by Gideon Marcus
Hard reality
"Fans are Slans", or so the legend goes. Inspired by the psychic supermen in A. E. Van Vogt's Slan, the notion is that SF fans are a breed apart. Better than the average Joe, who are comparative Palookas. And why not? We're obviously smarter, given our intellectual proclivities, and our favored choice of fiction has all the answers. A problem is presented, our brilliant heroes hatch a solution, and we live happily ever after.
How else to explain Fred Pohl's call for Galaxy readers to submit solutions (in 100 words or fewer!) to the Vietnam war? Never mind that the problem has occupied our greatest minds for two decades, with no solution in sight. Indeed, ever since the Tet offensive, things have gotten more complicated.
You see, according to the Pentagon (per Aviation Weekly and Space Report), we won the Tet offensive. Handily. And that onslaught was actually a desperate 'Hail Mary'–Soviet and Chinese advisors had told the North Vietnamese that they were losing, big-time, and they had to do something to shatter American and South Vietnamese morale, no matter the cost.
And it worked! It induced LBJ to throw in the towel, declare a bombing holiday, and start a peace process, the only tangible effect of which has been to allow the communists to resume logistical deliveries down the Ho Chi Minh Trail and to offload shipments of Soviet materiele in the port of Haiphong, which had been interdicted by the U.S. Air Force.
That's not the only setback to the Allied cause–Khe Sanh, that forward Marine base that held out against siege for a full season, has been abandoned. No good explanation has been forthcoming.
Now, I'm not defending our presence in Vietnam, and I'm not arguing against the peace process. I'm saying no science fiction writer, no matter how brainy, is going to have an answer. Not even an easy one. I don't think there is one.
But so long as easy solutions exist in our science fiction, we Slans will keep thinking there is. Certainly, this month's issue of Analog is chock full of solvable problems, a bunch of scenarios that might well have been developed by high school or college professors as logic puzzles for their students.These are the kind of stories you find most often in Analog, which aims at the clear-thinking, black-and-white engineering set.
Now, that's fine. Analog's job is to make money, and it has the most readers of any SF mag, so it must be doing something right. It's certainly not editor Campbell's job to disabuse fans of their Slan aspirations.
Nevertheless, as someone who isn't an engineer, I find Analog often to be a slog. I like to have more story in my stories. Sometimes Campbell lets a compelling tale slip into his pages; more often he does not. The proportion of story types usually determines whether I give an issue more or fewer than three stars.
Given the tone of this preamble, you can probably guess what kind of issue this will be…

by Kelly Freas
Logic Puzzles
The Baalim Problem, by Bruce Daniels

by Kelly Freas
Problem posed: the human race has spread throughout the stars, setting up all sorts of empires, nations, and leagues. They have never encountered evidence of aliens–until now: a putatively nonhuman distress beacon has gone off over an independent human world. Two polities, an extremely libertarian nation and a group-thinking bureaucracy, have, at their computers' recommendations, sent single representatives to investigate.
The beacon leads them both to a hostile world, one beyond the means of either of scouts to handle alone. So, these adversaries must work together to escape the planet and bring back news of what they've found.
And what they find is that the "alien" evidence is an obvious hoax, developed by…someone…for…some purpose. Who might have hatched the scheme and why is the puzzle to be deciphered by the reader. Or, if the reader be lazy, to simply read about as the characters in the story explain the answer to each other.
The sentiment is nice, but I'd rather have had the thing play out narratively rather than in narration.
Three stars.
The Fuglemen of Recall, by Jack Wodhams

by Leo Summers
Problem posed: a number of people seem to have lost their minds, convinced they are someone else. The Feds investigate and determine the common factor was that each had just had an engagement with Lidlun Spacial Electronic Enterprises. Some kind of mind/memory transfer hocus pocus is clearly afoot. But when they apprehend the President of Lidlun for interrogation, is he really who he seems?
I suppose the lesson of this tale is that cops should always have a picture of the person to prevent a false arrest.
Unfortunately, Wodhams had to write a bit too obliquely and clumsily, and also had to make the investigators morons, to make this puzzle a challenge for the reader.
Two stars.
How the Soviets Did it in Space, by G. Harry Stine
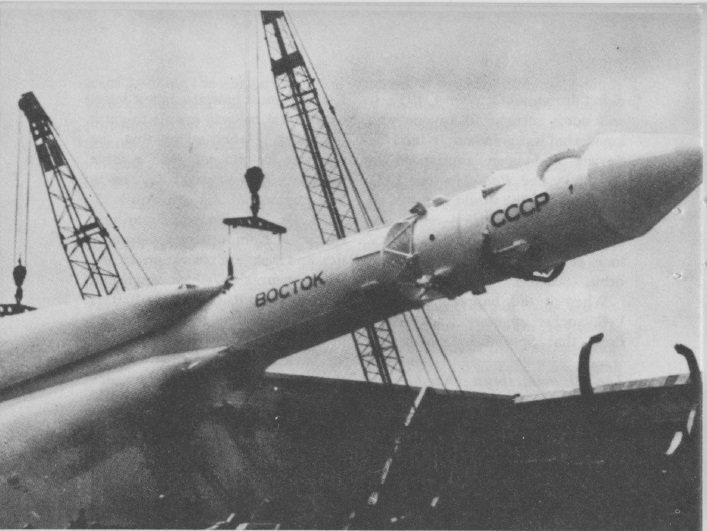

Problem posed: how did the USSR so handily beat us to orbit, and why did they keep scoring space spectaculars earlier than us?
If you've got a subscription to Aviation Weekly, you know the answer, but rocketry popularizer Stine does an excellent job of summarizing all the tidbits that have been leaked over the last few years. Now we know that the Soviets had a Saturn-class rocket from the beginning while we were still piddling around with Thors, Jupiters and Atlases.
So why didn't the Russkies keep their lead? Well, we don't know that another Soviet spectacular isn't around the corner. But assuming it isn't, I would guess it's because our Saturn 1 was the beginning of a family of superboosters whereas their Vostok/Luna/Zond launcher has already topped out its potential.
On the other hand, their new Proton rocket seems to be operational, and something launched Soyuz 1…
Great schematics, and I appreciated the strong line drawn between the development of ICBMs and the almost incidental exploitation of the rockets for civilian applications.
Four stars.
Appointment on Prila, by Bob Shaw

by Leo Summers
Problem posed: a gray terror, an alien being that can mimic anything perfectly, is trapped on a hostile cinder of a world when a Terran survey team arrives. Six self-contained pods leave the human mothership to conduct a geodetic survey; seven return. Worse still, the alien has the ability to take over any organic mind that it finds. Is there anything the team can do to withstand this menace?
Well, as it turns out, no. Indeed, the humans do precious little, and salvation relies on factors already baked into the scenario. I will confess that I had the ending spoiled for me before I started, so that might have diminished things.
That said, Shaw is a sensitive and evocative author, and this work is the highlight of the issue.
Three stars.
Satan's World (Part 4 of 4), by Poul Anderson

by Kelly Freas
Problem posed: Serendipity Inc., a knowledge broker for the loose knit Polesotechnic League of stars, is actually an intelligence-gathering front for the Shenn, an up-and-coming race of rapacious beings. Plenty of stuff happens as a lead up to this, the fourth installment in the serial, but most of it is inconsequential. This particular instance is concerned with the following questions:
1) Who are the Shenn, and how, with their frankly primitive, impulsive, and aggressive mindset, did they get control of an advanced, robotic civilization?
2) How can one reconcile their above racial habits with the fact that they are herbivores, who tend toward peaceful, communal societies?
3) How did the six human members of Serendipity's board end up in thrall to the Shenn, and how is that the linchpin to dealing with the seemingly implacable aliens?
These are all fine questions, and they are all answered tidily, in pages and pages of explanation that might well have been copied from a 30th Century encyclopedia. As often happens with Poul's work, he's created an interesting universe, only developed a plot for half of his story, and employed uninteresting caricatures to carry it out.
I'm sick of Nicholas van Rijn and his lusty Dutch oaths. I'm tired of the Buddhist dragon-centaur Adzel and the irritable (though admittedly adorable) Chee Lan, and the callow Davy Falkayn. Again, I want stories, not historical tracts of Anderson's future universe.
Two stars for this installment and 2.5 for the book as a whole.
Specialty, by Joe Poyer

by Kelly Freas
Problem posed: Tupac Araptha is an Alto Plano Peruvian, adapted to low pressure from birth. As a result, he is uniquely qualified to work on the moon. He can operate his suit at lower pressures, which means less resistance to movement, meaning he can work eight hours a "day" (twenty-four hour cycles are arbitrary on the moon) whereas lowlanders can barely manage three. How does Kelly, the local mining boss, handle the interpersonal jealousy that springs from this issue?
This story would be better served if it weren't set in the same timeline as "Spirits of '76", in which a dozen moonshiners (pun intended) establish a libertarian "republic" on the moon; it makes the context sillier, when the story is rather serious. I was also annoyed that Kelly's first solution was to suggest that Tupac beat up his rival in a manly display (on the moon? Surrounded by high vacuum?!), and when Tupac demurs, Kelly's next solution is to…take a leave of absence.
There could have been an interesting story here, but there ultimately isn't.
Two stars.
Harsh reality

Doing the math, Analog finishes at a mediocre 2.7. As uninspiring a finish as this is, it actually consitutes a median: Fantasy and Science Fiction (2.4) was worse, as were Fantastic (2.3) and Orbit 3 (2.3). IF (2.8) was a near tie.
The saving graces of this month were Famous Science Fiction (3.5), though that was mostly reprints, and Galaxy (3.9), which I seemed to like more than everyone else. Well, that's my privilege!
Despite the low aggregate ratings, there was actually enough good stuff to fill two decent sized magazines. Women contributed 10.5% of the new fiction this month, which sounds better than average, but all but one of the tales was in Orbit, which is technically a paperback rather than a magazine.
Bringing things full circle, the issue of getting more women in print has been a perennial one, one that has defied solution (or even the notion that it's a problem that needs solving). Since the magazines won't or can't fix the situation, women have moved to other media. So we see women in anthologies like Orbit. We see women like A. M. Lightner and Madeleine L'Engle writing "young adult" (the new term for juvenile) series. We see women prominent in the writing and production of science fiction shows like Star Trek.

I think it's fandom's loss when the SF mags become stag parties. I remember the salad days of Galaxy and F&SF back in the early '50s, and part of what made them great was the diversity of stories, the range of viewpoints and styles. I'd hate to lose that to other venues (though the mags' loss is obviously other media's gain).
How do we get more women back into the mags? How do we get folks to recognize the value of women in the mags? I wish I knew. After all, I'm no Slan, just a man…

![[July 31, 1968] No easy answers (August 1968 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/680731cover-672x372.jpg)

![[July 22, 1968] Shades and Shadows (August 1968 <i>Fantasy and Science Fiction</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/680722cover-664x372.jpg)





![[July 10, 1968] Back in the Saddle Again (August 1968 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/680710cover-672x372.jpg)









![[June 30, 1968] Hawk among the sparrows (July 1968 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/680630cover-672x372.jpg)










![[June 26, 1968] To far off lands (July 1968 <i>Fantasy and Science Fiction</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/680620cover-451x372.jpg)














![[June 10, 1968] Froth and Frippery (July 1968 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/680610cover-653x372.jpg)











![[June 8, 1968] Robert F. Kennedy (1925-1968)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/gettyimages-107635904-672x372.jpg)










![[May 31, 1968] Euler's Issue (June 1968 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/680531cover-672x372.jpg)








![[May 20, 1968] Dying, deflating, and deorbiting (June 1968 <i>Fantasy and Science Fiction</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/680520cover-665x372.jpg)





![[May 10, 1968] Horse race (June 1968 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/680510cover-393x372.jpg)