by Kaye Dee
Later today, the International Telecommunications Satellite Organization, better known as INTELSAT is going to launch its first satellite, INTELSAT-1, which goes by the nickname of ‘Early Bird’. This satellite is intended to be the beginning of a global satellite telecommunications network, which INTELSAT hopes to have in operation by about mid-1967.
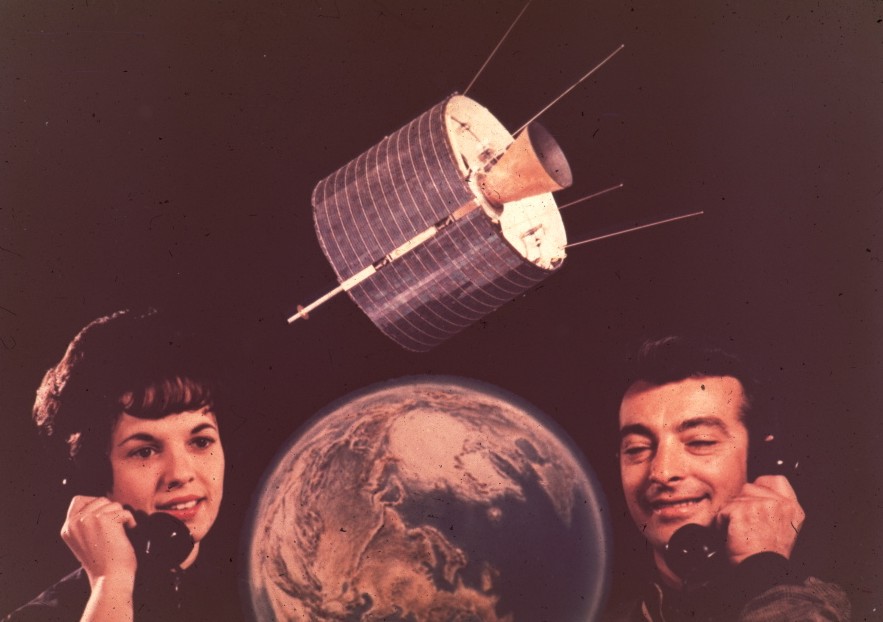

INTELSAT aims to connect us all via satellite – starting with the US and Europe
INTELSAT: Connecting the World with Space Technology
I wrote about INTELSAT last year, when the organization was first established in August 1964, with Australia as one of its 11 founding members. Around 45 countries have now joined the INTELSAT consortium and I’m certain that the creation of a world-wide telecommunications system that offers equitable access to all nations will improve international understanding and the prospects for world peace. Satellite communications will certainly prove a boon for countries with poorly-developed internal communications networks, as well as allowing major Southern Hemisphere nations like South Africa and Australia to have more rapid connections to Britain, Europe and North America.

One of the United States' first space stamps recognised the potential for satellite communications to promote world peace
Assuming all goes well with the launch this evening, INTELSAT-1 will be placed in a geostationary orbit at 22,300 miles above the equator, east of the Brazilian coast. Once the satellite has been thoroughly checked out to be sure it’s in full working order, it will go into operation, around the beginning of June, as the first commercial satellite providing regular telecommunications and broadcasting services between North America and Europe.
Soaring to New Heights
Of course, satellite communications between the Unites States and Europe isn’t completely new: Telstar and Relay 1 both provided this service back in 1962. But both satellites were only in low Earth orbit, so they could only provide intermittent service. When Syncom 2 and 3, were launched in 1963 and ’64, respectively, these experimental spacecraft built by the Hughes Aircraft Company demonstrated the feasibility of using satellites in geosynchronous and geostationary orbit to provide a world-wide communications system. They were so successful in connecting America with countries from Japan to Nigeria, that Syncom 3 was the prototype on which Early Bird has been modelled, and you can see the similarity in design.
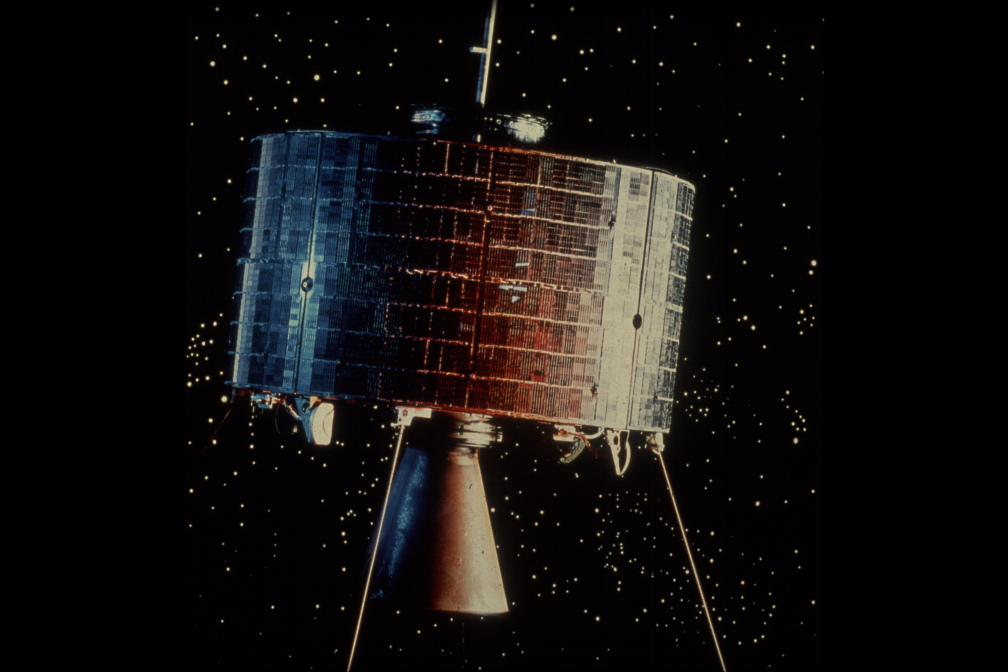
Syncom 3 above and Early Bird undergoing tests below
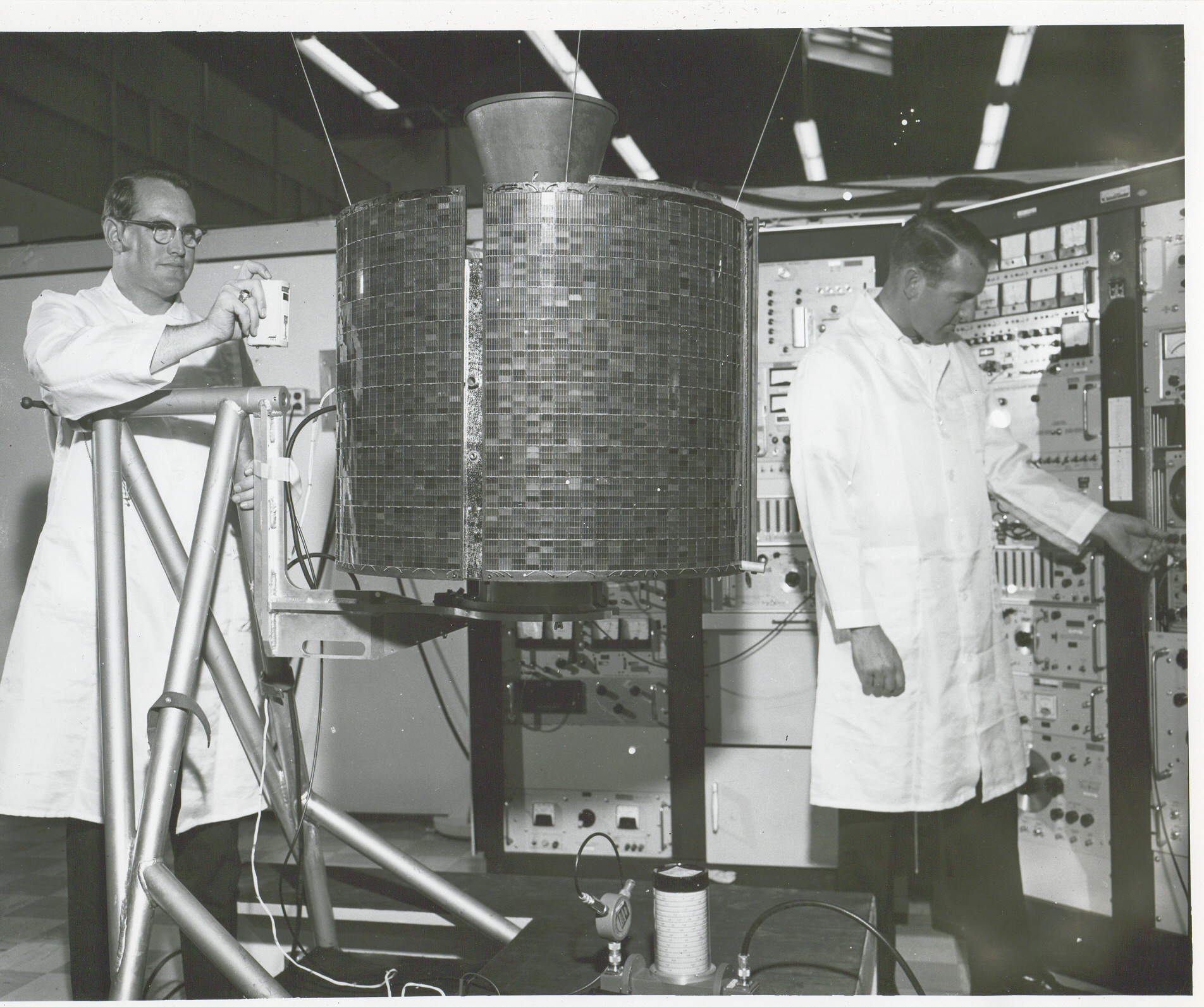

Like Syncom 3, INTELSAT-1 is spin stabilised, which is the reason for its cylindrical shape. It has two 6-Watt transponders that enable it to carry 240 two-way voice circuits and one television channel, although not simultaneously: in order to transmit television, all the telephone voice channels have to be shut down. An important difference between the two satellites, though, is that INTELSAT-1 uses commercial rather than military frequencies for its communications to and from the ground.
INTELSAT-1 weighs just 85-lb which, amazingly for its capabilities, is less than half that of Sputnik 1’s 184 pounds. It is covered with 6,000 solar cells that generate 45 Watts of power to operate the satellite. Early Bird’s capabilities are so advanced that it will actually be more economical to operate than international undersea cables, which carry fewer channels and cost nearly 10 times as much!
Getting into Position
Early Bird is being launched by a Thrust-Augmented Delta, the same type of rocket that was used to put Syncom 3 into orbit. This vehicle, also known as the Delta D, is essentially the same as its predecessor, the Delta C, but with the addition of three Castor-1 solid rocket boosters attached to the first stage. The launch is taking place at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 17A, which was also used for Syncom 3’s launch. The Delta will boost Early Bird into an elliptical orbit, taking it from 830 to 22,950 miles out in space. After 40 hours a series of delicate manoeuvres will place the satellite in its permanent orbital position.
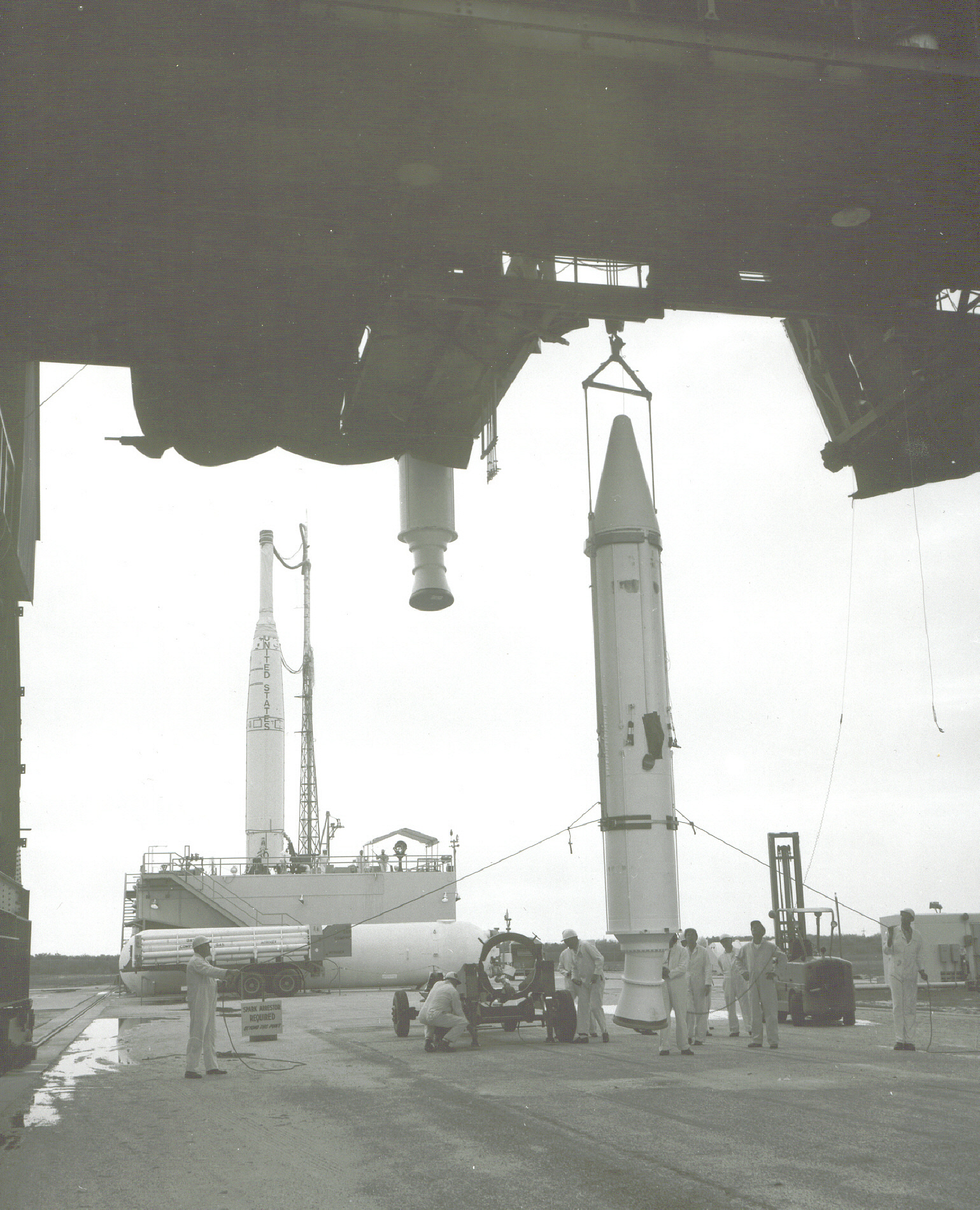
Early Bird's launch vehicle being assembled. The Castor-1 solid boosters are being hoisted into position while the Delta rocket core waits in the background. It will soon be brought forward for mating with the boosters
Demonstrating the Future
Although it will operate as a commercial service, Early Bird will also be used to demonstrate that international satellite telecommunication is commercially viable in the long-term. While its main ground stations will be the huge horn antennae originally built for Telstar, it will also use ground stations with large parabolic ground antennae with diameters of over 85 feet, like the one at Goonhilly in England, and perhaps smaller antennae as well.

The Telstar horn antenna at Pleumeur-Bodou, France, is now being used as an INTELSAT-1 ground station
From my friends at WRE who are involved with the NASA Gemini tracking station at Carnarvon, Western Australia, I understand that if the Early Bird experience goes well, the antennae for the INTELSAT-2 satellites, that are being contracted by NASA to support the Apollo programme, will be an unusual Cassegrain feed-horn design that is already being nicknamed the “sugar scoop”! I’m fascinated to see what this antenna will actually look like, with a nickname like that!
The other thing that INTELSAT-1 will be determining is whether or not the end to end signal delay of 250 milliseconds, while the signal goes up to the satellite and returns to the ground, will be acceptable to customers. Syncom 3 demonstrated that geostationary orbit is so high that, even at the speed of light, there is a perceptible time-lag between comment and response when communicating internationally. Whether people will find this too disconcerting for use with international satellite phone calls could have a significant influence on how future communications satellite systems are developed.
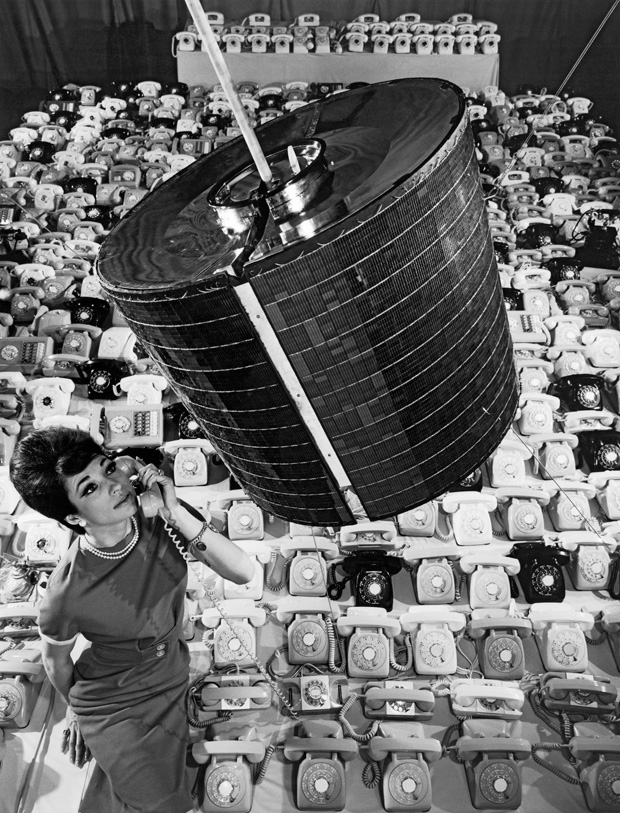

240 phones for 240 conversations simultaneously carried on via Early Bird. But will people accept the time-lag that comes with geostationary satellite communications?
So, my friends in the Northern Hemisphere, enjoy the convenience of satellite telecommunication that will soon be available to you-I can’t wait for it to come to Australia as well.
We had so much success with our first episode of The Journey Show (you can watch the kinescope rerun; check local listings for details) that we're going to have another one on April 11 at 1PM PDT with The Young Traveler as the special musical guest. As the kids say, be there or be square!



![[April 6, 1965] The Early Bird Catches the Worm (INTELSAT 1)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Intelsat-1-1-620x372.jpg)

![[August 29,1964] Coming to You Live via Satellite](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Mrs_ODonahue.jpg)

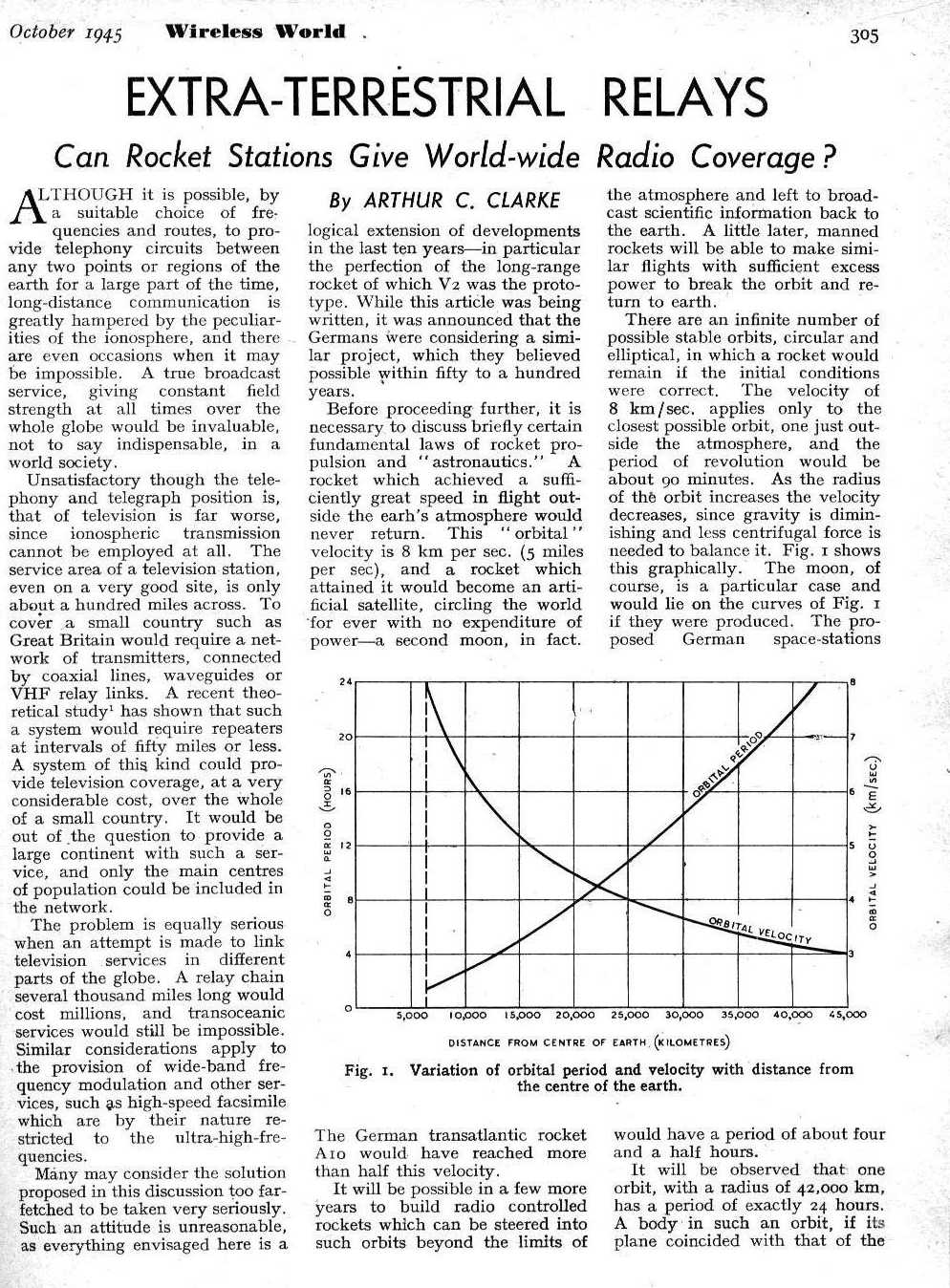 The first two pages of Mr. Clarke's seminal article on communications satellites. As a science fiction author, I guess he couldn't resist the title.
The first two pages of Mr. Clarke's seminal article on communications satellites. As a science fiction author, I guess he couldn't resist the title.

![[August 29, 1963] Why we fly (August Space Round-up)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/630829astronauts-672x372.jpg)