
by Mx. Kris Vyas-Myall
It may be a product of my age but I think cinema peaked in the early fifties, when I was just exiting my teenage years. Back then studios were willing to put out quiet meditative films. Today it is hard to see anyone making films like Harvey, The Day the Earth Stood Still or The Bishop’s Wife.

Then came the rise of television and the Cecil B. DeMille response. Since The Greatest Show On Earth, most science fiction and fantasy cinema seems to have moved away from doing anything deep or meaningful in favour of a spectacle of flashy explosions. The closest we have got are probably the bomb films like Dr. Strangelove or The Bedford Incident, which are only science fiction by the tiniest margin.

As such, when a good friend of mine got tickets to the Ninth London Film Festival, I wanted to see if there was anything I could see that would convince me that cinema still had the power to be a great speculative medium. Thankfully two European Films were able to do just that.
Alphaville: A Strange Case of Lemmy Caution

Jean Luc-Godard seems an odd choice to be doing science fiction, with his previous work always being much more centred in the real-world. I am primarily familiar with him from his crime thrillers, the très chic Breathless and his tongue-in-cheek The Outsiders, which speak to someone of a high cultural awareness but with little interest in the speculative side of film making.
“Everything weird is normal in this damn town!”
As Alphaville starts, it seems like it could be a standard spy thriller. Lemmy Caution arrives in Alphaville and checks into the hotel under a false name, claiming to be a journalist from the outer countries. The woman in the hotel room offers to sleep with him but he refuses. A man tries to kill him but he sees him off. So far, so Danger Man. Then things start to get stranger…

First off, the woman reveals herself to be a level-three seductress. We then just get causally dropped in:
Something was definitely awry in this galaxy’s capital.
Putting us straight into the science-fictional realm but said in a way that we might expect Bogart to reference New York or LA.
Lemmy receives a call telling him a Natacha Von Braun is here to be of service to him. Pulling out two photos we see one of them has written on the back:
Professor Leonard Von Braun inventor of the death ray and Alpha Rays. Must be brought in alive. Must be killed.
And a second photo is of a Henry Dickson with an address attached. He gets Natascha (Leonard’s daughter) to take him to Alex’s address

Lemmy finds him at The Red Star Hotel. Henry explains that people who cannot adapt to Alphaville are killed by the authorities or kill themselves. Enquiring about Alpha 60, we learn it is a supercomputer but incredibly more advanced governing Alphaville entirely by logic. Finally, we learn Leonard Von Braun was formerly an agent like Dickson and Caution, but he is now a “slave to the logic”.
Whilst a huge amount of heavy lifting is done by this conversation, it doesn’t feel like we are being spoonfed, rather just like two agents talking to each other. We also get put in the mind of 30s and 40s noir with both the intense dialogue and the agents having names from media of the period.

Going forward from here, it is largely a battle of identities between Leonard’s vision of a completely computerized society, Lemmy’s romantic vision of the importance of art and freedom, and Natascha somewhere between the two. In the end Lemmy kills Leonard, disrupts the control of Alpha 60, and helps Natascha leave Alphaville, hoping that it can become a happy place once again.
“Sometimes reality can be too complex to be conveyed by the spoken word”

Writing this synopsis doesn’t really do justice to this film. It could easily have ended up as a forgettable sub-Orwellian thriller, but instead is more like seeing Orson Welles adapt a Philip K. Dick Novel. There are a few reasons for this:
Eddie Constantine is excellent as a cynical hard-edged agent. He is angry at the injustice around him and unwilling to play by the rules of Alphaville. He is very much playing by Raymond Chandler’s much quoted maxim:
…down these mean streets a man must go who is not himself mean
But then he is also both our entry point into our world and the mouthpiece for the idea that art and love are more important than technological progress and logic.
Now there are many science fiction stories at the moment on the theme of the danger of a highly computerized society. But Godard manages to strike the balance well enough that you can treat it as being critique of a number of areas. Specificity of allegory can be a curse, as there is a tendency to see the story as just a mystery to be solved. By keeping it wide Godard allows for multiple interpretations of the piece.
Finally, I have to mention Godard’s direction which manages to create an amazing sense of unease throughout. I believe this is by constantly counterpointing everything we see to balance between the familiar and the strange. The music played often being the opposite of the mood of the scene we are watching, characters shake their head for yes and nod for no, and the we see technology that is both contemporary and futuristic side-by-side.
If I have one critique of this film, it is that most of the women are treated like possessions. However, as this is so literal, with women being in glass cabinets or having catalogue numbers shown I feel this is a definite attempt at satire.
I would give this a full five stars and also be willing to say it is my favourite science fiction film I have ever seen.
The other film I saw was one that may well be that in the realm of fantasy.
The Saragossa Manuscript

Unlike Godard I am completely unfamiliar with Wojeich Has’s work, nor do think have I seen a Polish film before. However, this is film impressed me greatly with its richness and complexity. I will definitely be looking out for others from Has in future.
"I don’t know where reality ends and fantasy begins"
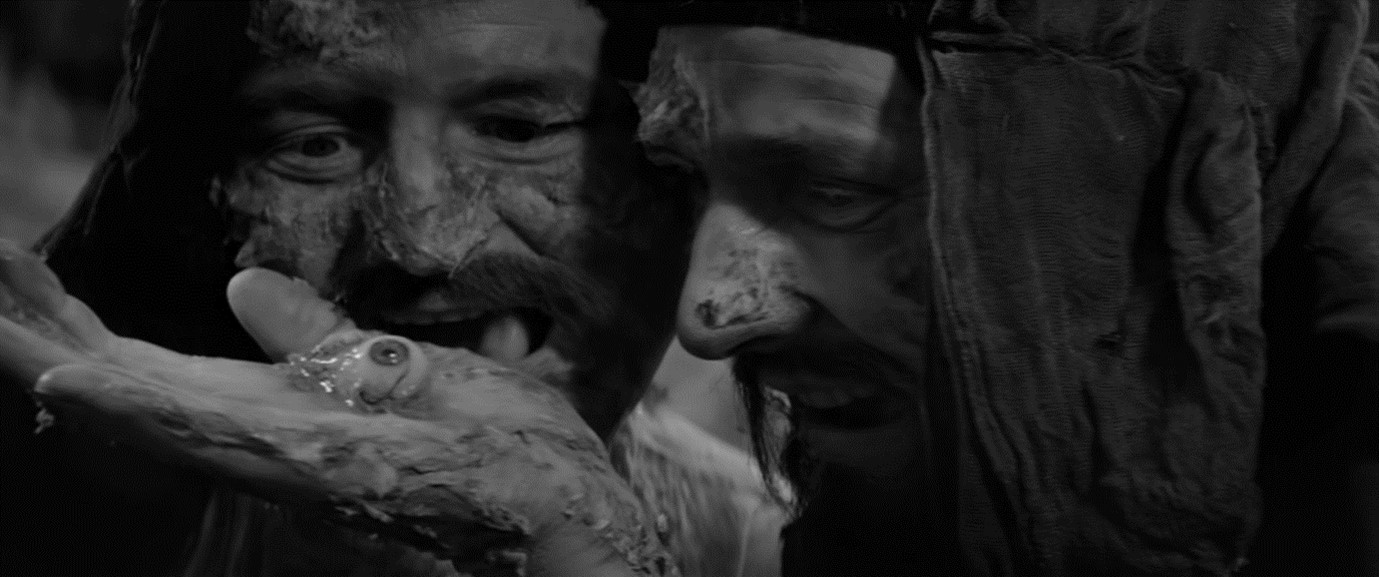

During the Peninsular War two soldiers find a book that the Captain says it is about his grandfather, Count Alfonse Ollavedez.
Ollavdez is finds an abandoned inn, Venta Queneda and is brought to a palace in the mountains. In the cave he meets two Tunisian princesses, who claim to be his cousins. They wish to marry him but only if he agrees to convert. After drinking from a skull chalice he awakes outside. Ollavdez tries to go to the palace again but only finds a small cave filled with bones and rats.
Riding on, he then comes to a small chapel with a hermit. Ollavdez tells how his father met his mother in these mountains. We also meet Pacheco who tells of a similar experience to Ollavdez’s at Venta Queneda.
After a night in the chapel, Ollavdez travels on but is arrested by the Inquisition. As he is being tortured, the princesses come to rescue him and they all flee back to the palace. The princesses then ask him to take their throne but a Sheik enters and he says he will kill him soon, telling him to once more drink from the skull chalice. Again, Ollavdez finds himself outside, however a Kabbalist is also there.
In order to avoid the inquisition, the Kabbalist says they should all head to his castle nearby.
That is where part one leaves off. Whilst this first half feels like Gawain and The Green Knight, the second half is closer to a Shakespearean comedy.
"Frasquetta told her story to Busqueros. He told it Lopez Soarez, who told it to Senor Avadoro. It’s crazy."

At the castle, Ollavdez looks through the library and finds a book illustrating the princesses (the same illustrations we saw in the original frame). Separately the Kabbalist is annoyed the book has been left open and worries if Ollavdez has read to the end, it will all be meaningless.
Then, a group of travellers arrive, led by Avedoro. His very intricate story will make up most of the second half:
It primarily concerns Lopez Soarez who is in love with Inez Moro, the daughter of a banker whom his father has an intense rivalry with. His friend Busqueros tries to help him out first by telling the story of Frasquetto whose, husband has her lover killed, and who she then attempts to scare to death until he is killed by a man hired by her lover before his death.
Next he attempts to sneak him in her window but instead he finds the wrong window and convinces an old cavalier he is being haunted by a ghost. Finally, when Lope Soarez comes to town they manage to engineer a situation which causes his father to forgive him and settle the disagreement with the Moro family.
Avedoro concludes his tale and The Kabbalist tells Ollavdez there are important matters he must attend to and so he rides out. Ollavdez follows a rider in black, but ends up back at Venta Queneda again.
Inside the place he finds the princesses and the Sheik. The Sheik reveals he was disguised as the hermit before but is actually the family Sheik. The princesses are pregnant with his children and everything he experienced was a test to see if the last male descendent of the line was worthy.
He drinks from the skull chalice one final time and awakes the book from the Kabbalist’s library. Back in a village, Olavdez writes his tale in the front of the book. However, he sees the princesses again out of the window in a mystical position summoning him.
In triumph he throws the book away (leaving it in the inn where it is found at the start) and rides back to the mountains once more.
“When a decent man is telling you a fascinating story you shouldn’t interrupt”
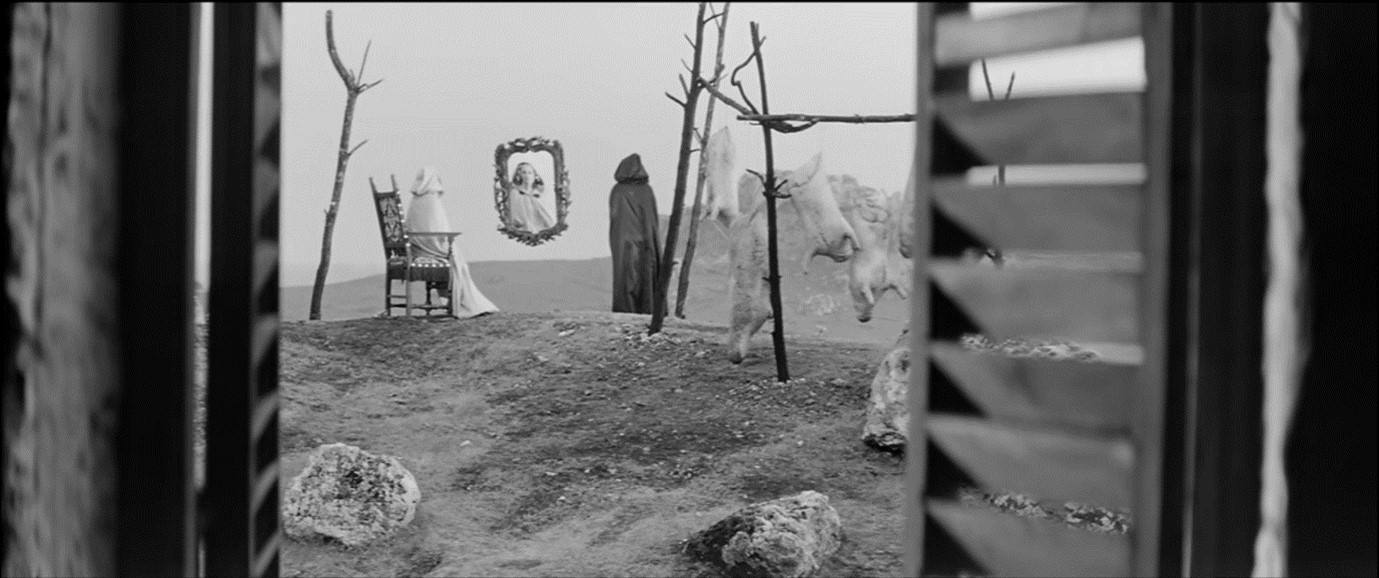

As you can probably tell this film is long and very complicated. Yet it never feels boring or contrived. Instead it is like an intricate watch put together in front of you. Even the depth of frame and questions of unreliable narratives never get confusing.
You could read the truth of the story in multiple ways because we do not truly know what happened. It could all have been Ollavdez’s dream from reading a book, it could be a plot engineered by The Sheikh, they could be evil spirits tempting him, perhaps he himself died and is in purgatory, or maybe he is just a Baron Munchausen teller of tall tales?
But it does not matter really as they are all interesting stories that add something to the narrative. Even Pacheco’s tale which we are explicitly told is untrue and does not seem to match the other facts as we know them. But it is still a great horror story that helps mirror Ollavdez’s experience and adds peril to the main tale.
Another element that has to be mentioned is the cinematography throughout the film is truly beautiful and I could have simply filled this review with hundreds of stunning photos and arresting images. Yet unlike other directors, such as Fellini, Has does not make it feel like he is doing so just in order to show his skill but to really tell a story and create an atmosphere.
The sense of the uncanny in this is incredible. During some scenes I was genuinely unnerved and unsure what was real. I don’t tend to be afraid in horror films but ideas about life and death, or the nature of reality are areas where I can encounter existential terror.
The soundtrack is also a really effective tool for displaying mood and period, helping us to be both reminded of where we currently are in the narrative and to move between humour and terror quickly.
This is truly one of the most literary films I have watched and an amazing work of fantasy. Five Stars.
The Future of fantastic cinema?
Going into the festival I worried that we would never see great speculative material on the silver screen again. Coming out of it I am very optimistic for what the future may hold.
I am not sure either of these are likely to appeal to a mass audience but they may well influence other film makers who can make interesting pieces. I hope so as these pictures show that the potential of great cinema is still alive.
The holidays are coming! Looking for the perfect gift for a niece, nephew, or other young relative? Kitra is the hopeful, found family novel that they've been waiting for. Buy a copy for them today…and perhaps one for yourself!



![[November 24, 1965] Books from Old Blighty (November Galactoscope)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/651124covers-672x372.jpg)




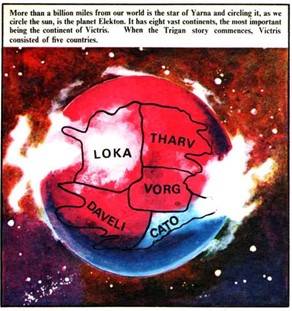
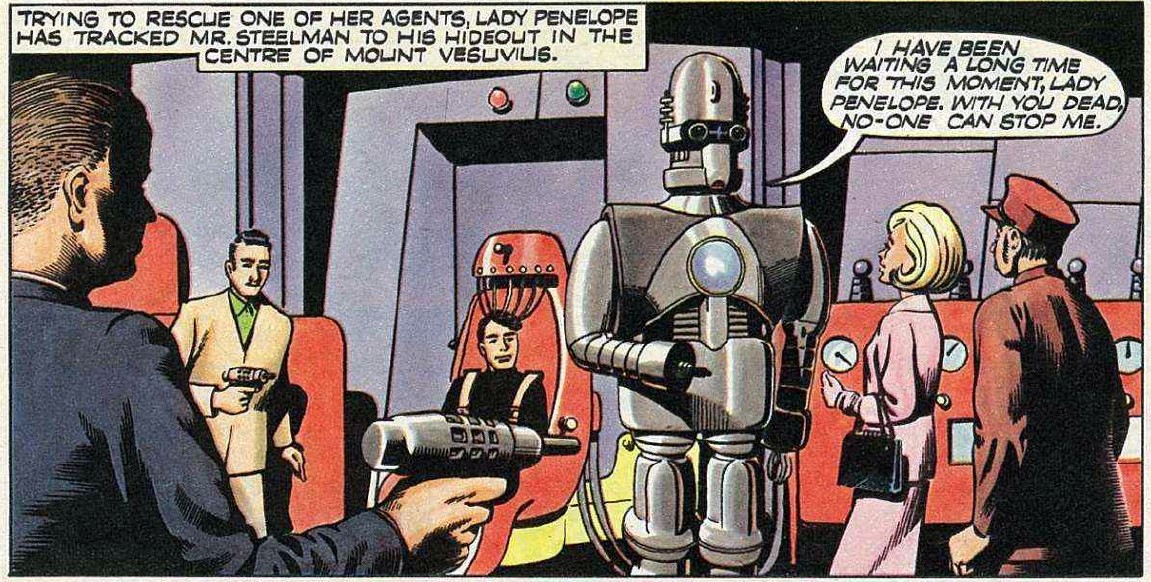
![[October 20, 1965] The Wonderful Shadow (A British Comics Overview)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Comics-Cover-Image-672x372.jpg)























![[September 2, 1965] A Clash of Cultures (THE 1965 WORLDCON)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Worldcon_1965_London_logo.jpg)














![[August 24, 1965] 13 French Science Fiction Stories](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/13-French-SF-384x372.jpg)



![[August 16, 1965] New Writings in S-F 5](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/New-Writings-in-SF5.jpg)






![[June 20, 1965] Ace Quadruple (June Galactoscope #1)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/650620cover-397x372.jpg)







 The first story "What Rough Beast?" is the story of a young immigrant named Mike Kronski trying to make his way in America. However, Mike is not the simple East European immigrant he appears to be. He comes from far further afield, from an alternate universe. He also has the ability to bend reality to his will and has accidentally changed his world into ours.
The first story "What Rough Beast?" is the story of a young immigrant named Mike Kronski trying to make his way in America. However, Mike is not the simple East European immigrant he appears to be. He comes from far further afield, from an alternate universe. He also has the ability to bend reality to his will and has accidentally changed his world into ours. "Second Class Citizen" is the story of researcher Charles Craven and the subject of his studies, the dolphin Pete. Craven has taught Pete to understand and speak English, spell simple words and even do chemical experiments. While Craven patronisingly presents Pete to some visitors, we learn from background conversations that there is an international crisis going on. Craven is convinced that this crisis will blow over, like any other crisis before.
"Second Class Citizen" is the story of researcher Charles Craven and the subject of his studies, the dolphin Pete. Craven has taught Pete to understand and speak English, spell simple words and even do chemical experiments. While Craven patronisingly presents Pete to some visitors, we learn from background conversations that there is an international crisis going on. Craven is convinced that this crisis will blow over, like any other crisis before. The novella "Be My Guest" is the story of Kip Morgan, a young man who finds himself possessed by four bickering ghosts after a poisoning attempt gone wrong. Kip also has another problem, he as well as two women of his acquaintance have become invisible to everybody but each other.
The novella "Be My Guest" is the story of Kip Morgan, a young man who finds himself possessed by four bickering ghosts after a poisoning attempt gone wrong. Kip also has another problem, he as well as two women of his acquaintance have become invisible to everybody but each other. "God's Nose" is a short vignette that does exactly what it says on the tin. The unnamed narrator and his female friend debate what the nose of God would look like. Eventually, her lover Godfrey arrives. He has a very prominent nose.
"God's Nose" is a short vignette that does exactly what it says on the tin. The unnamed narrator and his female friend debate what the nose of God would look like. Eventually, her lover Godfrey arrives. He has a very prominent nose. The final story "Catch That Martian" feels very much like a mix between The Rithian Terror and "Be My Guest". Once again, we have a dangerous alien, the titular Martian, who can take on the appearance of any human being. And once again, we have people abruptly taken out of the real world and turned into "ghosts". A young police officer is determined to crack the mystery of the ghosts and catch the Martian in the act. He deduces that the ghosts must have annoyed the Martian somehow, mostly via making noise, and that the Martian has a taste for musical theatre. So the narrator traces the Martian to a Broadway theatre, determined to apprehend him. But before he can give chase, he falls into the orchestra pit, straight onto a bass drum.
The final story "Catch That Martian" feels very much like a mix between The Rithian Terror and "Be My Guest". Once again, we have a dangerous alien, the titular Martian, who can take on the appearance of any human being. And once again, we have people abruptly taken out of the real world and turned into "ghosts". A young police officer is determined to crack the mystery of the ghosts and catch the Martian in the act. He deduces that the ghosts must have annoyed the Martian somehow, mostly via making noise, and that the Martian has a taste for musical theatre. So the narrator traces the Martian to a Broadway theatre, determined to apprehend him. But before he can give chase, he falls into the orchestra pit, straight onto a bass drum.
![[June 16, 1965] The International Poetry Incarnation](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Poster-550x372.jpg)










![[May 6, 1965] Back To Our Roots (<i>New Writings in SF4</i> & <i>Over Sea, Under Stone</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/New-Writings-and-Over-Sea-Under-Stone.jpg)






![[March 20, 1965] Clash of The Old & The New (February 1965 <i>Gamma</i> & <i>City of a Thousand Suns</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/650320covers-672x372.jpg)









