by Erica Frank
I have once again dipped into the magazine of "entertainment for men" who want to feel intellectually superior while they browse photos of mostly-naked women they like to imagine are sexually available to them.

There are some good stories. Some good political commentary. Some funny cartoons. And a whole lot of self-aggrandizing pontification, and a lot of wealthy white men insisting they know what's best for everyone, especially women.
The Fully Automated Love Life of Henry Keanridge by Stan Dryer (July)
Our protagonist, Henry Keanridge, has a wife, a mistress, and two girlfriends; he manages the scheduling for this complex arrangement of obligations and secret-keeping via a computer. That's our science fiction aspect. He works at a trucking company, and he has fed his own name into the system as a truck, and the four women as "stops" on his route, and it manages his schedule, reminds him of birthdays and holidays, and so on.
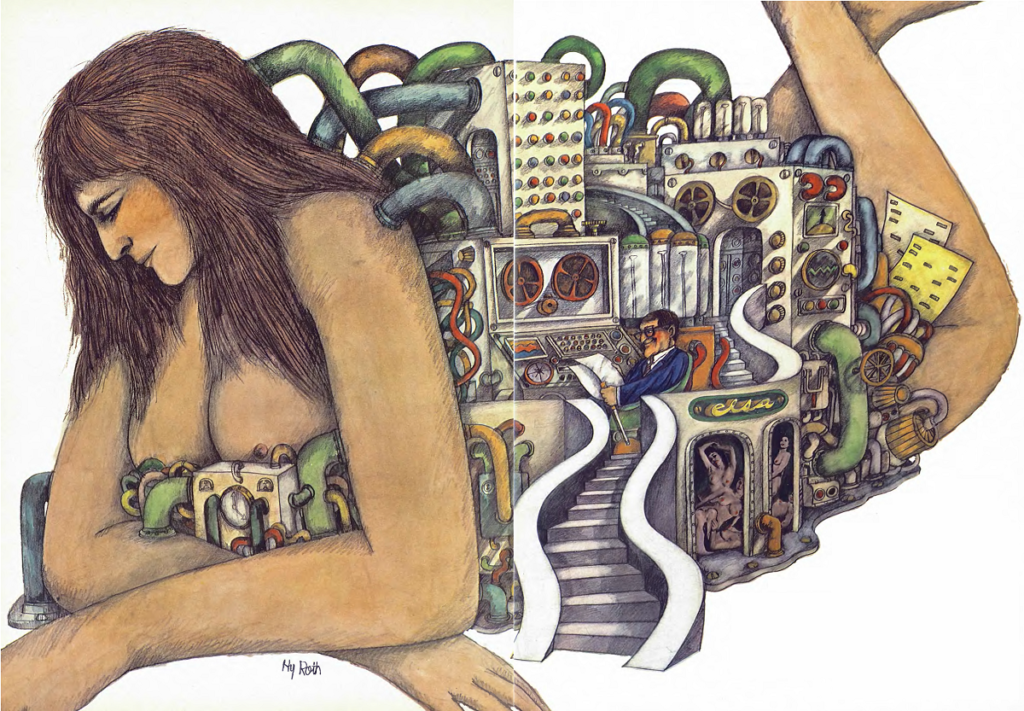

Hyman Roth's art led me to believe this story had more substance than it does.
Here's a quote: "Before their affair, Dee had been a girl of impeccable virtue. She would no more have thought of having a love affair than of, say, not wearing a hat to church." That tells you everything you need to know about both Dee and Henry.
As a story: Two stars, providing you can tolerate Henry's male chauvinist perspective on life.
As science fiction: One. I read it so you don't have to.
Masks by Damon Knight (July)
This one, unlike many of Playboy's stories, is unquestionably science fiction. Medical technology, full-body prosthesis, what happens to a human when you put his brain in a robot body? They can't get the robot to look fully human, can't give it a full range of facial expressions–that's okay, though; he can wear a mask.
But the project's funding is uncertain, so our protagonist–unnamed for the first half of the story–may have to justify his right to "two hundred million a year" in medical expenses, when normal full disability support is $30,000.
Two stars. Probably would've been three if it weren't for the sudden gratuitously violent twist.
Silverstein Among the Hippies by Shel Silverstein (July)
Shel Silverstein comments on the Hashbury community, mostly by drawing cartoons of hippies. They're clever and often insightful.

Why indeed? Headlines include: Detroit Burning, Kill 720 Viet Cong, Sniper Kills Six, Self, New Fallout Danger Warned, Girl Raped, Alabama Riot, War in Sinai…
The Trouble with Machines by Ron Goulart (August)
Maximo is a machine, a robot designed to hunt and kill the reporter who keeps criticizing technology companies. Maximo is disguised as a refrigerator which will be delivered to the reporter's house. …Maximo has, or acquires, some interests of its own, and runs off before it reaches its assigned destination.
This one had a plot twist I didn't see coming (wow, the sexy lady is actually a person! She is part of the plot!) and a story resolution that, while not groundbreaking, doesn't leave confusing loose ends.
A solid three stars.
More Silverstein Among the Hippies by Shel Silverstein (August)
He's back! Or maybe he just hasn't managed to escape yet.
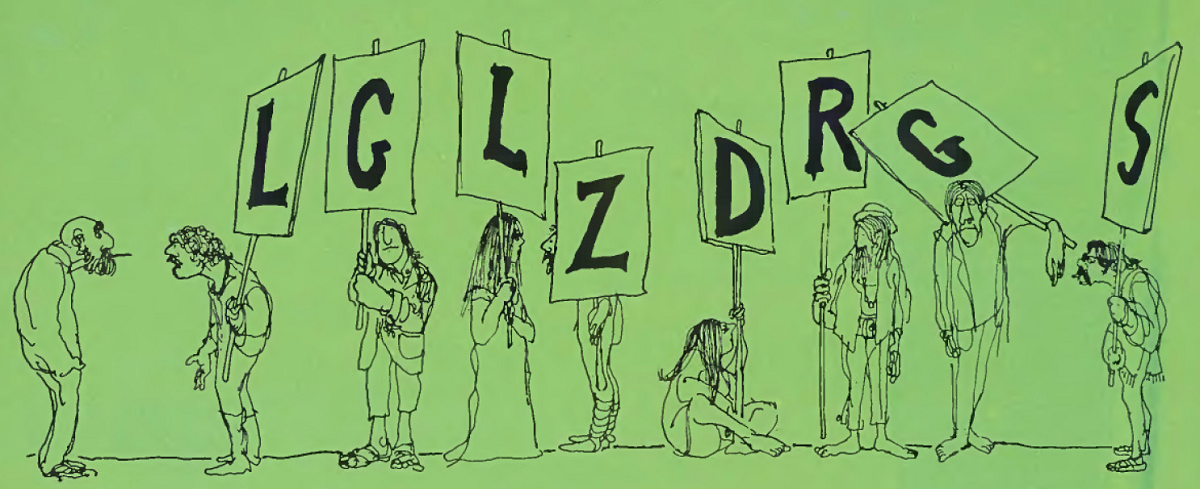

"It was supposed to say 'LEGALIZE DRUGS'… but E is out trying to score, A and I are on an acid trip, the other E just got busted, and U was simply too strung out to show up!"
Playboy Interview: Stanley Kubrik (September)
This is not just an interview; it begins with a few pages of biography and background information showing how Kubrick got his start in film: "He quit his job at Look, raised $20,000–mostly from his father and his uncle–and began shooting 'Fear and Desire'… Though rejected by all major distributors, 'Fear and Desire' toured the art-house circuit and eventually broke even."
On the one hand: It's got some solid information about how his career led up to 2001. On the other: Four pages in all-italics is hard on the eyes. Next time, Playboy, consider using a scene divider of some sort and leaving the introduction more readable.
For the actual interview, Kubrick is very full of himself. 2001: A Space Odyssey showcases his VISION!!! It has a MESSAGE!!!… which he is not going to explain, of course, because he is an artist–would we better appreciate La Gioconda (that's "the Mona Lisa" to us plebes) if Leonardo had explained why she was smiling? (I wish that were a made-up example. It is not; he directly compared his film to the Mona Lisa.)
Some words and phrases he throws around in the interview: Cosmos, man's destiny, the lumpen literati (he's not fond of his critics), grandeur of space, chrysalis of matter, tendrils of their consciousness… he does like to talk about his grand ideas. Much of the interview is him saying "What if…?" and the interviewer politely feeding him the next question. He did manage to say a few things I agreed with, including, "Why should a vastly superior race bother to harm or destroy us?"
Two and a half stars. I am neither a film buff nor an arts buff, so much of this is tedious to me. If you like rich guys with an interest in science fiction showing off their education, there's 16 pages of it here.
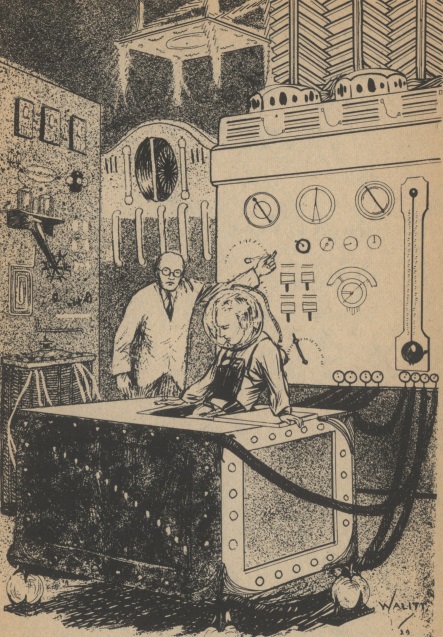
Fortitude by Kurt Vonnegut, Jr.
This is a story in teleplay script format, beginning with a discussion between the esteemed Dr. Norbert Frankenstein and his guest, Dr. Little. Frankenstein's assistant, Tom Swift, occasionally comments with details. His patient, Sylvia Lovejoy, is now only a head attached to a machine–apparently a popular concept in Playboy these days; new writers should consider submitting stories with similar themes as it seems like they're buying.
Sylvia's every mood is controlled by complex machinery, except occasionally a small spark of her former self begs to be allowed to die. Dr. Frankenstein has foreseen this desire, and has programmed her robot arms to be unable to point a gun at herself or bring poison to her lips.
Four stars; the reader is left wondering if Sylvia has any possible route to escape, even after the circumstances of her vigil have changed.
Here Comes John Henry! by Ray Russell (September)
John Henry is the first man on the moon–or rather, the first man to land on the moon and come back. The first lunar landing mission is a Black man teamed up with a Russian as a show of international cooperation. The media have a field day making corny slogans about the duo, often playing on tacky racial slurs. John Henry is not bothered by tacky media coverage; he's just thrilled to be going to the moon.
The two guys have a lot in common, it turns out, starting with their names. The other fellow is Ivan "Vanya" Genrikhovich–"John, son of Henry" in Russian. Both are from Georgia, just from different parts of the globe. Both are from the capital city. Both are descendants of slaves. ("My father's father was a serf," Vanya says.) They are becoming great friends, bonding over their shared joy of space, taking pictures on the moon… until they notice that their fuel measurement is a bit low.
Not a lot low. Not low enough that the ship can't make it back. It just… can't carry both of them back. They quickly realize they have been set up: this mission has been calculated down to the last ounce, the last paperclip's worth of mass. Someone decided that only one of them should come home, and didn't bother to tell either of the pilots.
I won't spoil the solution they find, because it's worth reading; it's so much better than the one proposed in Godwin's "The Cold Equations." Five stars.
Mr. Swift and His Remarkable Thing by Jeremiah McMahon (October)
Two modern hippies, Mommababy and Daddybaby, have settled down to suburban life after the unplanned arrival of Frankenbaby five years ago. They try to be properly hip and permissive, but Mommababy does not like their neighbor, Mr. Smith, who is making some kind of sculpture-thing in his back yard. It's ugly, and Mr. Smith is always walking around muttering things like "Is the missing factor X?"
She doesn't want Frankenbaby playing in Mr. Smith's yard. Frankenbaby, however, has his freedom: after he's sent to his room, his parents spend the evening focusing on the "good things–flowers, beards, sideburns and beads." Mommababy considers checking on Frankie at bedtime, but Daddybaby warns her against being overprotective, so Frankie manages to slip out of the house. They discover him missing after the great explosive blasts from next door rock the house.
It turns out the weird sculpture was a rocket ship, and Mr. Smith and Frankenbaby have blasted off. It's unclear if they have a destination or are just going on a joyride.
Another solid three stars: This is an enjoyable read; it just doesn't really have a point—much like Mommababy and Daddybaby.
What's Your SQ (Sexual Quotient)? (October)
"A man's love life—whether he be single or married—is intimately related to his business career, to his social pastimes and even to the car he drives."
This is a 54-question personality quiz; each question has 3 options, with a key provided at the end for interpreting the results. It tells readers that, if none of the answers seems to apply, just pick the one that seems least unlikely.
It is, of course, expecting all participants to be heterosexual men of reasonable wealth in 1968 America. "You" own a car, have a job, have an active sex life with women (which will usually be called "girls"), and so on. These biases are visible throughout the quiz.
Moreover, it is assumed that you perceive sex as something you do for personal reasons only, not a shared activity of mutual pleasure.

You are not, of course, concerned with whether your partner is enjoying herself.
The end result: Men's personalities can be sorted into three categories, although most men will have a blend of all three. Type A: "a Don Juan or a 'phallic narcissist'; a ladykiller." Type B: "his sense of security is strongly dependent upon being loved, cared for, and emotionally supported by others; he feels unworthy of this attention." Type C: "dedicated to fighting intemperance and immorality in all its forms; inflexible in both body and mind."
I can't figure out how to give this stars. I can say: If you're not a heterosexual man with the common mundane biases of current late-1960s America, the "analysis" after the quiz isn't going to be useful to you.
Colorless in Limestone Caverns by Allan Seager (November)
Our protagonist, Reinhart, is a dislikeable sort of fellow who tortures animals in the name of science and gets himself acclaim and tenure for it. He orders some blind cave fish on a whim, planning on researching their feeding habits, but instead, a change comes over him: From the first day he acquires them, he spends all day in the lab staring at them, and he becomes quiet and unresponsive at home. He feels a great kinship with the fish.
His wife worries. His mother worries. He thinks about fish. His wife and mother call in psychiatrists. He snaps out of his lethargic funk, speaks blithely of the research he's going to do, apologizes about worrying his family, and goes back to normal.
Two stars. I kept waiting for the story to start, and then it was over.
Scrutable Japanese Fare by Thomas Mario (November)
This article has nothing remotely science-fictional about it, and it is not related to the new-trending cultural shifts of which I am so fond. It's about dining in Japan, and since Gideon visits there occasionally, I thought I'd read it. It's one page of actual article followed by 10 recipes.
It mentions sukiyaki, shabu shabu–which it claims is a great food for dinner parties; host and guests share preparation activities–and tempura with random ingredients, "gleefully scattered over the tray in no fixed pattern." It talks about Japanese steakhouses that cook on a metal slab at the dining table, and describes how to prepare warm rice wine for best enjoyment.
It includes several recipes: Broccoli salad with golden dressing, cabbage salad with soy dressing, sesame dipping sauce, scallion dipping sauce, chicken yakitori, shrimp tempura, (which it insists should be eaten hot rather than prepared in advance; "One device for party service is to hire a domestic geisha who will fry and deliver it in large batches"), tempura batter & sauce, Japanese steak dinner and the shabu shabu the article begins by praising.
I found myself mildly disappointed by the lack of pictures of any of the food, and that the recipes aren't clear about how many servings they make–the "Japanese steak dinner" wants 4 lbs of steak, cut into ¾" cubes! That's not dinner for two or even for a family–that's the whole dinner party's meal. The recipes also don't list which cooking implements they need; that's folded into the narrative instructions.
Not rating for stars. It's a pleasant enough read, and the recipes are nice, although they lack a few details from being well-made.

Coming soon to a theatre near you! Finally, you can see the actual scenes from the pictorial review earlier this year.
The Mind of the Machine by Arthur C. Clarke (December)
Clarke discusses whether computers can be said to truly think (…no, despite a few radical fanatics here and there), and what it might mean to society if they could, or they gain the ability in the future. He takes it as a foregone conclusion that they will:
…[T]he fact that today's computers are very obviously not "intellectually superior" has given a false sense of security—like that felt by the 1900 buggy-whip manufacturer every time he saw a broken-down automobile by the wayside."
He also has a very narrow view of how the future needs to play out:
The problem that has to be tackled within the next 50 years is to bring the entire human race, without exception, up to the level of semiliteracy of the average college graduate. This represents what may be called the minimum survival level; only if we reach it will we have a sporting chance of seeing the year 2200.
Although there's some obvious pandering to those who believe themselves the intellectual elite, he does cover a lot of the current trends in computer development, and a reasonable amount of speculation about possible future ones, albeit with, like the SQ test above, a lot of unmentioned biases.
Three stars; a nice review of the current state of scientific development and good suggestions about what might come next.
Wealth versus Money, by Alan Watts (December)
Alan Watts is neither a science fiction writer nor a scientist; he is a philosopher and zen buddhist guru. However, his article begins with an emphatic statement that the United States of America will cease to exist by the year 2000–which puts it firmly in the realm of fantastic speculation, as much as any of the stories I've reviewed.
He points out that a nation has two definitions: One, its geography, biology, and acknowledged physical boundaries; the other, its culture and sovereignty as recognized by its people and others. He points out that this second aspect of the USA is on the verge of destroying the first, and that much of this problem is caused by the conflation of money and wealth.
Money is assigned by the government. It is a deliberately limited resource. Wealth is a matter of valuable resources that has nothing to do with numbers written on slips of paper. Money is a measurement—purportedly of wealth, but as with any measurement, it can be applied in multiple ways.
"[T]rue wealth is the sum of energy, technical intelligence, and raw materials," he says. And he continues to point out that mankind is not separate from the world around us, but part of it—"like a whirlpool is to a river"—we cannot "conquer" or "invade" our own home, and our best chance of survival in the future is to recognize the value of leisure and enjoy the wealth that surrounds us.
Four stars (although I am likely biased in this rating); I have a great fondness for anything that can make Playboy—an overtly libertarian, capitalistic publication—recognize other approaches to life.





![[March 10, 1970] Baby, It's Cold (And Dark) Outside (April 1970 <i>Fantastic</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/COVERSMALL-672x372.jpg)
![[October 8, 1969] Suddenly . . . (November 1969 <i>Amazing)</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/amz-1169-cover-672x372.png)






![[April 10, 1969] Low (May 1969 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/amz-0569-cover-490x372.png)




![[December 8, 1968] Hippies and Robots (July-December 1968 Playboy)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681212covere-672x372.jpg)








![[August 6, 1968] Treading Water (September 1968 <i>Amazing</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/amz-0968-cover-490x372.png)