
by Gideon Marcus
Return to sender
The French economy has been rocky ever since the wave of strikes and protests in May. As a result, France has been getting more and more goods from its industrial neighbor, West Germany. The problem is France has to buy German goods in francs, which means that, more and more, francs are ending up in West German hands. Franc reserves, at $6.9 billion in April 1968, are now down to $4 billion and plummeting.
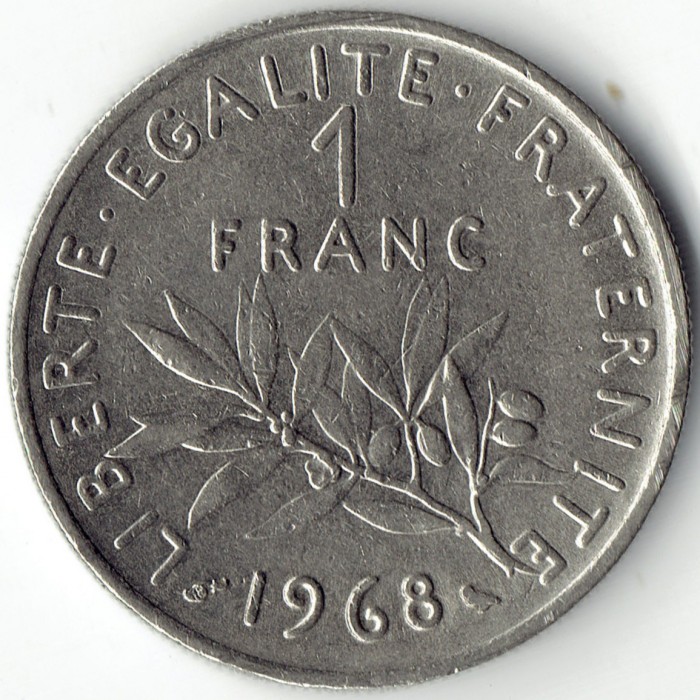

To forestall a devaluation of the franc (reducing its value, thus making imports more expensive and exports more affordable to other nations, but playing hell with international economic relations in the process), DeGaulle's government is evaluating all sorts of Hail Mary options to stabilize the economy. One that was rejected was the West German offer to invest directly in the French economy, which would leave them too in control of French assets (including the dwindling franc supply!) A proposal that was adopted was an increase in vehicle fuel costs; I gather fuel production is nationalized, and the government can't afford to sell it so cheaply.
But a sadder development involves the French post office-letters written to Santa Claus will no longer be answered. Previously, kids who wrote to St. Nick got a colorful postcard with a message of Christmas cheer. A West German offer to donate Elven postal braceros has been rejected.
Merry Christmas, indeed. Maybe DeGaulle should convert to Judaism. Then he can pray a great miracle will happen in Paris for Hannukah, and the franc reserve will last eight years instead of one…

Flickering candles
Here in the good old U.S. of A., we don't have such economic woes (though inflation is kicking in). All I have to worry about is whether the first Galaxy of the year is any good. In other words, has the value of the magazine been devalued? Let's find out!

by Gray Morrow
Foeman, Where Do You Flee?, by Ben Bova
On Titan, the alien machines (first seen six years ago in "The Towers of Titan") rumble on, their purpose unknown, as they have for millennia. Humanity, terrified of their implications, begins searching the stars for their creator. And so, one ship, the Carl Sagan, makes the 15 year trip to Sirius A-2, a barren but Earthlike world orbiting the blazing blue sun.
Sid Lee, an anthropologist onboard, is convinced that Earth once warred with the aliens who build the machines of Titan, and that humans lost, reverting to savagery. The crew of the Sagan are surprised not only to find a group of intelligent beings on the alien world, but that they are indistinguishable from Homo Sapiens Sapiens. Lee volunteers to live among them, hiding his extraterrestrial origin, to learn the truth of the Sirians, and how they fit into the ancient, hypothetical war.

by Reese
There's a lot to like about this piece, especially the methodical, painfully slow, expedition protocols. The crew wear suits when they go outside. Extreme caution is taken in scouting. It takes months before Lee is even allowed to infilitrate the aliens.
Bova reminds me a bit of Niven in his weaving together hard science fiction and a compelling story. However, the author does not have Niven's mastery of the craft, and the story feels a bit clunky. Moreover, the "revelations" of the tale are telegraphed, and the red herrings Bova throws in to keep the mystery going are not convincing.
I enjoyed the story, but it's difficult to decide if it's a high 3 or a low 4. I think I will go with the latter because it's clear this novella is only part of a bigger story, one that looks like it will be fascinating to read.
The Thing-of-the-Month Clubs, by John Brunner
In what looks like the final entry in the Galactic Consumer Report series, the editor of the fictional magazine reviews various [THING]-of-the-Month Clubs. Specifically, the editor is looking for high cost and ephemeral items for worlds with >100% income tax.
Droll. Forgettable. Three stars, I guess.
Parimutuel Planet, by James Tiptree, Jr.
by Blakely
A fellow named Christmas runs the premier racing planet in the galaxy: Raceworld! He deals with a number of headaches including various attempts to fix the games by a number of different species. The thing reads breezily, shallowly, in a style I was sure I'd read before…and sure enough, looking through back reviews, I found the story I was thinking of ("Birth of a Salesman") was, indeed, written by one James Tiptree Jr.
I found this story even less compelling. One star.
Dunderbird, by Harlan Ellison and Keith Laumer

by Jack Gaughan
I'm not sure how Harlan Ellison ends up bylining with so many different authors these days: Sheckley, Delany, and now Laumer.
The premise: a giant pteranodon falls out of the sky onto the streets of New York, crushing 83 people under its unnaturally heavy corpse. The rest of the story is a detailing of the many odd characters who come across the flying lizard and their reactions to it.
Pointless and unfunny, I have to wonder if Ellison attaches his name to things just to get them published for friends. It's not doing the brand any favors.
One star.
For Your Information: The Written Word, by Willy Ley
This is a nice piece on the history of writing materials (which is, by definition, the history of history) from Greek times to modern day.

Ley wraps up with a primer on how to send and decode interstellar messages, which I quite enjoyed.
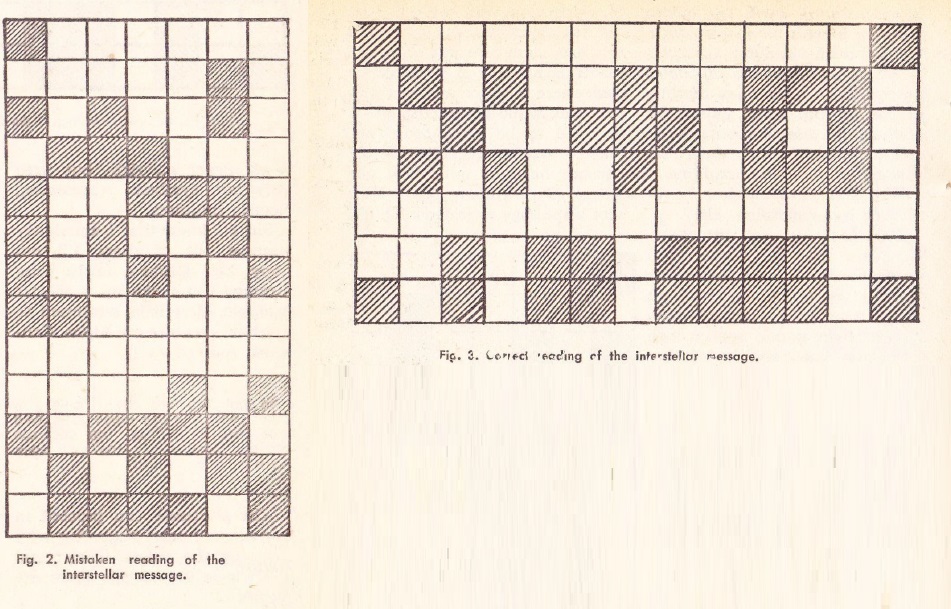
Interestingly, though he talks about microfiche and microfilm, he does not mention the possibility of more-or-less permanent documents within the memory banks of computers. I know it may seem frivolous to store the written word on such expensive media as the Direct Access Storage Devices (DASD) used by IBM 360 computers, but in fact, such is being done as we speak. I have used time share systems to send frivolous messages to others on home-grown "mail" systems, and also created data sets that were text files, both as memos and as "documents" for other users to read. And, of course, there are data sets that are programs that, once loaded into permanent memory via punch card or teletype, are there to stay. At least until an electrical pulse fries the whole thing.
Of course, that's a pretty rarefied use, but it's still interesting and relevant for those in the biz.
Anyway, four stars.
The Organleggers, by Larry Niven

by Jack Gaughan
Gil Hamilton, an agent of the the United Nations police force —Amalgamated Regional Militias (ARM)—is called regarding a death. Not because he's a cop, but because he's next of kin of the deceased, a Belter named Owen Jennison. The spaceman's demise looks like a particularly elaborate suicide: he is in a chair hooked up to a device that uses electric current to stimulate the pleasure center of one's brain, and he apparently starved, quite happily, to death.
But as Gil puts the pieces together, he comes to the conclusion that Jennison must have been murdered. Which means there's a murderer. Which means there are clues. And since it's Niven's Earth in the 22nd Century, organleggers are probably involved.
Did I mention that Gil also has psychic powers? He has a third, telekinetic arm, which comes in very handy. It's also the first time that I've seen this particular idea. It breathes new life into a hoary subject.
As does all of the story, honestly. Niven is simply a master of organically conveying information, letting you live in his universe, absorbing details as they become pertinent. There's nothing of the New Wave to his work save that his writing is qualitatively different from what we saw in prior eras.
He's also written a gripping fusion of the science fiction and detective genres, perhaps the best yet.
Five stars.
Welcome Centaurians, by Ted Thomas
Aliens arrive from Proxima Centauri. Though they make contact with many of Earth's nations while cautiously assaying us from orbit, their captain forms a bond with Colonel Lee Nessing of NORAD. After a long conversation, the aliens agree to land in New York, whereupon friendly relations are established.
This is a cute, nothing story whose charm comes mostly from the chummy relationship between Lee and "Mat", the Proximan that looks like a floor rug. My biggest issue is the gimmick ending, in which it is revealed that ancient Proximans caused the death of the dinosaurs by seeding the Earth with food animals—which turned out to be early mammals.
The problem: mammals evolved from reptiles 200 million years ago. That event is well documented in the fossil record and is referenced in my copy of The Meaning of Evolution (1949) by George Gaylord Simpson. This sort of basic evolutionary mistake seems pretty common in science fiction, where writers try to ascribe extraterrestrial origin to obviously terrestrial creatures (humans are the most frequent example).
Three stars.
Value for money
If there's anything the January 1969 issue of Galaxy proves, it's that even good money can't guarantee a return. Editor Fred Pohl paid 4 cents a word for all of the pieces in this issue, and to his credit, more than half the words are in four/five star pieces. On the other hand, two of the stories are mediocre, and two are absolutely awful. It's like Pohl got his tales from a mystery bag and had to take what he got, good or bad.
Well, the superior stuff would fill an ordinary sized magazine, so I shan't complain. Read the Bova, the Ley, and the Niven. Then put the issue under your tree for others to discover Christmas morning…

 Dr. Edward D. Goldberg of the Scripps Institute of Oceanography in La Jolla, California
Dr. Edward D. Goldberg of the Scripps Institute of Oceanography in La Jolla, California Col. Fletcher (r.) on his ice island in 1952. This was the most recent photo of him I could find.
Col. Fletcher (r.) on his ice island in 1952. This was the most recent photo of him I could find. Dr. William W. Kellogg of the National Center for Atmospheric Research, in Boulder, Colorado
Dr. William W. Kellogg of the National Center for Atmospheric Research, in Boulder, Colorado Cover by Gaughan. Supposedly suggested by Whipping Star, but it looks more like it illustrates Pressure Vessel to me.
Cover by Gaughan. Supposedly suggested by Whipping Star, but it looks more like it illustrates Pressure Vessel to me.
![[January 2, 1970] Under Pressure (February 1970 <i>IF</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/IF-1970-02-Cover-500x372.jpg)
![[December 10, 1968] Back and forth (January 1969 <i>Galaxy</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/681210cover-671x372.jpg)











