by Kaye Dee
Christmas is supposed to be a time of family celebration, but this year in Australia it has instead become a time of national mourning following the tragic disappearance of our Prime Minister, Mr. Harold Holt. The country is in shock as we come to terms with the loss of a relatively new national leader in an apparent drowning accident.

A Fateful Swim
The full circumstances surrounding the Prime Minister’s disappearance have yet to be established. What we do know is that on Sunday 17 December Mr. Holt was swimming off Cheviot Beach, south of the Victorian state capital of Melbourne, when he was lost to the view of friends onshore after swimming out into deep water and apparently being swamped by a large wave.
The Prime Minister’s love of the ocean is well known: he and his wife have beachside holiday homes in Queensland and at Portsea, not far from Cheviot Beach. A strong swimmer, fond of skindiving and spearfishing, Mr. Holt apparently claimed to “know Cheviot beach like the back of my hand”, and to be familiar with its sometimes treacherous offshore currents. While skindiving on an earlier visit, Mr. Holt had once recovered a porthole from the wreck of the SS Cheviot, the ship which broke up and sank near the beach, due to its dangerous currents, with the loss of 35 lives on 20 October 1887.
 On 17 December, while spending the weekend at Portsea, Mr. Holt and four companions decided to stop at remote Cheviot Beach for a swim before lunch when returning from a drive. The water conditions were rough and only one of Holt’s companions ultimately went into the water with him. Mr. Holt swam out into deep water and may have been caught in a rip current when he disappeared. Mrs. Gillespie, one of the group who remained on the shore, saw Mr. Holt disappear, describing it as “like a leaf being taken out […] so quick and final”.
On 17 December, while spending the weekend at Portsea, Mr. Holt and four companions decided to stop at remote Cheviot Beach for a swim before lunch when returning from a drive. The water conditions were rough and only one of Holt’s companions ultimately went into the water with him. Mr. Holt swam out into deep water and may have been caught in a rip current when he disappeared. Mrs. Gillespie, one of the group who remained on the shore, saw Mr. Holt disappear, describing it as “like a leaf being taken out […] so quick and final”. A Desperate Search
 The Prime Minister’s disappearance sparked “one of the largest search operations in Australian history”. Three amateur divers initially tried to brave the heavy seas but found them too turbulent. They were soon joined by the Victoria Police, deploying helicopters, watercraft, police divers, and two Navy diving teams. By the end of the day, more than 190 personnel were involved. However, the leader of one of the Navy teams apparently believed that “any chance of finding the Prime Minister was lost by the Sunday night”.
The Prime Minister’s disappearance sparked “one of the largest search operations in Australian history”. Three amateur divers initially tried to brave the heavy seas but found them too turbulent. They were soon joined by the Victoria Police, deploying helicopters, watercraft, police divers, and two Navy diving teams. By the end of the day, more than 190 personnel were involved. However, the leader of one of the Navy teams apparently believed that “any chance of finding the Prime Minister was lost by the Sunday night”.Despite this gloomy assessment, the number of searchers eventually increased to more than 340, including 50 divers, working in extremely difficult weather and sea conditions. The intense search continued until December 21, but was then scaled back, although the quest to find Mr. Holt’s body still continues.
Readers outside Australia may be wondering how the leader of the country could go swimming without being accompanied by a security detail. Australian leaders have traditionally not employed bodyguards or other protective measures and Mr. Holt similarly refused a security detail when he first assumed the Prime Ministership: he considered it was unnecessary and might distance him from the public. Although a couple of incidents in mid-1966 resulted in Holt grudgingly accepting a single bodyguard for his official duties, he continued to refuse any protection while on holiday, considering it a violation of his privacy. (Nasty rumour has it that he also wanted to conceal the extramarital affairs he has been suspected of indulging in). Thus, he was unaccompanied by any official security during his weekend break.
 The first searchers combing Cheviot Beach, looking for any clue to the Prime Minister's disappearance
The first searchers combing Cheviot Beach, looking for any clue to the Prime Minister's disappearanceA Man of the Twentieth Century
The third Australian Prime Minister to die in office, Mr. Holt was a relatively young man, only 59. The first of our national leaders to be born in the Twentieth Century, Holt believed it was his responsibility as Prime Minister “to reflect the modern Australia to my fellow countrymen, to our allies and the outside world at large”. Mr. Holt became Prime Minister when he assumed the leadership of the incumbent Liberal Party in January 1966.
A lawyer and political lobbyist before being elected to the Federal Parliament, Mr. Holt was an enthusiastic sportsman and swimmer, as well as an effective orator, making him a sharp contrast with his Prime Ministerial predecessors and most of his parliamentary colleagues. His popularity with the public was reflected in his crushing victory in the elections of late 1966.
 Mr. Holt (right), at Parliament House, during his period as Treasurer to his predecessor, Sir Robert Menzies (left)
Mr. Holt (right), at Parliament House, during his period as Treasurer to his predecessor, Sir Robert Menzies (left)With extensive political and governmental experience, serving as a Minister in several critical portfolios, Mr. Holt helped to transform post-War Australia into a modern democracy that now sees itself as more than just an outpost of the British Empire.
His important economic reforms have included the creation of the Reserve Bank of Australia and the introduction of decimal currency. As Prime Minister he also promoted significant political reforms, including the nation-building post-war immigration scheme; dismantling the shameful White Australia policy (which largely precluded non-white people from immigrating to Australia); and amending the Constitution to give the Federal Government responsibility for Aboriginal affairs. This latter change means that Australia’s first inhabitants can now be counted in the national census for the first time. (Yes, I’m embarrassed to say that until this year, our Constitution did not recognise Aboriginal Australians as citizens or count them in the population of the country!)
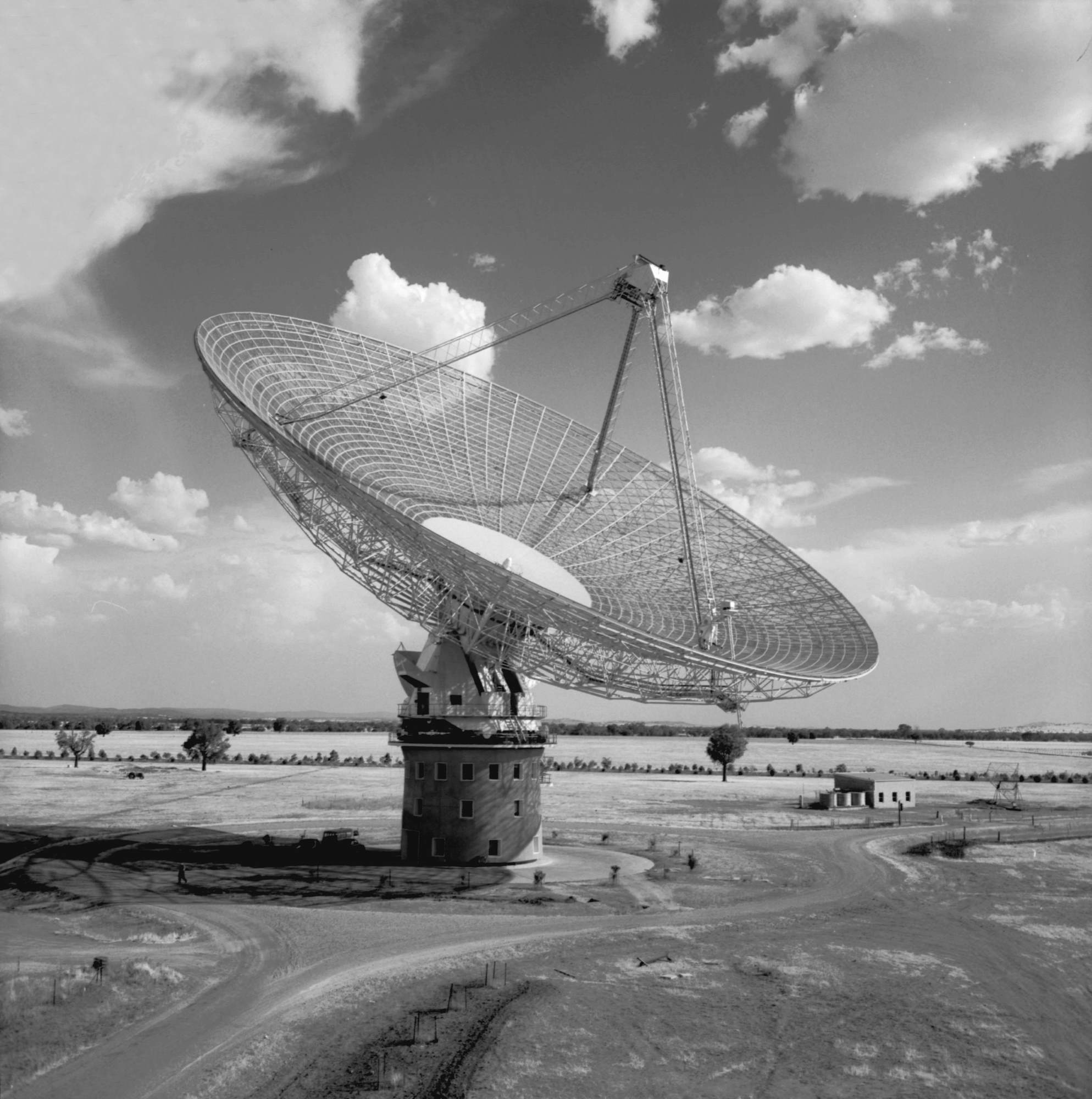
Mr. Holt supported Australia’s membership of INTELSAT and the expansion of the NASA tracking station networks in Australia. In June this year, he became the first Australian Prime Minister to make a satellite broadcast, appearing in the special “Australia Day” programme from Expo 67 in Montreal. In March, he officially opened the Manned Space Flight Network station at Honeysuckle Creek, near Canberra, which will play a major role in the Apollo Moon programme. While there, he received as a special gift from the staff, a portrait generated by one of the station computers!
 Mr. Holt's computer-generated portrait. It took the staff at the NASA Honeysuckle Creek tracking station about 20 hours to programme the computer to produce this image.
Mr. Holt's computer-generated portrait. It took the staff at the NASA Honeysuckle Creek tracking station about 20 hours to programme the computer to produce this image.Turning Our Eyes to Asia
Mr. Holt also had the foresight to recognise that, in a region of politically unstable nations, Australia needs to be better engaged with Asia and the Pacific. Earlier this year, he said in Parliament that “geographically we are part of Asia, and increasingly we have become aware of our involvement in the affairs of Asia – our greatest dangers and our highest hopes are centred in Asia's tomorrows”.
 Prime Minister Holt at the South East Asian Treaty Organisation's meeting in Manila in October 1966
Prime Minister Holt at the South East Asian Treaty Organisation's meeting in Manila in October 1966As Prime Minister, Mr. Holt's first overseas trip was to South-East Asia in April 1966, visiting Malaysia, Singapore, South Vietnam, and Thailand. This year, he toured Cambodia, Laos, South Korea, and Taiwan, and had planned future visits to other Asian nations.
Of course, in considering Australian involvement in Asia, we cannot ignore the ongoing conflict in Vietnam. Fervently opposed to Communism, Mr. Holt’s approach to national security emphasised countering Communist expansion. This lay behind his interest in encouraging greater engagement with Asia and his government’s expansion of Australia's involvement in the Vietnam War. In March 1966, Prime Minister Holt tripled the number of Australian troops in Vietnam to around 4,500, which included 1,500 conscript national servicemen: since October this year, with the most recent announcement of a troop increase, there are now over 8,000 Australian military personnel stationed in South Vietnam.
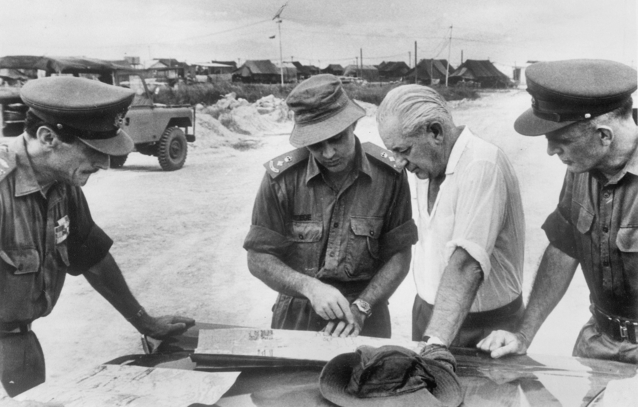

Although Mr. Holt’s expansion of Australia’s involvement in the Vietnam conflict was initially popular – and has been considered a key factor in his landslide election victory last year – the tide of public opinion has been turning against the war in recent months, especially as greater numbers of young men, conscripted into national service through a “birthday lottery” system that many people consider unfair, are being sent overseas to fight.
“All the Way with LBJ!”
The Vietnam War has dominated Australian foreign policy since Mr. Holt became Prime Minister, as he believed that “unless there is security for all small nations, there cannot be security for any small nation”. Believing that the United States provides a critical “shield” for Asian and South Pacific nations against Communist aggression, Mr. Holt cultivated a close relationship between Australia and America and formed a strong personal friendship with President Johnson, whom he had first met in 1942, when Mr. Johnson visited Melbourne as a naval officer.
 In 1966, Mr. Holt visited the U.S. twice. On his first visit, he made a comment at a White House address that has become somewhat controversial here in Australia. While apparently intending the remark to be taken as a “light-hearted gesture of goodwill”, Mr. Holt’s comment that “you have an admiring friend, a staunch friend that will be all the way with LBJ” (a reference, I’m told, to the slogan used in Mr. Johnson's 1964 presidential campaign), was seen by many in Australia as sycophantic and embarrassingly servile.
In 1966, Mr. Holt visited the U.S. twice. On his first visit, he made a comment at a White House address that has become somewhat controversial here in Australia. While apparently intending the remark to be taken as a “light-hearted gesture of goodwill”, Mr. Holt’s comment that “you have an admiring friend, a staunch friend that will be all the way with LBJ” (a reference, I’m told, to the slogan used in Mr. Johnson's 1964 presidential campaign), was seen by many in Australia as sycophantic and embarrassingly servile. Despite the controversy, I suspect that this jingle-like phrase will become one of Mr. Holt’s best-known utterances. It certainly appeared again when President Johnson made the first ever visit to Australia by a serving US President in October 1966. The President toured five cities, being greeted by both large crowds of the curious and anti-war demonstrators. I accompanied my sister and her family to join the crowds lining the motorcade route in Sydney, as I was certainly interested to get a glimpse of a US President!
Changing of the Guard
No trace of Mr. Holt was found by the evening of 18 December. At 10 p.m. that day the Governor-General announced that the Prime Minister was presumed dead. Since the country cannot be left without a leader, Mr. John McEwen, the leader of the junior government coalition party, the Country Party – and therefore the Deputy Prime Minister – has been sworn in as the interim Prime Minister, and the Liberal party will elect a new leader, and thus a new Prime Minister, early in the new year. Although Mr. Holt’s body still has not been found, a memorial service was held on 22 December, at St Paul's Anglican Cathedral, Melbourne. There were 2,000 people within the cathedral, while thousands more lined the nearby streets and listened through a public-address system. The funeral was broadcast on radio and television and, also via satellite to the United States, the UK and Europe. This was the first major satellite broadcast from Australia of a significant local news event.
 Interim Prime Minister McEwen with international dignitaries at Harold Holt's memorial
Interim Prime Minister McEwen with international dignitaries at Harold Holt's memorialInternational dignitaries and heads of state attended the memorial service, including Charles, Prince of Wales (representing Her Majesty the Queen), the Prime Minister and Opposition Leader of the UK, the UN Secretary General and President Johnson. Seven Prime Ministers and Presidents from Asian and Pacific Countries also attended, in addition to foreign ministers and ambassadors from many countries in the region and the Commonwealth.
A Tragic Accident, Suicide or Something More Sinister?
Without a body, no definitive conclusions can be reached as to what happened to the Prime Minister. The official view, and it seems that of his family, close friends and colleagues, is that Mr. Holt overestimated his swimming ability and went literally out of his depth in dangerous conditions, resulting in a tragic accidental drowning. Other possibilities include that he may have suffered a heart-attack or other sudden medical issue in the water (although his health was generally good), been stung by a deadly jellyfish (yes, we do have them in Australia), or attacked by a shark.
Some allegations have been raised that Mr. Holt committed suicide due to a number of political difficulties and controversies that have arisen in recent months. However, his wife and friends have rejected this as uncharacteristic of his personality. Already, outlandish theories have also been advanced for the Prime Minister’s disappearance, including suggestions that he has faked his own death in order to run off with a mistress, or that he has been assassinated by the CIA (but one would have to ask why, since he was so pro-American). As long as no body is found, I suspect that the mystery of Prime Minister Holt’s disappearance will continue to haunt, and fascinate, Australia – and that the bizarre theories will continue.
In the meantime, Australia mourns the loss of a forward-looking leader and the promise he might have represented.


![[December 26, 1967] The Prime Minister is Missing! (Disappearance of Australian Prime Minister Harold Holt)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/671226holt-672x372.jpg)
![[October 28, 1967] Unveiling Venus – at Least a Little (Venera-4 and Mariner-5)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Venus-desert.png)














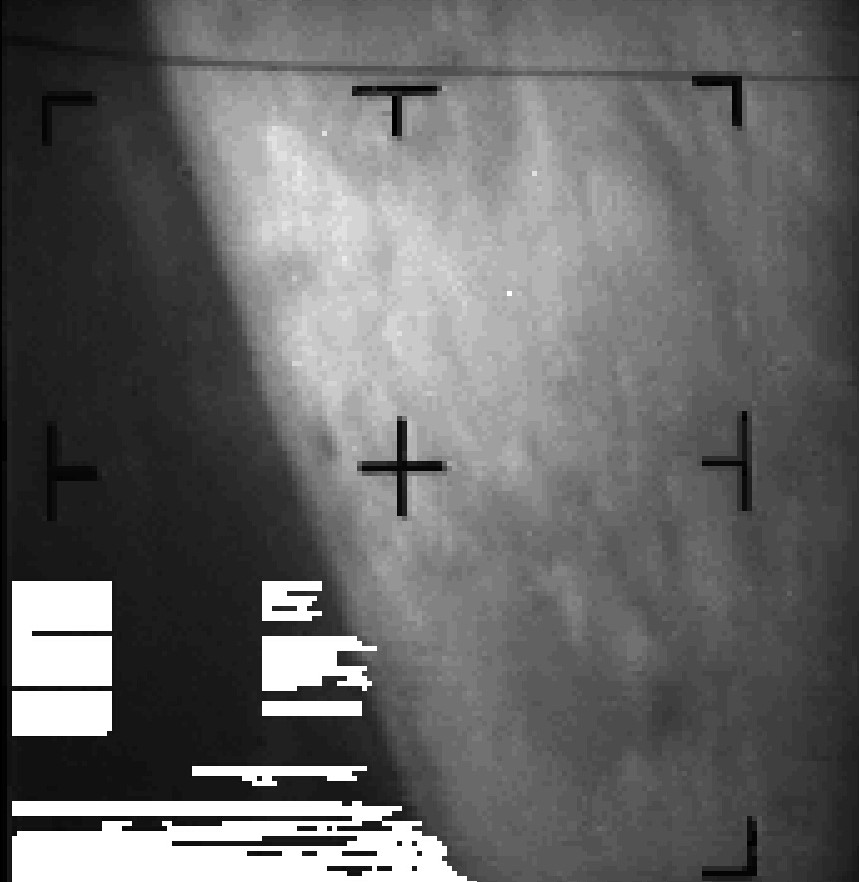
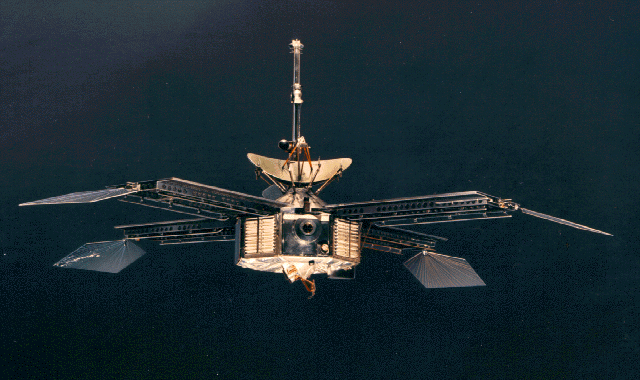
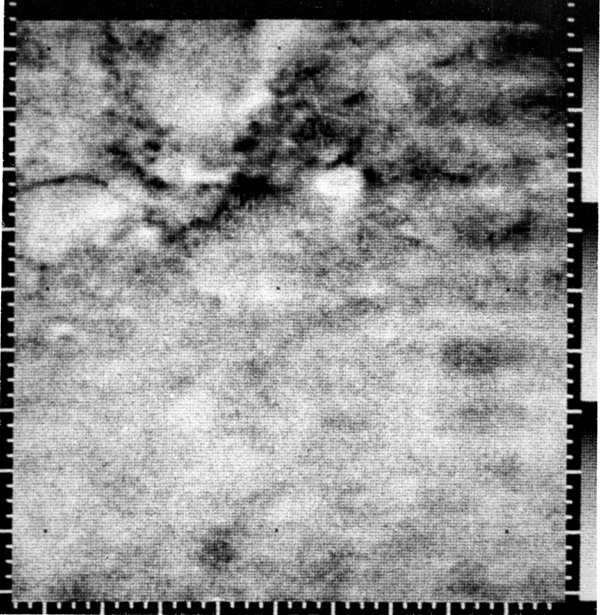
![[July 20, 1965] No War of the Worlds After All? (Mariner IV reaches Mars)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/mariner04-640x372.gif)