by Gideon Marcus
Tarnished Gold
I am an avid fan of science fiction magazines. It would not be going too far to say that Galactic Journey's original purpose was to document these delightful digests as they came out (since then, our scope has crept quite a bit, even as far as the opening of a publishing company!)
If you've been following my column, you know that I view some magazine editors more favorably than others. For instance, I have a great deal of respect for Fred Pohl, who helms Galaxy, IF AND Worlds of Tomorrow, all of them quite good reads. Then there's Cele Goldsmith (now Lalli) who took on both Amazing and Fantastic, and while neither are unalloyed excellence, they are improved over where they were before she came on, and there's usually something excellent in at least one of the mags every month.
My relationship with Fantasy and Science Fiction's Avram Davidson is more complicated; I understand he's moved to Berkeley and is retiring from the editorship of that magazine to devote himself to writing. I think that's probably better for everyone involved. Still, there have been some good issues under Davidson, and I can't let curses go without some grudging admiration.
And then there's John W. Campbell.
Look. I recognize that his Astounding kicked off the Golden Age of Science Fiction, and that, for a while, his magazine (and its sister, Unknown) were the best games in town, by far. But Campbell went off the deep end long, long ago, with his pseudo-science, his reactionary politics, his heavy-handed editorial policy that ensures that White Male Terrans are usually the stars (and writers) of his stories, and his inflammatory editorials that I gave up reading a while ago.
Asimov's long-since turned his back on him. Even I've rattled sabers with him. But the most poignant declaration against Campbell is a recent one, given by prominent writer Jeannette Ng at a local conference. She minced no words, denouncing his male-chauvinism, his racism, his authoritarianism, and urged that the genre be freed from the overlong shadow he casts.

Jeannette Ng, iconoclast
While Campbell's influence in SF is somewhat on the wane, Analog still has double the circulation of the next biggest competitor, four times that of F&SF, where the majority of the women SF writers publish. It's people like Ms. Ng, pointing at the naked Emperor and noting the ugliness, who will advance the New Wave, the post-Campbellian era.
All I have to say is "bravo".
The Issue at Hand
The ironic thing is that the current issue of Analog is actually pretty good (full disclosure: I didn't read the editorial, which is probably awful). Just the cover, illustrating the latest Lord D'Arcy story is worth the price of admission.

by John Schoenherr
Opening up the pages, things are pretty good inside, too. At least until the end.
the risk takers, by Carolyn Meyer

This article on the use of mannequins in aeronautical and medical science is lively, much more Asimovian than most of the non-fiction Campbell has subjected us to recently. And, it's the first time a woman author has graced the science column of Analog. While the piece is comparatively brief and perhaps aimed at a more general (dare I say "younger") audience than the average Analog reader, I enjoyed it.
Four stars.
A Case of Identity, Randall Garrett
Randall Garrett is possibly the author I've savaged the most during my tenure running the Journey, but even I have to admit that the fellow's latest series is a winner. Lord D'Arcy is a magical detective hailing from an alternate 1964. In this installment, the Marquis of Cherbourg is missing, and coincidentally, an exact double has just been found dead and naked near the docks. There's witchcraft afoot, and the good Lord, along with his sorcerer assistant, Master Sean O Lochlainn, are on the case.

by John Schoenherr
This story doesn't flow quite as smoothly as the first one, spending many inches on the historical background of this brand-new world. It's still a superlative tale, however.
Four strong stars.
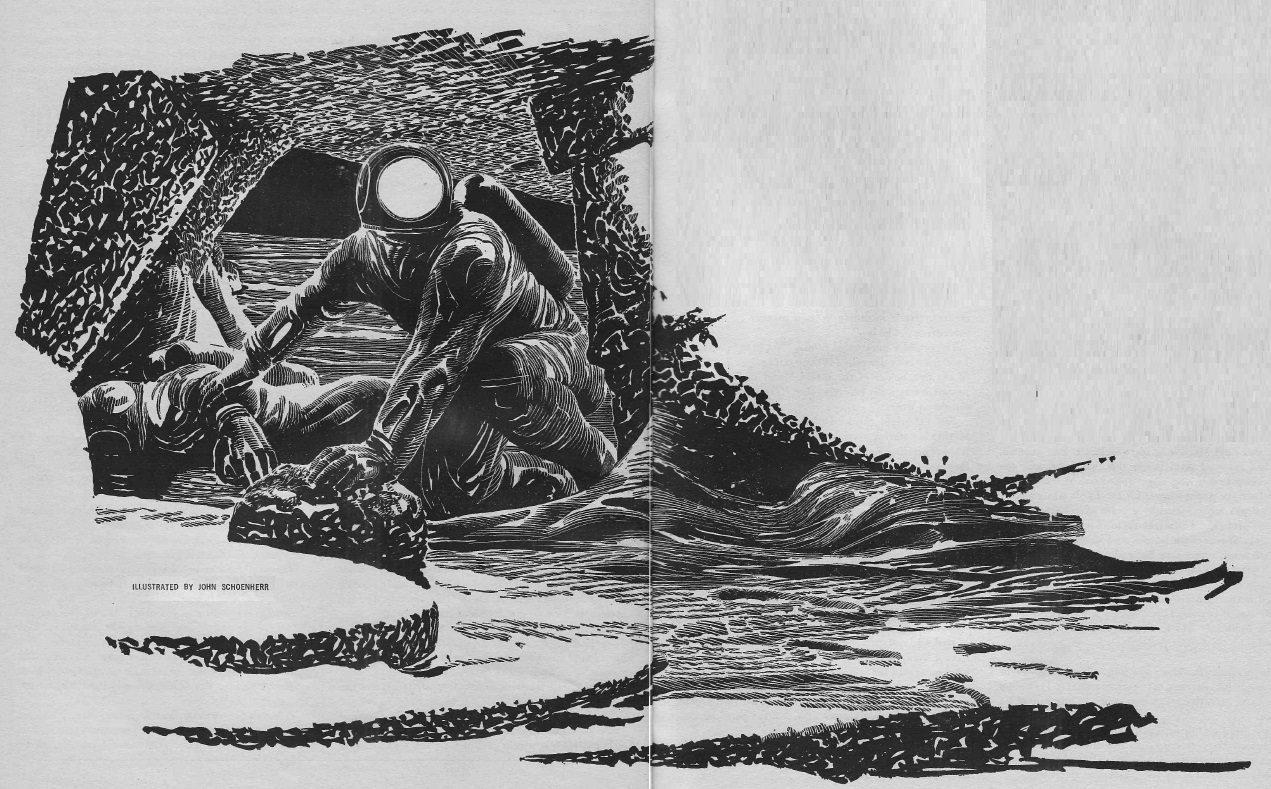
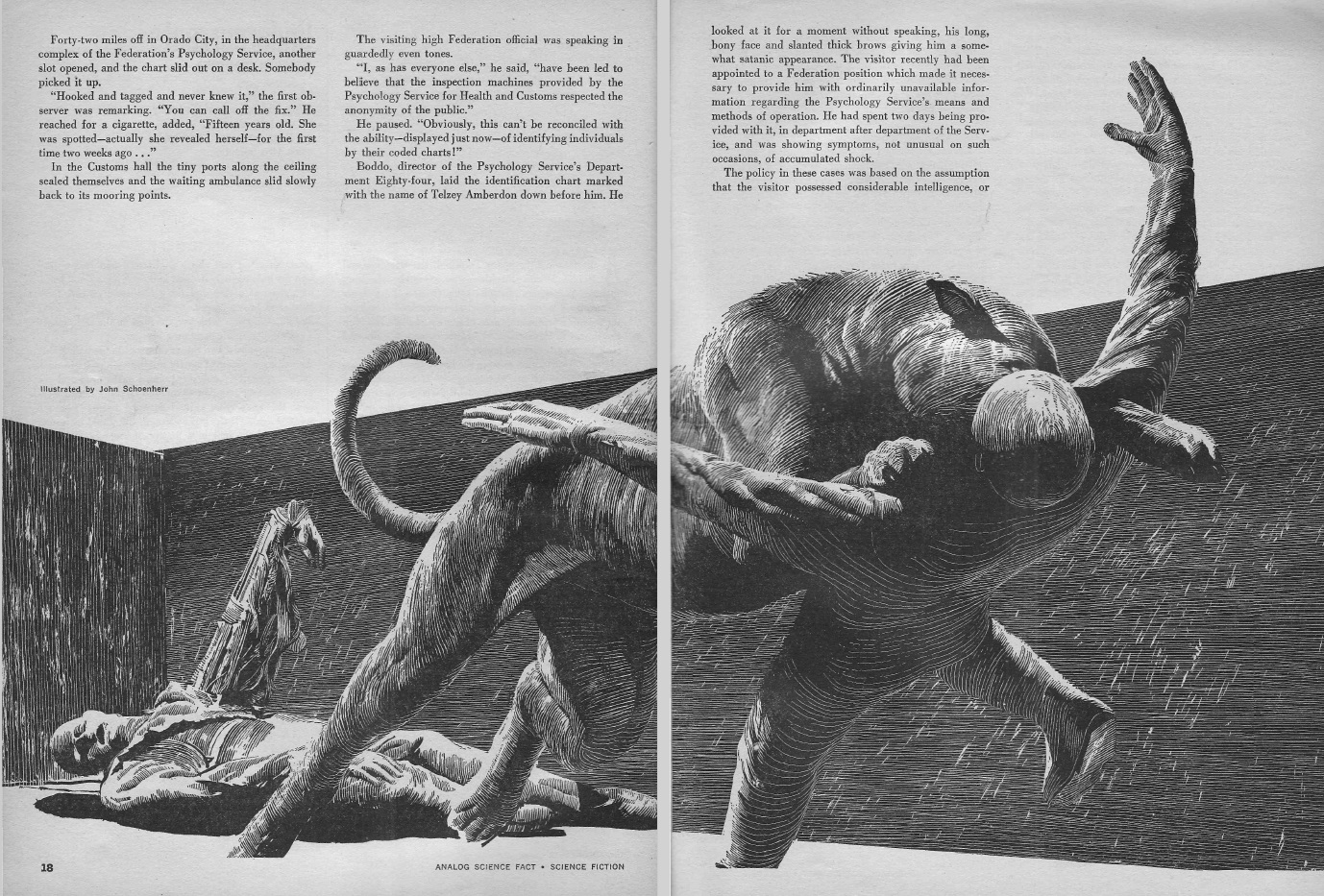
The Machmen, James H. Schmitz

by John Schoenherr
An interstellar survey group is overpowered by a group of ambitious cyborgs. The goal of these so-called "Machmen" (presumably pronounced "Mash-men"?) is to forcibly convert the captured team of eggheads into brainwashed cybernetic comrades and start a colony. But one the scientists has gotten loose, and he has a risky plan to thwart the nefarious scheme that just…might…work.
It's not a bad piece. In fact it moves quite nicely, far more readily than the author's latest (and disappointing) Telzey Amberdon story. But on the other hand, it reads like it might have come out in the 1930s. I wonder if it's been hiding in a desk from the early days of Schmitz' career.
Three stars.
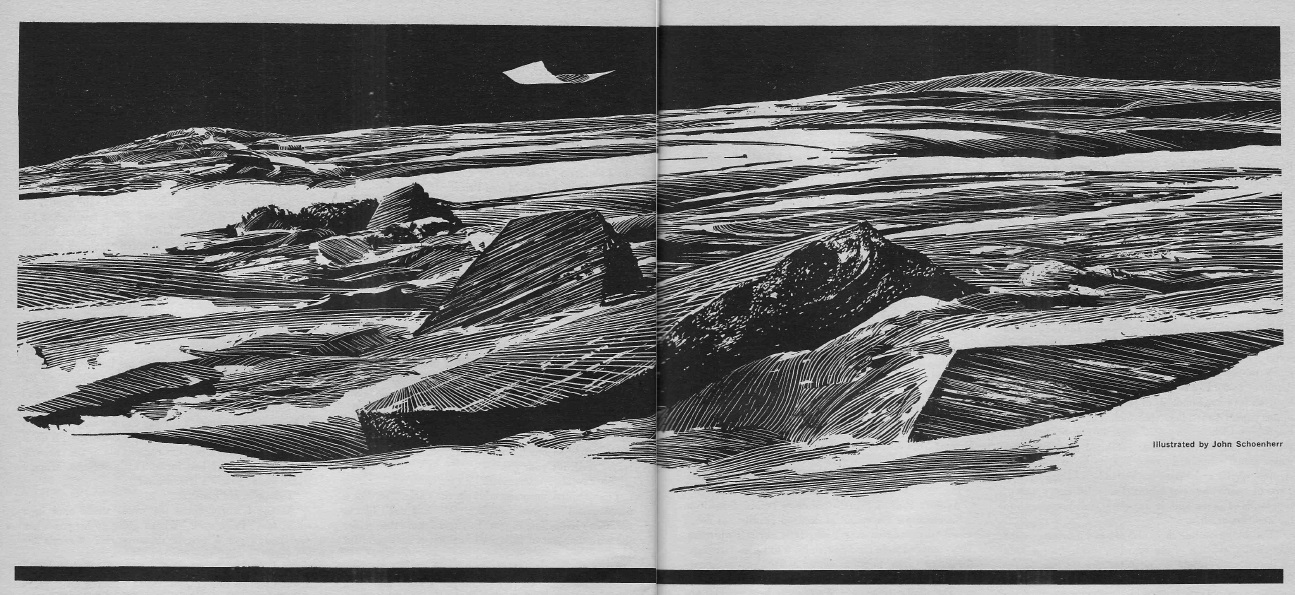
Sheol, Piers Anthony and H. James Hotaling

by John Schoenherr
This is an odd piece about the Government postman who delivers parcels to the oddballs who live in the suburbs. It's quite deftly written, but there's weird social commentary that, while not offensive, feels Campbellian. Tailor made for John, or doctored after the fact? There's no way to tell.
Three stars.
Sleeping Planet (Part 3 of 3), William R. Burkett, Jr.

by Kelly Freas
Last up, we have the conclusion to Sleeping Planet. What started out as a promising novel about the sudden subjugation of the Earth has ended up exactly as predicted. The few unsleeping humans, along with their robotic allies (abruptly introduced near the end of the last installment), put on a movie show that convinces the invaders that the dead spirits of Earth are taking out their revenge. This confusion facilitates the final gambit of the Terrans: to infiltrate and revive one of the planetary defense stations in El Paso. After that, it's all over but the shouting.
There are several problems with this last part. First off, it's essentially unnecessary. There are no surprises, the human plan pretty much going as discussed in the last part. That's the big picture. Smaller picture issues include:
- Why were Earth's defense centers even vulnerable to the sleeping dust in the first place? Wouldn't it make sense for them to have their own air supplies against chemical/biological attack?
- The amazingly human-like aliens (another Campbellian feature) are always played for suckers. I was almost rooting for them to win at the end, so arrogant and annoying were the humans.
- At the end, Earth's leaders make light of the attack, calling it a brief nap (but a warning as to what might happen NEXT TIME). I understand this is largely to quell panic and outrage. At the same time, though, it is mentioned numerous times that hundreds, maybe thousands of women were revived and rendered stupefied so that the might "service" the alien troops. That this mass rape goes unaddressed and essentially laughed off really bothered me. Honestly, even including this element was disgusting and unnecessary, especially in a story that mostly kept a light tone.
Two stars for this segment, two-and-a-half for the book as a whole. We'll see if it gets picked up for separate print.
Summing Up

Thus ends another edition of the magazine that Campbell built, representative of the best and worst of the man. This time, the positive aspects have won out, resulting in a 3.2 star issue. This is surpassed this month only by Fantasy and Science Fiction (3.4). There was no IF this month due to a problem at the printers, the result of shifting from bimonthly to monthly. That leaves the new New Worlds (3.1), Amazing (2.7), and Fantastic (2.6) scoring below Analog and F&SF. An unusual month, indeed.
Women wrote 6 of 38 pieces (1 of 4 science articles, 5 of 34 fiction pieces), a fairly average month. Despite the paucity of magazines, there was enough high quality material to make a decently sized issue. Now that I'm in the anthology business, perhaps I'll do just that…
SPEAKING OF WHICH:
We have exciting news! Journey Press, the publishing company founded by the team behind Galactic Journey, has just launched its first book. We know you will enjoy Rediscovery: Science Fiction by Women (1958-1963), a curated set of fourteen excellent stories introduced by the rising stars of 2019.

If you enjoy Galactic Journey, you'll want to purchase a copy today — available physically and virtually! Not only will you find it excellent reading, but it will support our efforts and allow us to make more of the material you enjoy! Thank you for your support!

![[September 2, 1964] Taking on The Man (September 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/640902cover-495x372.jpg)


![[August 3, 1964] Running hot and cold (August 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/640803cover-672x372.jpg)











![[July 2, 1964] Completing the Tour (July 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/640702cover-672x372.jpg)















![[June 2, 1964] June Gloom (June 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/640602cover-672x372.jpg)








![[May 2, 1964] The Big Time (May 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/640502cover-672x372.jpg)







![[Apr. 2, 1964] The Joke's on me (the uninspiring April 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/640402cover-672x372.jpg)












![[March 3, 1964] Out and about (March 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/640303cover-460x372.jpg)







![[February 1, 1964] The Vast Wasteland (February 1964 <i>Analog</i>)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/640201cover-672x372.jpg)






![[January 2, 1964] All's well that ends well (January 1964 <i>Analog</i> science fiction)](https://galacticjourney.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/640102cover-653x372.jpg)






















