant a fig tree, I figured he was referencing this line:
"But they shall sit every man under
his vine and under his fig-tree;
And none shall make them afraid;"
(Micah 4:4, Tanakh, New Jewish Publication Society of America; a similar quote can be found in 2 Kings 18:31-32 Christian Bible, Revised Standard Version)
The thing about fig trees is they require pollinators. Trees can't ask other trees on dates – or kidnap them for 150 years to flirt with them in incomprehensible energy being ways – so they rely on wind or other species for reproduction. Many trees are self-fertile, meaning the adventuring pollinator need only traipse from one blossom to the next on the same branch, finding different reproductive parts at every turn in a complex mosaic. A few dioecious trees segregate these roles tree-by-tree, but most are self-fertile and don't break into easy categories like "male" or "female."
In general I find, the more I know about plants and pollinators, the less concepts like "male" and "female" mean anything at all.

"Yes. The matter of gender could change the entire situation."
Take figs, as Mr. Cochrane so clearly wants to. Figs can only be pollinated by a tiny wasp who crawls through their fleshy outsides to get to tiny flowers inside, sometimes ripping its wings off in the exercise because the fit is so tight, and spreading pollen as it goes. You see, the fruity flesh we love to eat on toast or in jams is not actually a fruit, botanically speaking, but mushy flowers. The wasp repeats this journey from flower to flower until, exhausted, it lays its eggs and dies inside the fig, to be consumed by those flowers. One portion of the baby wasps – once they metamorphosize from eggs to adults and mate with their own siblings – will live and die without ever leaving that fruit, spending their entire lives carving tunnels for the other portion to escape and continue the cycle.
I don't know about you, but very little of the above sounds like human sex to me, whether the act or the category.

"The idea of male and female are universal constants." Really?
Still, human scientists often slap labels like "female" on the wasps that climb into figs and "male" onto those who never leave them. They even do so for other pollinators for whose societies those categories fit even less well, like European honeybees, who have at least three clear reproductive roles, and for whom scientists have weirdly assigned "male" to two of (drones and workers) and "female" to the third (queen). The nature I work with every day is vastly more creative and varied than "male" and "female" – a fact which Jewish scholars know well, as the Talmud references up to eight sexes (zachar, nekevah, androgynos, tumtum, aylonit hamah, aylonit adam, saris hamah, and saris adam).
What about an alien society with three sexes, or eight, or none at all, or one who relies on star-blown space ships for their own reproduction? What if Hedford's death had been framed as part of the life-cycle needs of the energy being and not the pale nothing it was?
Now that is science fiction I would love to watch.
As Lorelei points out, this episode had so much promise. While I don't expect television writers to love the complex realities of Earth's natural world in the way that most gardeners do, I do expect them to do even the most basic of research about the world we all share every day, rather than slapping labels on alien life in ways that limit our imaginations rather than expanding them.
Two stars.
The next episode of Trek is tomorrow! Apparently, we're going to meet Spock's parents…
Come join us!

![[November 16, 1967] <i>Star Trek</i>: "Metamorphosis"](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/671116title-672x372.jpg)







![[November 12, 1967] Still in the Race! (Apollo-4, Surveyor-6, OSO-4 and Cosmos-186-188)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Apollo-4-672x372.jpg)



 The F-1 rocket motor, five of which power the Saturn V’s S1-C first stage, is the most powerful single combustion chamber liquid-propellant rocket engine so far developed (at least as far as we know, since whatever vehicle the USSR is developing for its lunar program could have even more powerful motors).
The F-1 rocket motor, five of which power the Saturn V’s S1-C first stage, is the most powerful single combustion chamber liquid-propellant rocket engine so far developed (at least as far as we know, since whatever vehicle the USSR is developing for its lunar program could have even more powerful motors). 



 Lunar Orbiter-3 image of the Moon's far side, showing the crater Tsiolkovski
Lunar Orbiter-3 image of the Moon's far side, showing the crater Tsiolkovski
 OSO-4 under construction
OSO-4 under construction


![[November 10, 1967] Mudd in the computer (<i>Star Trek</i>: "I, Mudd")](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/671110title-672x372.jpg)











![[November 8, 1967] Four to go (December 1967 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/671108cover-672x372.jpg)










![[November 6, 1967] Reaching the Peak (Doctor Who: The Abominable Snowmen [Part 2])](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/671106snowmenonthemountain.jpg)












![[November 4, 1967] Conflicts (December 1967 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/IF-1967-12-Cover-672x372.jpg)

 Joan Baez is arrested in Oakland.
Joan Baez is arrested in Oakland. Fr. Berrigan pouring blood into a file drawer.
Fr. Berrigan pouring blood into a file drawer. Futuristic combat in The City of Yesterday. Art by Chaffee
Futuristic combat in The City of Yesterday. Art by Chaffee McCullough helps Walters deal with a tear in his suit. Art by Morrow
McCullough helps Walters deal with a tear in his suit. Art by Morrow If you’re going to use art to boost the title, it should be more interesting than this. Art by Gaughan
If you’re going to use art to boost the title, it should be more interesting than this. Art by Gaughan Pay attention to me! Art by Gaughan
Pay attention to me! Art by Gaughan Latpur running errands for the Prognosticator. Art by Vaughn Bodé
Latpur running errands for the Prognosticator. Art by Vaughn Bodé J-1001011 begins an attack run. Art by Gaughan.
J-1001011 begins an attack run. Art by Gaughan. This is actually one of the less ridiculous moments of combat. Art by Gaughan
This is actually one of the less ridiculous moments of combat. Art by Gaughan Art uncredited
Art uncredited The protagonist has found someone who doesn’t care about his hated name. Art by Castellon
The protagonist has found someone who doesn’t care about his hated name. Art by Castellon A new Zelazny is a good sign, and Saberhagen could be good.
A new Zelazny is a good sign, and Saberhagen could be good.![[November 2, 1967] Trouble and Toil (<i>Star Trek</i>: Catspaw)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/671102title-672x372.jpg)













![[October 31, 1967] Same ol' (November 1967 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/671031cover-672x372.jpg)










![[October 28, 1967] Unveiling Venus – at Least a Little (Venera-4 and Mariner-5)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Venus-desert.png)












